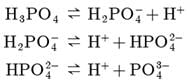Assertion & Reason Test: Acids, Bases & Salts - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Assertion & Reason Test: Acids, Bases & Salts - 2
Direction: In the Following Questions, A Statement of Assertion (A) Is Followed by A Statement of Reason (R). Mark The Correct Choice As:
Assertion : In water, Hydrochloric acid behaves as a weak monobasic acid.
Reason : In water, Hydrochloric acid acts as a proton donor.
Assertion : The acidity of Mg(OH)2 is two.
Reason : The acidity of a base is equal to the number of hydroxyl ions.
Assertion : The aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not show acidic character. Reason : Aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not give H+ ions.
Assertion : When zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen is given off.
Reason : Hydrogen chloride molecules contain hydrochloric acid and hydrogen atoms.
Assertion : Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloride acid.
Reason : Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
Assertion : During electrolysis of concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen is produced at anode and chlorine gas is produced at cathode.
Reason : Ions get attracted to oppositely charged electrodes.
Assertion : pH = 7 signifies pure water.
Reason : At this pH, [H+] = [OH-]= 10-7.
Assertion : Weak acids have low electrical conductivity.
Reason : Strong acids and weak acids have equal concentration of hydrogen ions in their solutions.
Assertion : H3PO4 and H2SO4 are known as polybasic acids.
Reason : They have two or more than two protons per molecule of the acid.
Assertion : If the pH inside the mouth decreases below5.5, the decay of tooth enamel begins.
Reason : The bacteria present in the mouth degrades the sugar and left over food particles and produce acids that remain in the mouth after eating.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: After white washing the walls, a shiny white finish on walls is obtained after two to three days.
Reason: Calcium Oxide reacts with Carbon dioxide to form Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate which gives shiny white finish.
Assertion (A): Ammonia solution is an alkali.
Reason (R): Ammonia solution turns blue litmus paper red.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): When common salt is kept open, it absorbs moisture from the air.
Reason (R): Common salt contains magnesium chloride.
Direction: In the Following Questions, A Statement of Assertion (A) Is Followed by A Statement of Reason (R). Mark The Correct Choice As:
Assertion : Pure water is neither acidic not basic.
Reason : The pH of a solution is inversely proportional to the concentration of hydrogen ions in it.
Assertion : Plaster of Paris is used by doctors by setting fractured bones.
Reason : When Plaster of Paris is mixed with water and applied around the fractured limbs, it sets into a hard mass.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|