Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 10 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 10
What is the direction of flow of electrons in an electrolytic cell?
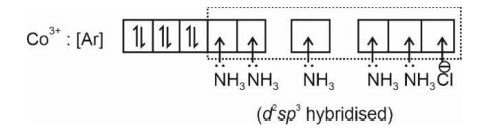
The spin only magnetic moment of the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl] Cl2 in BM is
The hybridization of cobalt in the above coordination entity is
- The coordination number of cobalt in the above coordination entity is
The primary valence of Co in above coordination entity is
What is the standard potential E° of the cell
Zn | Zn2+ (IM) || I- (IM) | CuI | Cu of Eo Zn2+ | Zn = -0.76 V and Eo Cu+ | Cu = -0.17 V?
When initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life period of a zero order reaction
An endothemic reaction A → B has an activation energy 15 kcal/mole and energy of reaction 5 kcal/mole. The activation energy of the reaction B → A is
The molar conductance of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
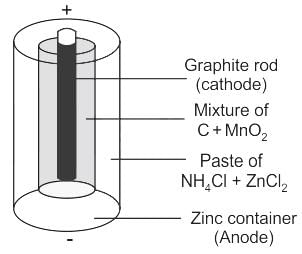
In a dry cell, which of the following are used as electrolytes?
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of a salt bridge?
Which of the following factors does not affect the electrode potential of an electrode?
When equilibrium is reached inside the two half-cells of the electrochemical cells, what is the net voltage across the electrodes?
In which of the following solutions will the Van’t Hoff Factor for the solute be lesser than 1?
The depression of freezing point of a solution of acetic acid in benzene is – 0.2°C. If the molality of acetic acid is 0.1 m, then find the ratio of the normal mass to the abnormal mass. (Assume Kf of acetic acid = 4.0°C m-1)
Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the least boiling point?
Acetic acid associates as dimers in benzene. What is the Van’t Hoff factor (i) if the degree of association of acetic acid is 50%?
The pH of a 2 M solution of a weak monobasic acid (HA) is 4. What is the value of the Van’t Hoff factor?
What is the Van’t Hoff Factor for 1 mole of BaCl2, assuming 100% dissociation?
What is the value of the Van’t Hoff factor (i) for solutes that dissociate in water?
What is defined as the concentration of dissolved solute in a solvent beyond which none of it, if added to the solvent, will increase the concentration further more?
In a saturated solution with endothermic dissolution, how does the concentration of dissolved solute change with increasing then decreasing temperature?
When CO2 is introduced into aerated drinks and sealed, what is the nature of the graph between partial pressure of CO2 and its concentration in the drink?
Which of the following best describes the difficulty in breathing as one climbs to higher altitudes?
What is the substance, present in a larger quantity that tends to establish homogenous bonds with a foreign substance, introduced in smaller quantity?
What is the solubility product expression for silver chromate dissolving in water?
What characteristic of water accounts for its unique properties as a solvent?
Which of the following compound releases heat when dissolved in water?
|
39 docs|148 tests
|



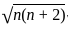 BM
BM