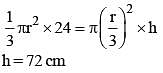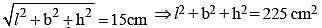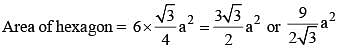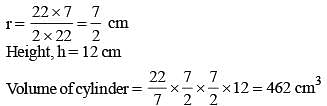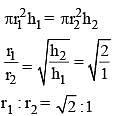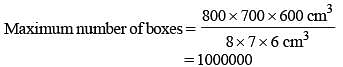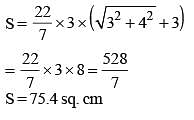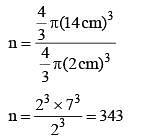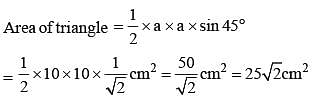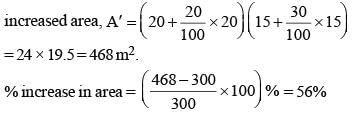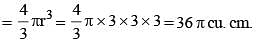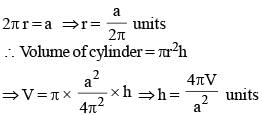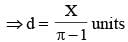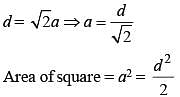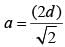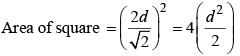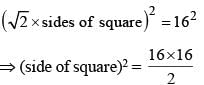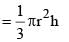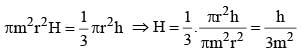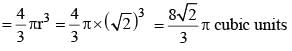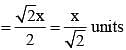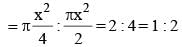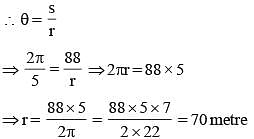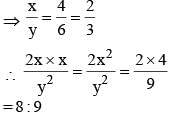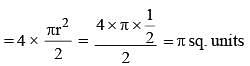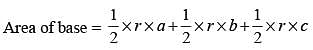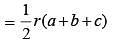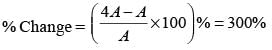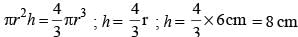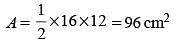SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Mensuration - 3 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Previous Year Papers - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Mensuration - 3
A flask in the shape of a right circular cone of height 24 cm is filled with water. The water is poured in a right circular cylindrical flask whose radius is 1rd/3 of the radius of the base of the circular cone. Then the height of the water in the cylindrical flask is (SSC CHSL 2014)
If the sum of the dimensions of a rectangular parallelepiped is 24 cm and the length of the diagonal is 15 cm, then the total surface area of it is (SSC CHSL 2014)
Area of a regular hexagon with side 'a' is (SSC CHSL 2014)
A sphere is placed inside a right circular cylinder so as to touch the top, base and the lateral surface of the cylinder. If the radius of the sphere is R, the volume of the cylinder is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
A rectangular piece of paper of dimensions 22 cm by 12 cm is rolled along its length to form a cylinder. The volume (in cm3) of the cylinder so formed is (use π = 22/7) (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
Two circular cylinders of equal volume have their heights in the ratio 1 : 2; Ratio of their radii is (Take π = 22/7) (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
A wooden box of dimension 8 metre × 7 metre × 6 metre is to carry rectangular boxes of dimensions 8 cm × 7 cm × 6 cm.
The maximum number of boxes that can be carried in 1 wooden box is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
The radius of a right circular cone is 3 cm and its height is 4 cm. The total surface area of the cone is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2014)
A spherical ball of lead of radius 14 cm is melted and recast into spheres of radius 2 cm. The number of the small spheres is (SSC Multitasking 2014)
Length of each equal side of an isosceles triangle is 10 cm and the included angle between those two sides is 45°. Find the area of the triangle. (SSC Multitasking 2014)
The length and breadth of a rectangle are 20 m and 15 m respectively. If length is increased by 20% and the breadth by 30%, the percentage increase in its area is (SSC Multitasking 2014)
A sphere of diameter 6 cm is dropped in a right circular cylindrical vessel partly filled with water. The diameter of the Cylindrical vessel is 12 cm. If the sphere is just completely submerged in water, then the rise of water level in the cylindrical vessel is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The perimeter of the base of a right circular cylinder is 'a' unit. if the volume of the cylinder is V cubic unit. then the height of the cylinder is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The difference of perimeter and diameter of a circle is X unit. The diameter of the circle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If the diagonal of a square is doubled, then its area will be (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The biggest possible circle is inscribed in a rectangle of length 16 cm and breadth 6 cm. Then its area is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
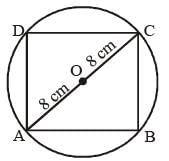
A square is inscribed in a circle of radius 8 cm. The area of the square is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
A conical flask is full of water. The flask has base radius r and height h. This water is poured into a cylindrical flask of base radius mr. The height of water in the cylindrical flask is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The total surface area of a sphere is 8 p square unit. The volume of the sphere is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The diameters of two circles are the side of a square and the diagonal of the square. The ratio of the areas of the smaller circle and the larger circle is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
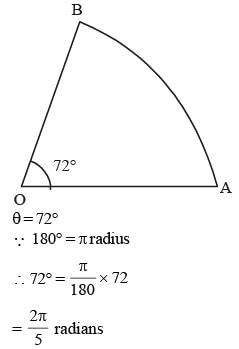
A horse is tied to a post by a rope. If the horse moves along a circular path always keeping the rope stretched and describes 88 metres when it has traced out 72° at the centre the length of the rope is (Take π = 22/7) (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If the perimeters of a rectangle and a square are equal and the ratio of two adjacent sides of the rectangle is 1 : 2 then the ratio of area of the rectangle and that of the square is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
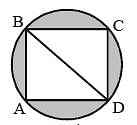
A square ABCD is in scribed in a circle of unit radius. Semicircles are described on each side as a diameter. The area of the region bounded by the four semicircles and the circle is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
The base of a right prism is a triangle whose perimeter is 28 cm and the inradius of the triangle is 4 cm. If the volume of the prism is 366 cc, then its height is (SSC CHSL 2013)
The length and breadth of a rectangle are doubled. Percentage increase in area is (SSC CHSL 2013)
If the total surface area of a cube is 96 cm2, its volume is (SSC CHSL 2013)
The volume of air in a room is 204 m3. The height of the room is 6 m. What is the floor area of the room? (SSC CHSL 2013)
What is the height of a cylinder that has the same volume and radius as a sphere of diameter 12 cm? (SSC CHSL 2013)
The sides of a triangle are 16 cm, 12 cm and 20 cm. Find the area (SSC CHSL 2013)
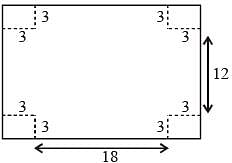
A square of side 3 cm is cut off from each corner of a rectangular sheet of length 24 cm and breadth 18 cm and the remaining sheet is folded to form an open rectangular box. The surface area of the box is (SSC CHSL 2013)
|
316 docs|268 tests
|