Test: Work, Energy & Power - 2 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 11 - Test: Work, Energy & Power - 2
A person applies a constant force 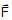 on a particle of mass m and finds that the particle moves in a circle of radius r with a uniform speed v as seen (in the plane of motion) from an inertial frame of reference
on a particle of mass m and finds that the particle moves in a circle of radius r with a uniform speed v as seen (in the plane of motion) from an inertial frame of reference
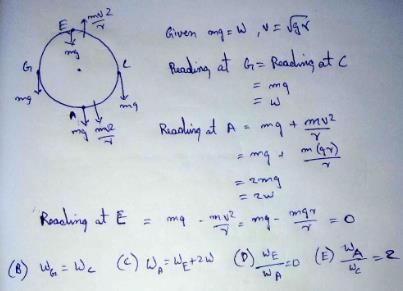
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage at the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speed
v = 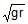 . The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
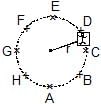
A simple pendulum of length l and mass (bob) M is oscillating in a plane about a vertical line between angular limits _f and f. For an angular displacement q, [|q| < f] the tension in the string and velocity of the bob are T and v respectively. The following relations hold good under the above conditions :
A spot light S rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of 0.1 rad/s. The spot of light p moves along the wall at a distance 3 m. What is the velocity of the spot P when q = 45° ?
Two moving particle P and Q are 10 m apart at a certain instant. The velocity of P is 8m/s making an angle 30° with the line joining P and Q and that of Q is 6m/s making an angle 30° with PQ as shown in the figure. Then angular velocity of P with respect to Q is
The magnitude of displacement of a particle moving in a circle of radius a with constant angular speed w varies with time t as
A particle moves along an arc of a circle of radius R. Its velocity depends on the distance covered as v = a, where a is a constant then the angle a between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s will be
A particle A moves along a circle of radius R = 50 cm so that its radius vector r relative to the point O (Fig.) rotates with the constant angular velocity w = 0.40 rad/s. Then modulus of the velocity of the particle, and the modulus of its total acceleration will be
Tangential acceleration of a particle moving in a circle of radius 1 m varies with time t as (initial velocity of particle is zero). Time after which total cceleration of particle makes and angle of 30º with radial acceleration is
A stone of mass of 16 kg is attached to a string 144 m long and is whirled in a horizontal smooth surface. The maximum tension the string can withstand is 16 newton. The maximum speed of revolution of the stone without breaking it, will be :
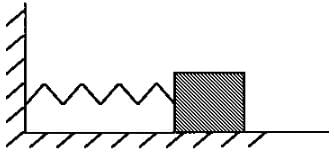
One end of a light spring of spring constant k is fixed to a wall and the other end is tied to a block placed on a smooth horizontal surface. In a displacement, the work done by the spring is . The possible cases are:
A particle with constant total energy E moves in one dimension in a region where the potential energy is U(x). The speed of the particle is zero where
A block of mass m slides down a plane inclined at an angle q. Which of the following will NOT increase the energy lost by the block due to friction ?
A box of mass m is released from rest at position on the frictionless curved track shown. It slides a distance d along the track in time t to reach position 2, dropping a vertical distance h. Let v and a be the instantaneous speed and instantaneous acceleration, respectively, of the box at position 2. Which of the following equations is valid for this situation?
A ball of mass m is attached to the lower end of light vertical spring of force constant k. The upper end of the spring is fixed. The ball is released from rest with the spring at its normal (unstreched) length, comes to rest again after descending through a distance x.
A cart moves with a constant speed along a horizontal circular path. From the cart, a particle is thrown up vertically with respect to the cart
The potential energy in joules of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in a plane is given by U = 3x + 4y, the position coordinates of the point being x and y, measured in meters. If the particle is initially at rest at (6, 4), then
A particle of mass m is released from a height H on a smooth curved surface which ends into a vertical loop of radius R, as shown
Choose the correct alternative(s) if H = 2R
If q is instantaneous angle which the line joining the particle and the centre of the loop makes with the vertical, then identify the correct statement(s) related to the normal reaction N between the block and the surface
The minimum value of H required so that the particle makes a complete vertical circle is given by
Which of the following laws/principles of physics can be applied on the spring block system
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|



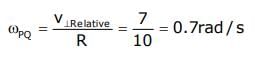


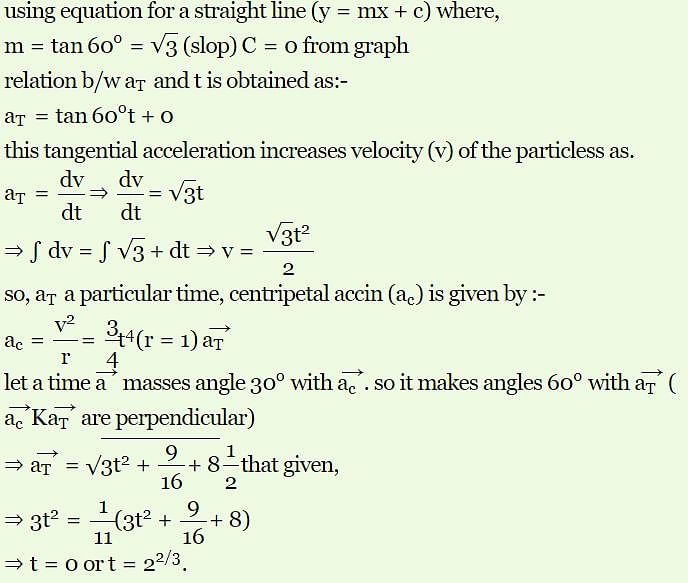
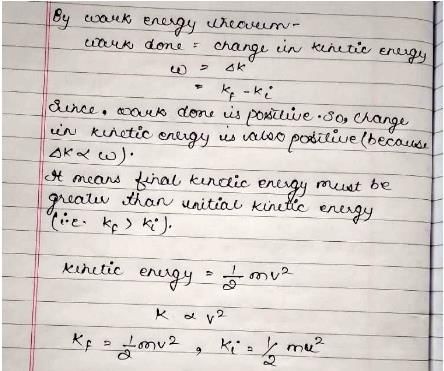


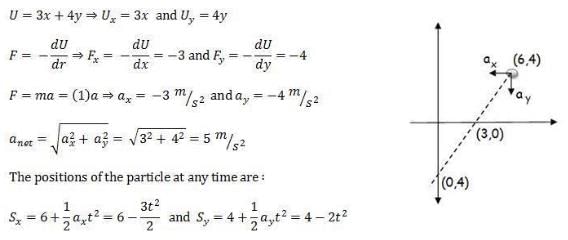
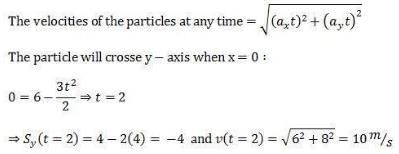 Similarly you can find that the particle crosses x - axis at (3, 0) with a velocity 7.07 m/s
Similarly you can find that the particle crosses x - axis at (3, 0) with a velocity 7.07 m/s