Test: File Handling - Humanities/Arts MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Computer Science for Class 12 - Test: File Handling
What happens when the following statement is executed and file1.txt is not present in the current directory?
file_obj = open("file1.txt", "r")
(1) Python creates a new file ‘file1.txt’
(2) Raises a FileNotFoundError
(3) Raises an IOError
(4) Does nothing
file_obj = open("file1.txt", "r")
(1) Python creates a new file ‘file1.txt’
(2) Raises a FileNotFoundError
(3) Raises an IOError
(4) Does nothing
Select the statement that is not true for r+ mode.
(1) If the file does not exist, it gives an error.
(2) Both reading and writing can be performed.
(3) If the file does not exist, it creates a new file.
(4) Existing data is not truncated.
(1) If the file does not exist, it gives an error.
(2) Both reading and writing can be performed.
(3) If the file does not exist, it creates a new file.
(4) Existing data is not truncated.
What is the full form of CSV file?
1) Colon Separated Values
2) Context Separated Values
3) Comma Separated Values
4) Caps Separated Values
1) Colon Separated Values
2) Context Separated Values
3) Comma Separated Values
4) Caps Separated Values
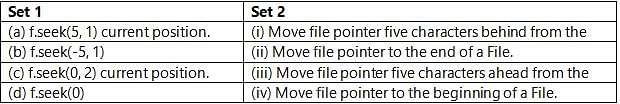
Which of the following option is true?
fp.seek(10, 1)
(1) Move file pointer ten characters behind from the current position.
(2) Move file pointer ten characters ahead from the current position.
(3) Move file pointer ten characters ahead from the beginning of a file.
(4) Move file pointer ten characters behind ahead from the end of a file.
Which one is the following advantage of using with clause while opening a file.
A ___________ method is used to position the file object at a particular position in a file.
The following code will perform which operation?
object.readline(10)
You are given the text file, file1.txt whose contents are:
hello everyone
today is a monday
all the best for your exams
What will be the output of the following code?
myfile = open("file1.txt", "r")
str = myfile.readline(20)
print(str)
myfile.close()
With reference to file handling in Python, which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
a. The file seek points are 0, 1, and 2.
b. The seek() function works differently for text and binary files.
c. When a file is opened in binary mode, the seek() method can have a negative offset value.
d. The offset in the seek() function specifies the number of bits by which the file pointer is to be moved.
|
1 videos|26 docs|18 tests
|