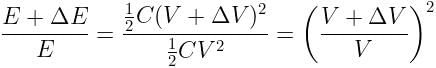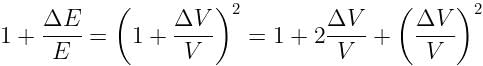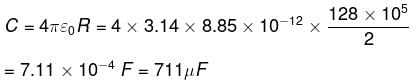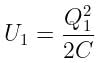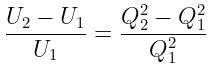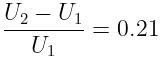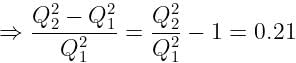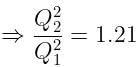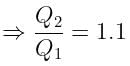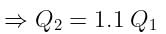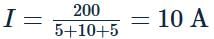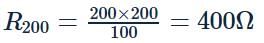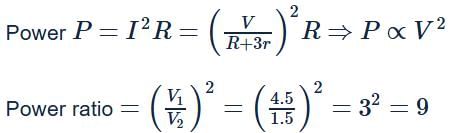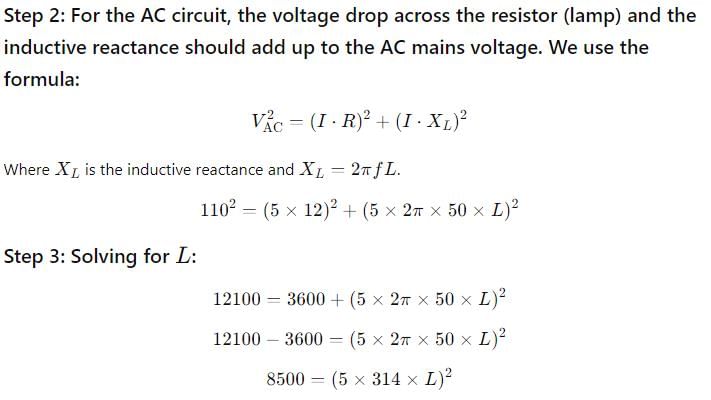Physics: CUET Mock Test - 6 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 6
The difference in mass of a nucleus and its constituent nucleons is called the ____________.
The shortest wavelength in the Lyman series of the hydrogen spectrum is 912 Å. The shortest wavelength present in Paschen series of spectral lines will be:
The ratio maximum wavelength to minimum wavelength in Lyman series is :
If a light ray travels from denser to rarer medium. Which of the following statement/s are correct?
(A) Energy increases
(B) Frequency remain same
(C) Phase changes by 90°
(D) Velocity increases
(E) Wavelength decreases
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
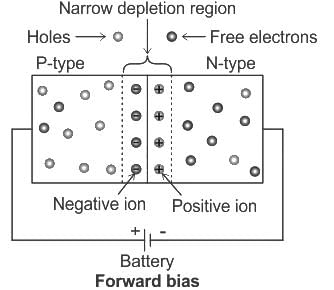
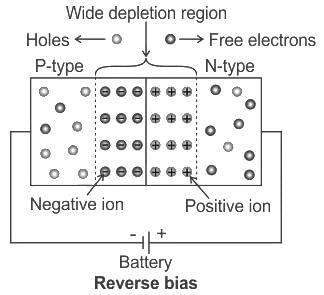
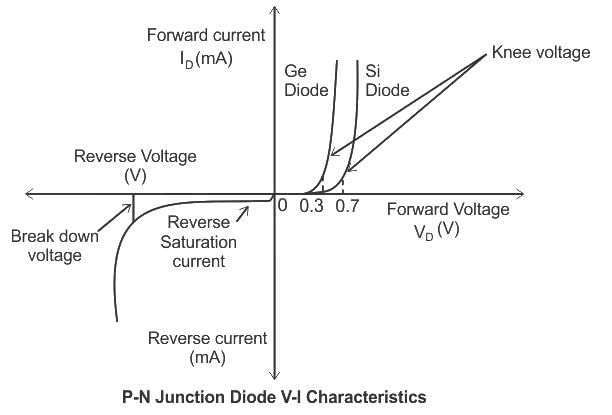
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction diode, then :
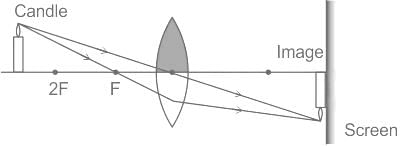
While looking at an image formed by a convex lens one half of the lens is covered with a black paper. What will be its effect on the image formed?
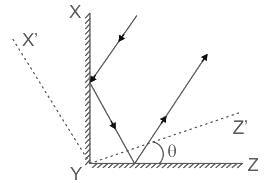
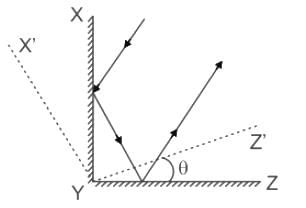
Shown in the figure are two plane mirrors XY and YZ (XY ⊥ YZ) joined at their edge. Also shown is a light ray falling on one of the mirrors and reflected back parallel to its original path as a result of this arrangement. The two mirrors are now rotated by an angle θ to their new position X'YZ', as shown. As a result the new reflected ray is at an angle α from the original reflected ray. Then :
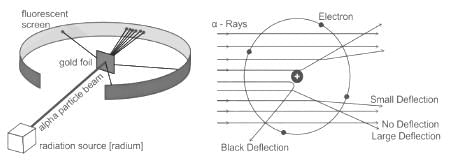
In Rutherford's gold foil experiment, thin sheets of gold foil was bombarded with _________ to understand the nuclear model of atom.
Which of the following pairs of physical phenomenon and the discover is/are correctly matched?
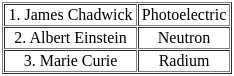
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
If the potential difference between the plates of a capacitor is increased by 0.1%, the energy stored in the capacitor increases by nearly:
If the diameter of earth is 128 x 102 km, then its capacitance will be:
If the charge on a capacitor is increased by 2 coulomb, the energy stored in it increases by 21%. The original charge on the capacitor (in coulomb) is:
In series combination of capacitors, potential drops across the individual capacitors are equal to_______
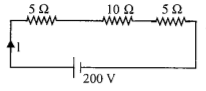
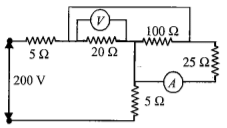
In the figure, voltmeter and ammeter shown are ideal. Then voltmeter and ammeter readings, respectively, are
The operating temperature of the filament of lamp is 2000∘C. The temperature coefficient of the material of filament is 0.005∘C−1. If the atmospheric temperature is 0∘C, then the current in the 100 W, 200 V rated lamp when it is switched on is nearest to
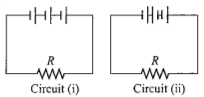
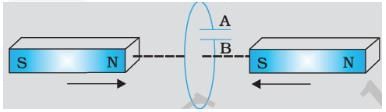
Three identical cells, each having an e.m.f. of 1.5 V and a constant internal resistance of 2.0Ω, are connected in series with a 4.0Ω resistor R, first as in circuit (i), and secondly as in circuit (ii).
What is the ratio 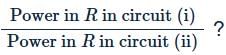
The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by:
Two thin long parallel wires separated by a distance b are carrying a current i ampere each. The magnitude of the force per unit length exerted by one wire on the other is
Predict the polarity of the capacitor in the situation described by fig.
A circular coil of radius 8.0 cm and 20 turns is rotated about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of 50 rad s-1 in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 3×10-2 T. If the coil resistance is 10Ω, maximum emf induced in the coil,maximum value of current in the coil and average power loss due to Joule heating are
In which of the following cases the power factor is not equal to 1
What is the inductance of a choke required for a lamp running at 60 volt d.c consuming 5 A current connected to 110 volt, 50 Hz ac mains?
Which of these mechanisms can be used to produce electromagnetic waves?
The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic electromagnetic wave in vacuum is B0= 510 nT. Amplitude of the electric field part of the wave is
It is necessary to use satellites for long distance TV transmission because
In a single slit experiment, suppose the slit width is equal to the wavelength of light used, then:
|
39 docs|145 tests
|


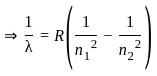
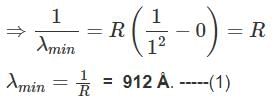
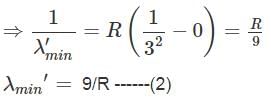

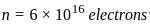
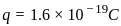
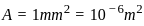
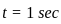
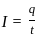
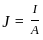
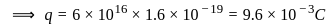
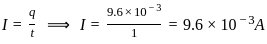
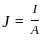
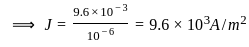
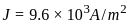 .
.