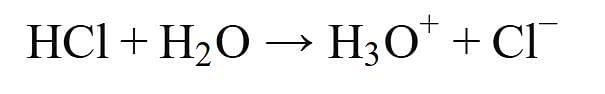Assertion & Reason Test: Acids, Bases & Salts - 1 - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Assertion & Reason Test: Acids, Bases & Salts - 1
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: After white washing the walls, a shiny white finish on walls is obtained after two to three days.
Reason: Calcium Oxide reacts with Carbon dioxide to form Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate which gives shiny white finish.
Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
Assertion (A): Ammonium hydroxide solution is an alkali.
Reason (R): Ammonium hydroxide solution turns blue litmus paper red.
Assertion (A): Baking soda creates acidity in the stomach.
Reason (R): Baking soda is alkaline.
Assertion (A): Plaster of Paris is used by doctors for setting fractured bones.
Reason (R): When Plaster of Paris is mixed with water and applied around the fractured limbs, it sets into a hard mass.
Direction: In the Following Questions, A Statement of Assertion (A) Is Followed by A Statement of Reason (R). Mark The Correct Choice As:
Assertion: While dissolving an acid or base in water, the acids must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring.
Reason: Dissolving an acid on a base in water is a highly exothermic reaction.
Assertion : On adding H2SO4 to water the resulting aqueous solution gets corrosive.
Reason: Hydronium ions are responsible for corrosive action.
Assertion : Phenolphthalein gives pink colour in basic solution.
Reason : Phenolphthalein is a natural indicator.
Assertion : HCl produces hydronium ions (H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl-) in aqueous solution.
Reason : In presence of water, bases give H+ ions.
Assertion: Sodium hydroxide reacts with zinc to produce hydrogen gas.
Reason : Acids react with active metals to produce hydrogen gas.
Assertion: Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of magnesia), a mild base, is used to neutralize the excess acid produced during indigestion.
Reasoning: The stomach produces hydrochloric acid to aid in digestion, but an excess of this acid during indigestion causes pain and irritation. Antacids, which are bases, help neutralize this excess acid and relieve the discomfort.
Assertion: Rubbing the area with the leaf of the dock plant helps neutralize the painful stings caused by the nettle plant.
Reasoning: The stinging hair of the nettle plant secretes methanoic acid, causing pain. The dock plant is used as a traditional remedy because its leaves have a neutralizing effect on the acid, relieving the sting.
Assertion: Common salt is an important raw material for the production of various materials like sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
Reasoning: Common salt is processed to obtain different substances, and each of these substances plays a crucial role in daily use, such as in cleaning, cooking, and chemical processes.
Assertion: HCl gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper.
Reason: HCl gas dissolves in the water present in wet litmus paper to from H+ ions.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A) : The acid must always be added to water with constant stirring.
Reason (R) : Mixing of an acid with water decreases the concentration of H+ ions per unit volume.
|
83 videos|437 docs|74 tests
|