Test: Pure Substances - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Pure Substances - 1
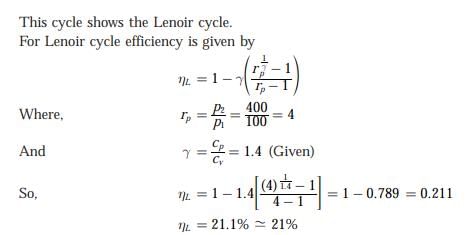
In the figure shown, the system is a pure substance kept in a piston-cylinder arrangement. The system is initially a two-phase mixture containing 1 kg of liquid and 0.03 kg of vapour at a pressure of 100 kPa. Initially, the piston rests on a set of stops, as shown in the figure. A pressure of 200 kPa is required to exactly balance the weight of the piston and the outside atmospheric pressure. Heat transfer takes place into the system until its volume increases by 50%. Heat transfer to the system occurs in such a manner that the piston, when allowed to move, does so in a very slow (quasi-static I quasi-equilibrium) process. The thermal reservoir from which heat is transferred to the system has a temperature of 400°C. Average temperature of the system boundary can be taken as 17°C. The heat transfer to the system is I kJ, during which its entropy increases by 10 J/K. Atmospheric pressure.
Specific volumes of liquid (vf) and vapour (vg) phases, as well as values of saturation temperatures, are given in the table below.

At the end of the process, which one of the following situations will be true?
In the figure shown, the system is a pure substance kept in a piston-cylinder arrangement. The system is initially a two-phase mixture containing 1 kg of liquid and 0.03 kg of vapour at a pressure of 100 kPa. Initially, the piston rests on a set of stops, as shown in the figure. A pressure of 200 kPa is required to exactly balance the weight of the piston and the outside atmospheric pressure. Heat transfer takes place into the system until its volume increases by 50%. Heat transfer to the system occurs in such a manner that the piston, when allowed to move, does so in a very slow (quasi-static I quasi-equilibrium) process. The thermal reservoir from which heat is transferred to the system has a temperature of 400°C. Average temperature of the system boundary can be taken as 17°C. The heat transfer to the system is I kJ, during which its entropy increases by 10 J/K. Atmospheric pressure.

Specific volumes of liquid (vf) and vapour (vg) phases, as well as values of saturation temperatures, are given in the table below.

The net entropy generation (considering the system and the thermal reservoir together) during the process is closest to:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
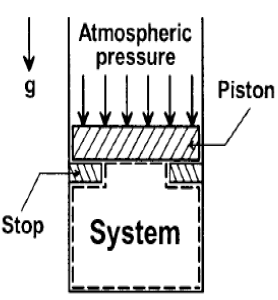
A thermodynamic cycle with an ideal gas as working fluid is shown below.
If the specific heats of the working fluid are constant and the value of specific heat ratio γ is 1.4, the thermal efficiency (%) of the cycle is:
Constant pressure lines in the superheated region of the Mollier diagram have what type of slope?
The following table of properties was printed out for saturated liquid and saturated vapour of ammonia. The titles for only the first two columns are available. All that we know is that the other columns (columns 3 to 8) contain data on specific properties, namely, internal energy (kJ/kg), enthalpy (kJ/kg) and entropy (kJ/kgK)
The specific enthalpy data are in columns
When wet steam flows through a throttle valve and remains wet at exit
One kilomole of an ideal gas is throttled from an initial pressure of 0.5 MPa to 0.1 MPa. The initial temperature is 300 K. The entropy change of the universe is:
The given diagram shows an isometric cooling process 1–2 of a pure substance. The ordinate and abscissa are respectively
The given diagram shows the throttling process of a pure substance.
The ordinate and abscissa are respectively
A piston –cylinder device contains 0.06m3 of saturated water vapour at 350 kPa pressure. Determine the temperature and mass of the vapour inside the cylinder.
Assertion (A): At a given temperature, the enthalpy of super-heated steam is the same as that of saturated steam.
Reason (R): The enthalpy of vapour at lower pressures is dependent on temperature alone.
Which one of the following is correct?
The specific volume of water when heated from 0°C
No substance can exist in the liquid phase in stable equilibrium
Consider the following statements about critical point of water:
1. The latent heat is zero.
2. The liquid is denser than its vapour.
3. Steam generators can operate above this point.
Of these statements
Saturated liquid at a high pressure P1 having enthalpy of saturated liquid 1000 kJ/kg is throttled to a lower pressure P2. At pressure p2 enthalpy of saturated liquid and that of the saturated vapour are 800 and 2800 kJ/kg respectively. The dryness fraction of vapour after throttling process is:
In a throttling process, which one of the following parameters remains constant?
The throttling process undergone by a gas across an orifice is shown by its states in the following figure:
Assertion (A): On the enthalpy-entropy diagram of a pure substance the constant dryness fraction lines start from the critical point.
Reason (R): All the three phases co-exist at the critical point.
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|