Test: Pure Substances - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Pure Substances - 2
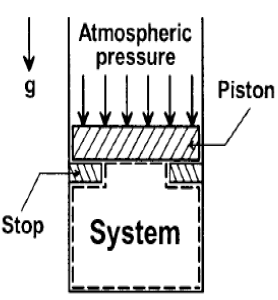
In the figure shown, the system is a pure substance kept in a piston-cylinder arrangement. The system is initially a two-phase mixture containing 1 kg of liquid and 0.03 kg of vapour at a pressure of 100 kPa. Initially, the piston rests on a set of stops, as shown in the figure. A pressure of 200 kPa is required to exactly balance the weight of the piston and the outside atmospheric pressure. Heat transfer takes place into the system until its volume increases by 50%. Heat transfer to the system occurs in such a manner that the piston, when allowed to move, does so in a very slow (quasi-static I quasi-equilibrium) process. The thermal reservoir from which heat is transferred to the system has a temperature of 400°C. Average temperature of the system boundary can be taken as 17°C. The heat transfer to the system is I kJ, during which its entropy increases by 10 J/K. Atmospheric pressure.
Specific volumes of liquid (vf) and vapour (vg) phases, as well as values of saturation temperatures, are given in the table below.

The work done by the system during the process is:
A thermodynamic cycle with an ideal gas as working fluid is shown below.
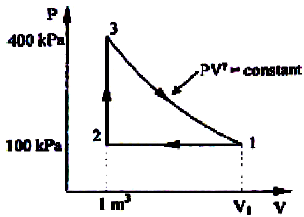
Q.
The above cycle is represented on T-S plane by
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The following table of properties was printed out for saturated liquid and saturated vapour of ammonia. The titles for only the first two columns are available. All that we know is that the other columns (columns 3 to 8) contain data on specific properties, namely, internal energy (kJ/kg), enthalpy (kJ/kg) and entropy (kJ/kgK)
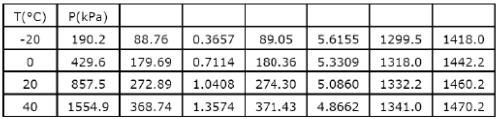
When saturated liquid at 40°C is throttled to -20°C, the quality at exit will be
When an ideal gas with constant specific heats is throttled adiabatically, with negligible changes in kinetic and potential energies
Where h, T and S represent respectively, enthalpy, temperature and entropy, temperature and entropy
Assertion (A): Water is not a pure substance.
Reason (R): The term pure substance designates a substance which is homogeneous and has the same chemical composition in all phases.
The ordinate and abscissa in the given figure showing the saturated liquid and vapour regions of a pure substance represent:
Consider the following statements for a throttling process:
1. It is an adiabatic process.
2. There is no work transfer in the process.
3. Entropy increases in throttling process
Which of these statements are correct ?
Consider the following:
1. Air
2. Gaseous combustion products
3. Steam
Which of these are pure substances, assuming there is no phase change?
Considers the following properties of vapour:
1. Pressure
2. Temperature
3. Dryness fraction
4. Specific volume
Which of these two properties alone are not sufficient to specify the condition of a vapour?
Which p–v diagram for steam illustrates correctly the isothermal process undergone by wet steam till it becomes superheated?
Consider the phase diagram of a certain substance as shown in the given figure. Match List-I (Process) with List-II (Curves/lines) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
The conversion of water from 40°C to steam at 200°C pressure of 1 bar is best represented as
The p-v-T surface of a pure substance is shown in the given p figure. The two-phase regions are labelled as:
Which one of the following is correct?
At critical point the enthalpy of vaporization is
Which one of the following statements is correct when saturation pressure of a vapour increases?
Which one of the following represents the condensation of a mixture of saturated liquid and saturated vapour on the enthalpy-entropy diagram?
Consider the following statements regarding the throttling process of wet steam:
1. The steam pressure and temperature decrease but enthalpy remains constant.
2. The steam pressure decreases, the temperature increases but enthalpy remains constant.
3. The entropy, specific volume, and dryness fraction increase.
4. The entropy increases but the volume and dryness fraction decrease.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements:
When dry saturated steam is throttled from a higher pressure to a lower pressure, the
1. Pressure decreases and the volume increases
2. Temperature decreases and the steam becomes superheated
3. Temperature and the dryness fraction increase
4. Entropy increases without any change in enthalpy
Which of these statements are correct?
A fluid flowing along a pipe line undergoes a throttling process from 10 bar to 1 Bar in passing through a partially open valve. Before throttling, the specific volume of the fluid is 0.5 m3 /kg and after throttling is 2.0 m3 /kg. What is the Change in specific internal energy during the throttling process?
In the figure shown, throttling process is represented by
Assertion (A): Air, a mixture of O2 and N2, is a pure substance.
Reason(R): Air is homogeneous in composition and uniform in chemical aggregation.
Assertion (A): Air is a pure substance but a mixture of air and liquid air in a cylinder is not a pure substance.
.Reason (R): Air is homogeneous in composition but a mixture of air and liquid air is heterogeneous.
Two-phase regions in the given pressure-volume diagram of a pure substance are represented by
Entropy of a saturated liquid at 227°C is 2.6 kJ/kgK. Its latent heat of vaporization is 1800 kJ/kg; then the entropy of saturated vapour at 227°C would be:
A piston –cylinder device contains 0.06m3 of saturated water vapour at 350 kPa pressure. Determine the temperature and mass of the vapour inside the cylinder.
Constant pressure lines in the superheated region of the Mollier diagram have what type of slope?
In the following P-T diagram of water showing phase equilibrium lines, the sublimation line is:
Assertion (A): In Mollier chart for steam, the constant pressure lines are straight lines in wet region.
Reason (R): The slope of constant pressure lines in wet region is equal to T.
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|

















