NEET Unit Test - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2025 Pattern - NEET Unit Test - 2
A body weighs 72 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it, at a height equal to half the radius of the earth?
A circular steel wire 2.00 m long must stretch no more than 0.25 cm when a tensile force of 400 N is applied to each end of the wire. What minimum diameter is required for the wire? Given that the Young's modulus for steel is Young's modulus of the material is 2.00×1011 N/m2)
A particle is projected upward from the surface of earth (radius = R) with a speed equal to the orbital speed of a satellite near the earth’s surface. The height to which it would rise is
In an equilateral triangle of length 6 cm , three masses m1= 40g , m2= 60g and m3= 60g are located at the vertices. The moment of inertia of the system about an axis along the altitude of the triangle passing through m1 is
What would be the horse power of a steam engine with average pressure of steam 9x 104 Nm-2 , the area of cross section of the piston is 0.2 m2, length of stroke is 0.6 m and piston makes 5 revolutions per second?
A steel rod 2.0 m long has a cross-sectional area of 0.30 cm2 . It is hung by one end from a support, and a 550-kg milling machine is hung from its other end. Determine the resulting strain. Young's Modulus of Steel (Y) = 20×1010 Pa
Equal masses of three liquids of specific heats C1, C2 and C3 at temperatures t1, t2 and t3 respectively are mixed. If there is no change of state, the temperature of the mixture is
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is 3P where P is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one fifth., the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
Direction (Q. Nos. 22-27) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage l
Isotope of oxygen with mass number less than 16 undergoes β+ -emission. Assume an equimolar mixture of 14O and 15O, Also t50 (14O) = 71s, t50 (15O) = 124s.
Q. Ratio of rate constants of 14O to 15O is
The value of Henry's law constant for some gases at 293K is given below. Arrange the gases in the increasing order of their solubility.
He = 144.97kbar; H2 = 69.16kbar
N2 = 76.48kbar; O2 = 34.86kbar
Vapour pressure of a pure liquid X is 2 atm at 300 K. It is lowered to 1 atm on dissolving 1 g of Y in 20 g of liquid X. If molar mass of X is 200, what is the molar mass of Y?
Given below are few mixtures formed by mixing two components. Which of the following binary mixtures will have same composition in liquid and vapour phase?
(i) Ethanol + Chloroform
(ii) Nitric acid + Water
(iii) Benzene + Toluene
(iv) Ethyl chloride + Ethyl bromide
Rate of formation of SO3 in the reaction below is 100 kg min-1.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
Hence, rate of disappearance of SO2 will be:
The activation energy of the reaction at a given temperature is found to (2.303 RT) J mol-1. The ratio of rate constant to the Arrhenius factor is
How many Na+ ions are present in 100 mL of 0.25 M of NaCl solution?
During complete combustion of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of heat is released. The thermochemical reaction for above change is ΔfU0 of formation of CH4 (g) at certain temperature is –393 kJ mol−1. The value of ΔfH0is
What is the mass of urea required for making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution?
The following reaction can take place in both directions:
For the forward reaction, the rate varies with the concentration of A as and for the backward reaction,
Hence, net reaction rate is:
What will be the temperature change of 1.00 mole of CH3OH(g) if 100 J of heat is added to it under constant volume conditions?

Given a graph with light intensity on the x-axis and photosynthesis rate on the y-axis, at what point does the rate of photosynthesis stop increasing with increased light intensity due to other limiting factors?
Read the following four statements carefully.
(i) Asthma is a difficulty in breathing causing wheezing due to inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles.
(ii) The part of the respiratory system starting with the external nostrils up to the terminal bronchioles constitutes the respiratory or exchange part of the respiratory system.
(iii) During swallowing epiglottis can be covered by a thin elastic cartilaginous ilap calied glottis to prevent the entry of food into the larynx.
(iw) Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is primarily related to partial pressure of O2. Which of the above two statements are correct?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for cell elongation in plants?
What is the primary site for the exchange of gases in the human body?
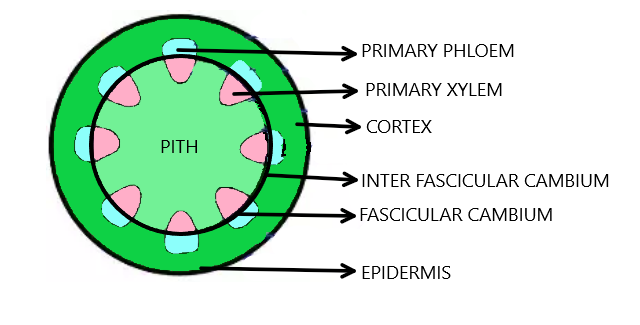
Vascular bundles in which cambium is present between xylem and phloem is called as
The course of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called
Refer the given equation.
2(C51H98O6) + 145O2 → 102CO2 + 98H2O + Energy
The RQ in this case is
|
1 videos|18 docs|80 tests
|