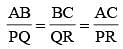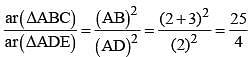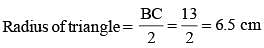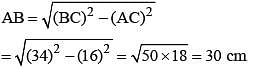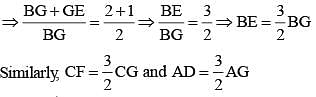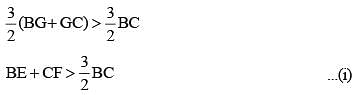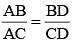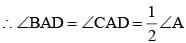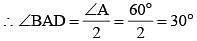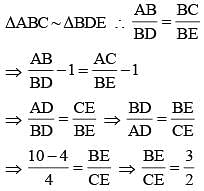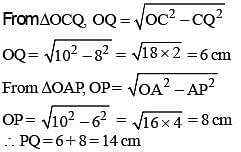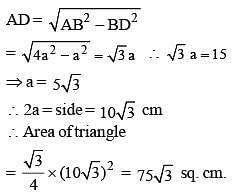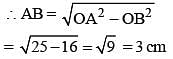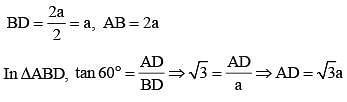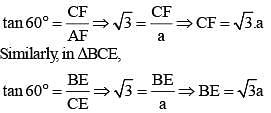SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 4 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Previous Year Papers - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Geometry- 4
If the sides of a right angled triangle are three consecutive integers, then the length of the smallest side is (SSC CHSL 2014)
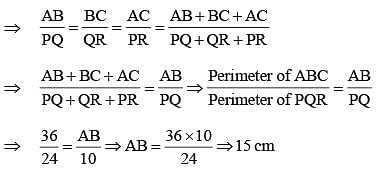
The perimeters of two similar triangles ΔABC and ΔPQR are 36 cm and 24 cm respectively. If PQ = 10 cm, the AB is (SSC CHSL 2014)
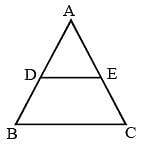
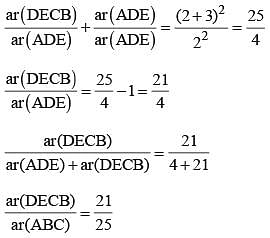
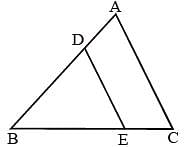
In ΔABC, D and E are two points on the sides AB and AC respectively so that DE || BC and 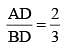 . Then
. Then  is equal to (SSC CHSL 2014)
is equal to (SSC CHSL 2014)
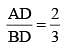 . Then
. Then  is equal to (SSC CHSL 2014)
is equal to (SSC CHSL 2014)The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is 1444°. The number of sides of the polygon is (SSC CHSL 2014)
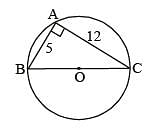
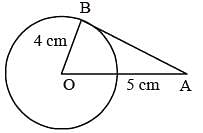
If AB = 5 cm, AC = 12 and AB ⊥ AC then the radius of the circumcircle of ΔABC is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
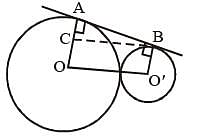
Two circles with radii 25 cm and 9 cm touch each other externally. The length of the direct common tangent is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
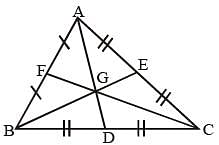
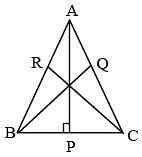
In a ΔABC, 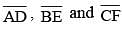 are three medians. Then the ratio
are three medians. Then the ratio 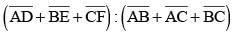 is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
In a ΔABC, AD, BE and CF are three medians. The perimeter of ΔABC is always (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
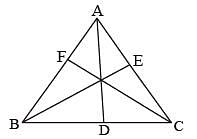
In a ΔABC, 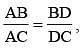 ∠B = 70° and ∠C = 50°, then ∠BAD =? (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
∠B = 70° and ∠C = 50°, then ∠BAD =? (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
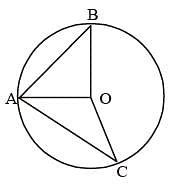
A, B and C are the three points on a circle such that the angles subtended by the chords AB and AC at the centre O are 90° and 110° respectively. ∠BAC is equal to (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
In ΔABC, DE || AC. D and E are two points on AB and CB respectively. If AB = 10 cm and AD 2.4 cm, then BE : CE is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
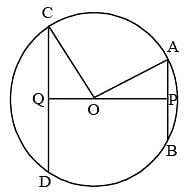
Two parallel chords of a circle, of diameter 20 cm lying on the opposite sides of the centre are of lengths 12 cm and 16 cm.
The distance between the chords is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The height of an equilateral triangle is 15 cm. The area of the triangle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
A cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is such that AB = BC, AD = DC, AC ⊥ BD, ∠CAD = θ. Then the angle ∠ABC = (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The length of the tangent drawn to a circle of radius 4 cm from a point 5 cm away from the centre of the circle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
In ΔABC, ∠A + ∠B = 65°, ∠B + ∠C = 140°, then find ∠B. (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The sum of three altitudes of a triangle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If the inradius of a triangle with perimeter 32 cm is 6 cm, then the area of the triangle (in sq. cm) is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
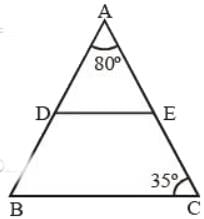
D and E are the mid-points of AB and AC of ΔABC. If ∠A = 80°, ∠C = 35°, then ∠EDB is equal to (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
When two circles touch externally, the number of common tangents are (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
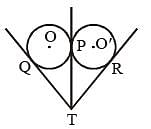
Two circles of equal radii touch externally at a point P. From a point T on the tangent at P, tangents TQ and TR are drawn to the circles with points of contact Q and R respectively. The relation of TQ and TR is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
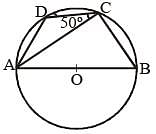
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral, AB is a diameter of the circle. If ∠ACD = 50°, the value of ∠BAD is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
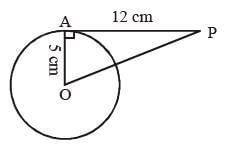
The length of tangent (upto the point of contact) drawn from an external point P to a circle of radius 5 cm is 12 cm. The distance of P from the centre of the circle is (SSC CGL Ist. Sitt. 2013)
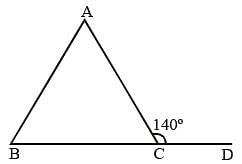
Side BC of ΔABC is produced to D. If ∠ACD = 140° and ∠ABC = 3∠BAC, then find ∠A. (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
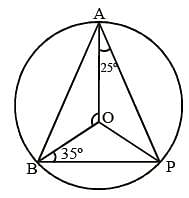
A, B, P are three points on a circle having centre O. If ∠OAP = 25° and ∠OBP = 35°, then the measure of ∠AOB is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
In a triangle, if three altitudes are equal, then the triangle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
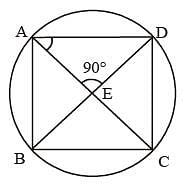
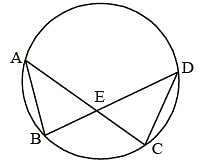
A, B, C, D are four points on a circle. AC and BD intersect at a point E such that ∠BEC = 130° and ∠ECD = 20°. ∠BAC is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
A vertical stick 12 cm long casts a shadow 8 cm long on the ground. At the same time, a tower casts a shadow 40 m long on the ground. The height of the tower is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
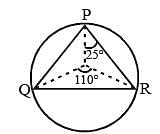
If O be the circumcentre of a triangle PQR and ∠QOR = 110°, ∠OPR = 25°, then the measure of ∠PRQ is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
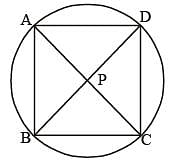
The diagonals AC and BD of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point P. Then, it is always true that (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
|
316 docs|268 tests
|