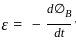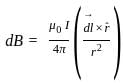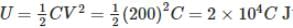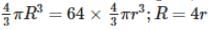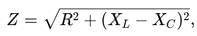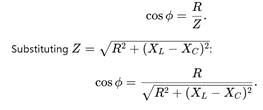Physics: CUET Mock Test - 7 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 7
Identify the process in which an electron escapes from the metal surface.
Read the following statements with reference to electronic devices.
(A) A transistor is used as a rectifier
(B) A zener diode is used as a voltage regulator
(C) A NOT gate is a universal gate
(D) A transistor is used as an amplifier
(E) A photodiode is used as an oscillator
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Read the following statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Electric current is a vector quantity.
Reason (R): Electric current is a quantity having magnitude as well as direction.
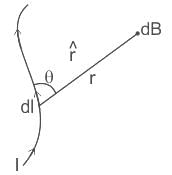
Which of the following statements are true regarding Biot – Savart’s law?
(i) According to biot – savart’s law magnetic field is directly proportional to the length of the element.
(ii) Biot – Savart’s law deals with electric field.
(iii) Magnetic field is directly proportional to current through the conductor.
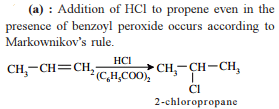
A capacitor of capacitance C is fully charged by a 200 V supply. It is then discharged through a small coil of resistance wire embedded in a thermally insulated block of specific heat 2.5×102Jkg−1K−1 and of mass 0.1 kg. If the temperature of the block rises by 0.4 K, what is the value of C?
64 water drops having equal charges combine to form one bigger drop. The capacitance of the bigger drop, as compared to that of smaller drop will be:
An electrolytic capacitor is marked 8 μF, 220 V. It can be used in a circuit where the p.d. across the capacitor may be:
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is 5 μF. When a glass slab of thickness equal to the separation between the plates is introduced between the plates, the potential difference reduces to 1/8 of the original value. The dielectric constant of glass is
For a parallel plate capacitor ______________ possible potential difference between the capacitor plates.
Three similar light bulbs are connected to a constant voltage d.c. supply as shown in Fig. Each bulb operates at normal brightness and the ammeter (of negligible resistance) registers a steady current.
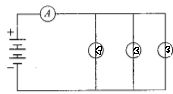
The filament of one of the bulbs breaks. What happens to the ammeter reading and to the brightness of the remaining bulbs?
Ammeter reading _______ & Bulb brightness _______
In a meter bridge experiment a balance point is obtained at a distance of 60 cm from the left end when unknown resistance R is in a left gap and 8 ohms resistor is connected in the right gap. When the position of R and 8 ohm resistor is interchanged the balance point will be at distance of
The following fig. shows I-V graph for a given metallic wire at two temperatures T1and T2.Then,
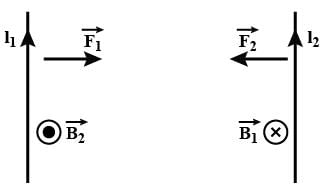
In two current carrying conductors parallel currents________, anti parallel currents_________ .
No force is exerted by a magnetic field on a stationary –
Along an infinitely long conductor carrying a current of 8 A we keep another conductor of length 5 m carrying a current of 3 A. Both the conductors are 10 cm apart. Find the force on small conductor.
We use _________ to find the direction of force when two current carrying conductors are kept parallel to each other.
In a series LCR what will be phase difference between voltage drop across inductor and capacitor
Probability of backward scattering (i.e., scattering of α -particles at angles greater than 90∘) predicted by Thomson’s model is
In Geiger-Marsden experiment very small deflection of the beam was expected because
The radius of a nucleus is directly proportional to (A=mass number)
The volume of atom in comparison of volume of nucleus is of the order of
If the voltage across the electrodes of a cathode ray tube is 500 volts then energy gained by the electrons is
If work function of a metal plate is negligible then the K.E.of the photoelectrons emitted when radiations of 1000 Â are incident on the metal surface is
|
39 docs|145 tests
|