Case Based Questions: Periodic Classification of Elements - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science and Technology Class 10 (Maharashtra SSC Board) - Case Based Questions: Periodic Classification of Elements
From the following part of the periodic table, answer the question :
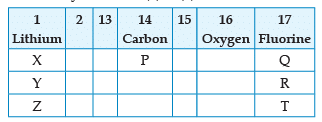
Which is the most reactive metal ?

From the following part of the periodic table, answer the question :
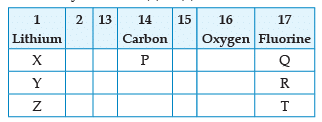
Which other element is likely to present in the group in which fluorine is present:

From the following part of the periodic table, answer the question :
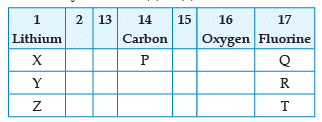
Name the family of fluorine Q, R, T:

From the following part of the periodic table, answer the question :
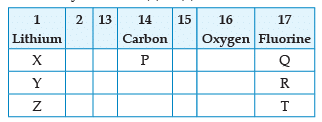
Name the element P placed below Carbon in group 14:
From the following part of the periodic table, answer the question :
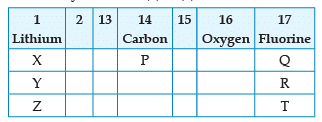
Which of the following elements belongs to group 2?
Read the passage and answer the question from :
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but are different in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of elements D is almost neutral.
Q. Which of the following is likely to be halogen?
Read the passage and answer the question from :
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but are different in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of elements D is almost neutral.
Q. Which one of the following will have the largest atomic radii?
Read the passage and answer the question from :
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but are different in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of elements D is almost neutral.
Q. Which one of the following elements is likely to be a noble gas?
Read the passage and answer the question from :
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but are different in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of elements D is almost neutral.
Q. To which period the listed elements belong?
Read the passage and answer the question from :
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but are different in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of elements D is almost neutral.
Q. Which two elements amongst these are likely to be the non–metals ?
Using the given part of the periodic table, answer the question :
![]()
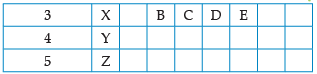
Which of these elements have the smallest atomic size?
Using the given part of the periodic table, answer the question :
![]()
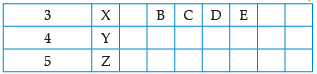
Q. The number of period that the modern periodic table has
Using the given part of the periodic table, answer the question :
![]()
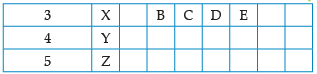
Write valency of element E.
Using the given part of the periodic table, answer the question :
![]()
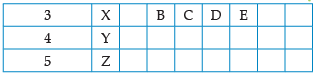
Which of them will have largest atomic radii:
Using the given part of the periodic table, answer the question :
![]()
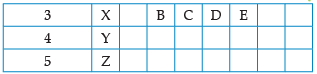
Q. Identify the elements which have similar chemical properties as the element X.
Read the passage and answer the questions :
Mendeleev was a Russian chemist, who contributed the most for the development of periodic table of elements wherein the elements were arranged on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties. Only 63 elements were known at his time. He arranged the 63 elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and found that there was a periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties. He observed that elements with similar properties fall in the same vertical column. These vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows of elements are called periods. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
Q. Mendeleev arranged the periodic table on the basis of their fundamental property:
Read the passage and answer the questions :
Mendeleev was a Russian chemist, who contributed the most for the development of periodic table of elements wherein the elements were arranged on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties. Only 63 elements were known at his time. He arranged the 63 elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and found that there was a periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties. He observed that elements with similar properties fall in the same vertical column. These vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows of elements are called periods. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
Q. Mendeleev’s periodic table has :
Read the passage and answer the questions :
Mendeleev was a Russian chemist, who contributed the most for the development of periodic table of elements wherein the elements were arranged on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties. Only 63 elements were known at his time. He arranged the 63 elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and found that there was a periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties. He observed that elements with similar properties fall in the same vertical column. These vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows of elements are called periods. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
Q. Eka aluminium and eka silicon were later replaced respectively as :
Read the passage and answer the questions :
Mendeleev was a Russian chemist, who contributed the most for the development of periodic table of elements wherein the elements were arranged on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties. Only 63 elements were known at his time. He arranged the 63 elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and found that there was a periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties. He observed that elements with similar properties fall in the same vertical column. These vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows of elements are called periods. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
Q. How do we classify these newly discovered elements (eka-aluminium and eka-silicon)?
Read the passage and answer the questions :
Mendeleev was a Russian chemist, who contributed the most for the development of periodic table of elements wherein the elements were arranged on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties. Only 63 elements were known at his time. He arranged the 63 elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and found that there was a periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties. He observed that elements with similar properties fall in the same vertical column. These vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows of elements are called periods. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
Q. The elements eka aluminium and eka silicon discovered by Mendeleev later found place in the periodic table. Both of these elements belong to :
|
26 videos|131 docs|27 tests
|
|
26 videos|131 docs|27 tests
|



















