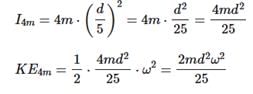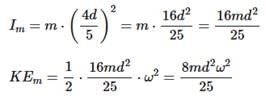Physics: Topic-wise Test- 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Physics: Topic-wise Test- 2
A uniform disc of radius 20 cm and mass 2 kg is fixed at its centre and can rotate about an axis through the centre and perpendicular to its plane. A massless cord is round along the rim of the disc. If a uniform force 2 newton is applied on the cord, tangential acceleration of a point on the rim of the disc will be
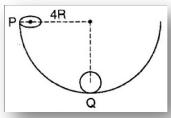
Fig shows a hemisphere of radius 4R A ball of radius R is released from position P. It rolls . A ball of without slipping along the inner surface of the hemisphere. Linear speed of its centre of mass when the ball is at position Q is
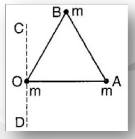
Three point masses, each m, are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side ‘α" Moment of inertia of the system about the axis COD which passes through the mass at O and lies in the plane of triangle and perpendicular to OA is
An object of mass m is projected with a velocity u at an angle 45° with the horizontal. When the object is at maximum height, its angular momentum about the point of projection is
At what height above the earth’s surface does the acceleration due to gravity fall to 1% of its value at the earth’s surface?
A ring has a total mass m but not uniformly distributed over its circumference. The radius of the ring is R. A point mass m is placed at the centre of the ring. Work done in taking away the point mass from centre to infinity is
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is R−5/2 , then T2 is proportional to
Two point masses of mass 4m and m respectively separated by d distance are revolving under mutual force of attraction. Ratio of their kinetic energies will be :
If G is the universal gravitational constant and ρ is the uniform density of spherical planet.
Then shortest possible period of the planet can be
A planet is moving in an elliptical path around the sun as shown in figure. Speed of planet in positional P and Q are υ1 and υ2 respectively with SP = r1 and SQ = r2 , then υ1/υ2 is equal to
Consider two configurations of a system of three particles of masses m, 2m and 3m. The work done by external agent in changing the configuration of the system from figure (i) to figure (ii) is
A spherical ball of mass 2 kg is rolling without slipping with a speed 4 m/s on a rough floor. Its rotational kinetic energy is :
A thin wire of length L and uniform linear mass density r is bent into a circular loop with centre O as shown. The moment of inertia of the loop about the axis XX is
Refrigerators X and Y are removing 1000 J of heat from the freezer. Refrigerator X is working between -5° C and 25° C and refrigerator Y is working between -20° C and 20 °C. Find efficiency of refrigerator X and Y?
For proper utilization of exergy, it is desirable to make first law efficiency ____ and the source and use temperatures should ____.
If the door of refrigerator is left open inside a closed room, what would happen to the temperature of the room?
Suppose we have a box filled with gas and a piston is also attached at the top of the box.What are the ways of changing the state of gas (and hence its internal energy)?
Hot coffee in a thermos flask is shaken vigorously, considering it as a system which of the statement is not true?
Which wall would allow the flow of thermal energy between systems A and B to achieve thermal equilibrium?
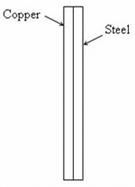
Two identical rectangular strips, one of copper and the other of steel, are riveted as shown to form a bi-metal strip. On heating, the bi-metal strip will
Four cylindrical rods of different radii and lengths are used to connect two heat reservoirs at fixed temperatures t1 and t2 respectively. From the following pick out the rod which will conduct the maximum quantity of heat:
The temperature for which the reading on Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are identical is
A steel tape is calibrated at 20° C. A piece of wood is being measured by steel tape at 10°C and reading is 30 cm on the tape. The real length of the wood is:
The coefficient of liner expansion of a cubical crystal along three mutually perpendicular direction is  and
and  . What is the coefficient of cubical expansion of crystal?
. What is the coefficient of cubical expansion of crystal?
An Indian rubber cube of side 10 cm has one side fixed while a tangential force of 1800 N is applied to the opposite side. Find the shear strain produced. Take η = 2 x 106 N/ m2.
The length of the wire is increased by 1 mm on the application of a given load. In a wire of the same material but of length and radius twice that of the first, on application of the same force, extension produced is
The volume of a spherical body is decreased by 10-3% when it is subjected to pressure of 40 atmospheres. Find the bulk modulus of body.
(1 atm = 1.01 x 105 N/m2).