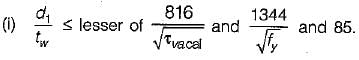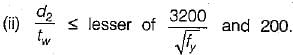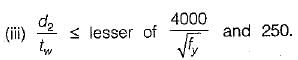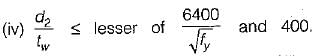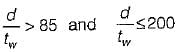Test: Plate Girders - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Plate Girders - 2
The intermediate transverse stiffener is needed in plate girder when (d/tw) of web is
where d = depth of web;
tw = thickness of web plate
where d = depth of web;
tw = thickness of web plate
Shear buckling of web in a plate girder is prevented by using
Consider the following statements:
Bearing stiffeners are provided in a plate girder
1. to avoid local bending failure of flange
2. to prevent buckling of web
3. to strengthen the web
4. under the uniformly distributed loads
Which of these statements are correct?
For a welded plate girder with vertical stiffeners, what is the maximum depth of web provisionable in design when the thickness of the web plate is 5 mm?
List-I contains some elements in design of a simply supported plate girder and List-II gives some qualitative locations on the girder. Match the items of two lists as per good design practice and relevant coda! provisions.
List-I
A. Flange splice
B. Web splice
C. Bearing stiffeners
D. Horizontal stiffener
List-ll
1. At supports (minimum)
2. Away from centre of span
3. Away from support
4. In the middle of span
5. Longitudinally somewhere in the compression flange
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 2 3 1 5
(b) 4 2 1 3
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 1 5 2 3
Horizontal stiffener in a plate girder is provided- to safeguard against
Minimum thickness of web in a plate girder, when the plate is accessible and also exposed to weather, is
When vertical intermediate stiffeners are subjected to bending moments due to eccentricity of vertical loads, their moment of inertia (cm4) is increased by
Where,
M = the applied bending moment kN-m
D = overall depth of girder in mm
E = Young’s modulus in MPa
t = thickness of web, mm
The web crippling due to excessive bearing stress can be avoided by
|
31 docs|280 tests
|