Test: Nervous & Muscular Coordination - Class 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Test: Nervous & Muscular Coordination
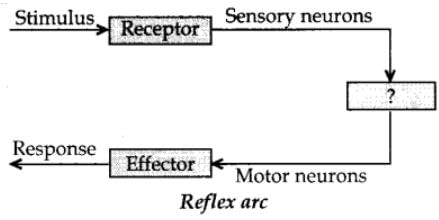
Why are reflex arc connections between input and output nerve made at spinal cord?
A part of the body which responds to the in-structions sent from nervous system is called
Which nerves transmit impulses from the cen¬tral nervous system towards muscle cells?
The part of a neuron where information is acquired is:
A microscopic gap between a pair of adjacent neurons over which nerve impulses pass is called
Which part of the nervous system controls the reflex activities of the body?
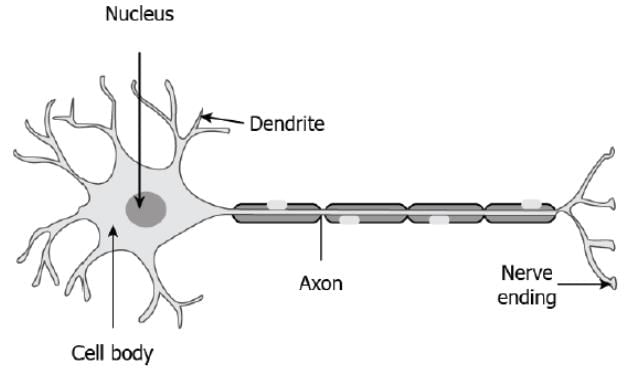
The image shows the structure of a neuron.
Which of the following options shows the mechanism of the travelling of sense in our body after our nose senses a smell?
How will information travel within a neuron?
Which of the following option shows the order of events correctly when a bright light is focused on our eyes?
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|