Test: Enzymes - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biochemistry for MCAT - Test: Enzymes - 1
Consider a biochemical reaction A → B, which is catalyzed by A–B dehydrogenase. Which of the following statements is true?
Some enzymes require the presence of a nonprotein molecule to behave catalytically. An enzyme devoid of this molecule is called a(n):
In the equation below, substrate C is an allosteric inhibitor to enzyme 1. Which of the following is another mechanism necessarily caused by substrate C?
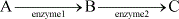
The graph below shows kinetic data obtained for flu virus enzyme activity as a function of substrate concentration in the presence and absence of two antiviral drugs.
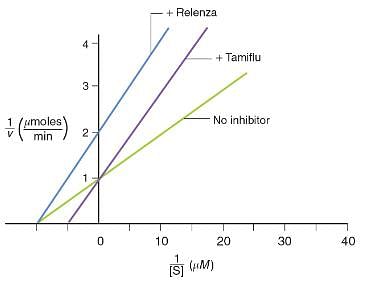
Based on the graph, which of the following statements is correct?
The conversion of ATP to cyclic AMP and inorganic phosphate is most likely catalyzed by which class of enzyme?
A certain cooperative enzyme has four subunits, two of which are bound to substrate. Which of the following statements can be made?
Which of the following is NOT a method by which enzymes decrease the activation energy for biological reactions?
Which of the following is LEAST likely to be required for a series of metabolic reactions?
How does the ideal temperature for a reaction change with and without an enzyme catalyst?
|
138 videos|21 docs|4 tests
|




















