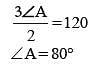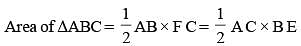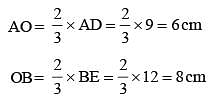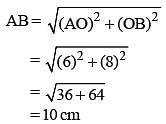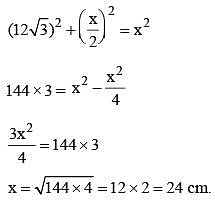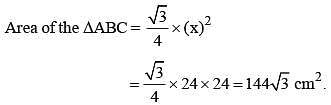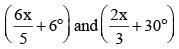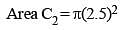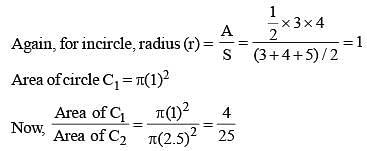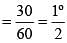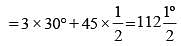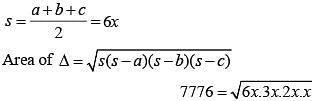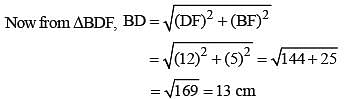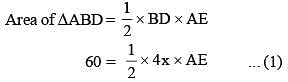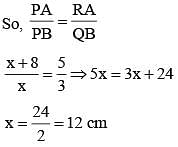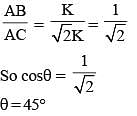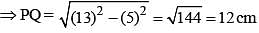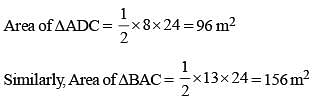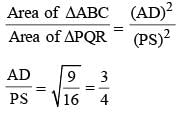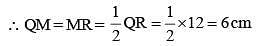SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 3 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Previous Year Papers - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 3
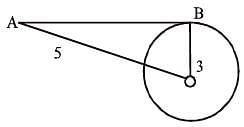
O is the centre of a circle and AB is the tangent to it touching at B. If OB = 3 cm. and OA = 5 cm, then the measure of AB in cm is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
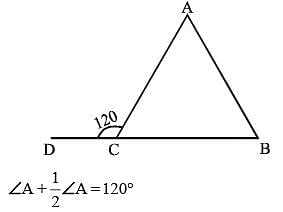
In a ΔABC, BC is extended upto D: ∠ACD = 120°, ∠B = 1/2∠A. Then ∠A is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
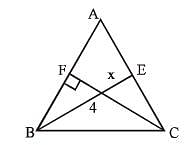
BE and CF are two altitudes of a triangle ABC. If AB = 6 cm, AC = 5 cm and CF = 4 cm, then the length of BE is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
O is the orthocentre of ΔABC , and if ∠BOC = 110° then ∠BAC will be (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2016)
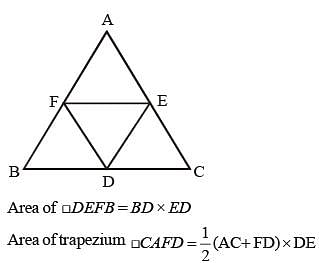
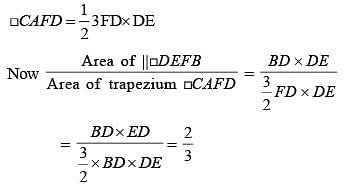
If D, E and F are the mid points of BC, CA and AB respectively of the ΔABC then the ratio of area of the parallelogram DEFB and area of the trapezium CAFD is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
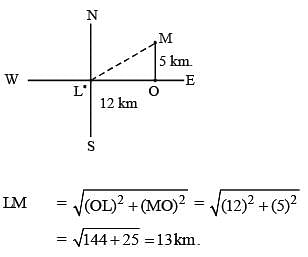
If a person travels from a point L towards east for 12 km and then travels 5 km towards north and reaches a point M, then shortest distance from L to M is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
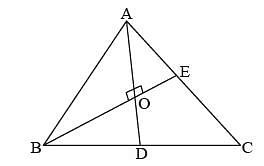
G is the centroid of ΔABC. The medians AD and BE intersect at right angles. If the lengths of AD and BE are 9 cm and 12 cm respectively; then the length of AB (in cm) is? (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
If the measure of three angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 5, then the triangle is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
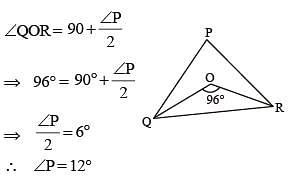
Internal bisectors of ∠Q and ∠R of ΔPQR intersect at O. If ∠ROQ = 96° then the value of ∠RPQ is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
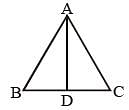
If the altitude of an equilateral triangle is 12√3 cm, then its area would be: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
If the number of vertices, edges and faces of a rectangular parallelopiped are denoted by v, e and f respectively, the value of (v – e + f) is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
If the three angles of a triangle are:
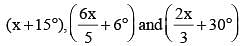 then the triangle is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
then the triangle is: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
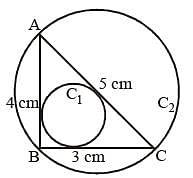
Let C1 and C2 be the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle with sides 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm then area of C1 to area of C2 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
If a clock started at noon, then the angle turned by hour hand at 3.45 PM is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
In a parallelogram PQRS, angle P is four times of angle Q, then the measure of ∠R is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
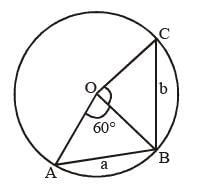
Two chords of length a unit and b unit of a circle make angles 60° and 90° at the centre of a circle respectively, then the correct relation is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
The sides of a triangle having area 7776 sq. cm are in the ratio 3 : 4 : 5. The perimeter of the triangle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
The measure of an angle whose supplement is three times as large as its complement, is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
Two poles of height 7 m and 12 m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between their feet is 12 m, the distance between their top will be (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
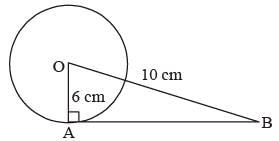
A tangent is drawn to a circle of radius 6cm from a point situated at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the circle.
The length of the tangent will be (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
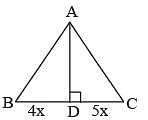
In ΔABC, a line through A cuts the side BC at D such that BD : DC = 4 : 5. If the area of ΔABD = 60 cm2, then the area of ΔADC is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2015)
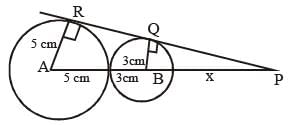
Two circles of radii 5 cm and 3 cm touch externally, then the ratio in which the direct common tangent to the circles divides externally the line joining the centres of the circles is: (SSC CHSL 2015)
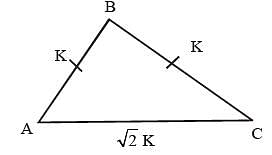
In ΔABC, AB = BC = K, AC = √2 K, then ΔABC is a: (SSC CHSL 2015)
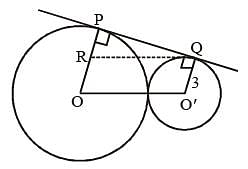
The distance between centres of two circles of radii 3 cm and 8 cm is 13 cm. If the points of contact of a direct common tangent to the circles are P and Q, then the length of the lien segment PQ is: (SSC CHSL 2015)
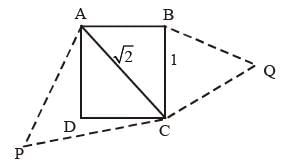
ABCD is a square. Draw a triangle QBC on side BC considering BC as base and draw a triangle PAC on AC as its base such that Δ QBC ~ Δ PAC.
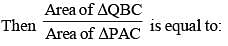 (SSC CHSL 2015)
(SSC CHSL 2015)
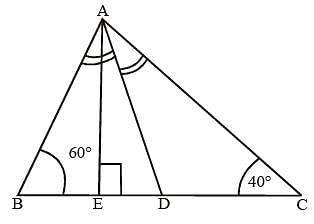
In ΔABC, ∠B = 60°, and ∠C = 40°; AD and AE are respectively the bisector of ∠A and perpendicular on BC. The measure of ∠EAD is: (SSC CHSL 2015)
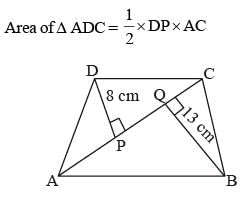
The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24m an d the perpendiculars dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 8m and 13m. The area of the field is: (SSC Sub. Ins. 2015)
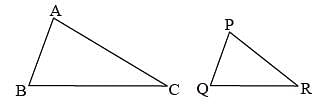
The perimeters of two similar triangles are 30 cm and 20cm respectively. If one side of the first triangle is 9cm. Determine the corresponding side of the second triangle: (SSC Sub. Ins. 2015)
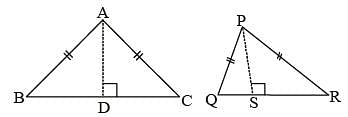
Two isosceles triangles have equal vertical angles and their areas are in the ratio 9 : 16. Then the ratio of their corresponding heights is: (SSC Sub. Ins. 2015)
Two circles of radii 10 cm and 8 cm intersect and the length of the common chord is 12 cm. Then the distance between their centres is: (SSC Sub. Ins. 2015)
|
316 docs|268 tests
|