Test: Irrigation - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Civil Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Test: Irrigation - 1
The area in which crop is grown at a particular time of crop season, is called
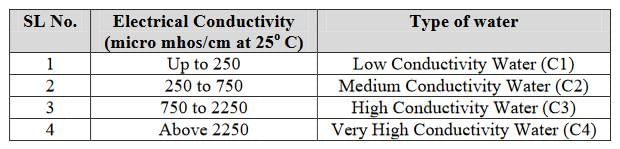
When electrical conductivity of irrigation water is upto ______ micro mhos/cm, it is called low conductivity water
The following structure serves the purpose of a ‘safety valve’ for a canal
The following data pertain to a natural drain crossing an irrigation canal
Which one of the following types of crossdrainage should be recommended in this case ?
What type of cross drainage work is provided when the canal runs below the drain, with FSL of canal well below the bed of the drain ?
Consider the following statements :
An aqueduct is a cross drainage work in which
1. a canal is carried over the drainage channel.
2. a drainage channel is carried over the canal.
3. both drainage channel and canal are at the same level.
Which of these statements is/are correct ?
Consider the following statements :
- The canal flows below the drain in aqueduct and syphon aqueduct, and the canal flows above the drain in super passage and syphon.
- The drain flows below the canal in aqueduct and syphon aqueduct, and the drain flows above the canal in super passage and syphon.
- It is engineer's choise to let the drain flow above or below the canal in aqueduct and syphon aqueduct and also in super passage and syphon.
Which of these statements are correct ?
The main advantage offered by Bentonite layer lining in an irrigation canal is that:
Under-drainage arrangements in canals are necessarily required in
In the alignment of an irrigation channel wherefrom offtakes have to be provided at regular intervals, changes in the given channel parameters are made use of. The correct sequence of the decreasing order of preference of these parameters is
Water-logging of cropped land leads to reduced crop yields, due to
Which one of the following does not contribute to water logging?
Which one of the following is not a remedial measure for water logging?
The method, which uses dead furrows on cropped farms for drainage of excess irrigation or rain water, is called:
A recently reclaimed alkaline soil should preferably be sown with a salt resistant crop, like
|
2 videos|133 docs|55 tests
|