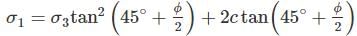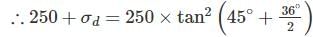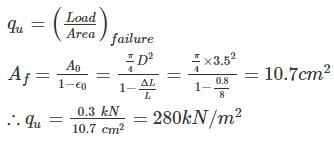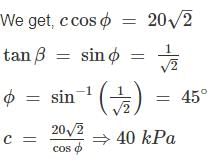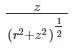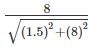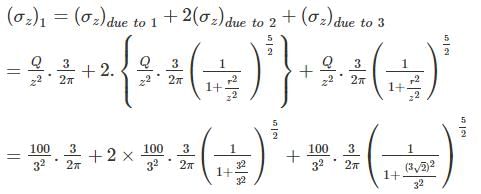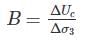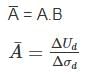Test: Soil Mechanics- 6 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Soil Mechanics- 6
The Contact pressure and settlement distribution for the footing are shown in the figure.
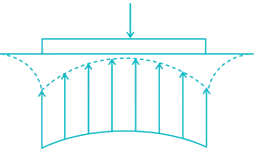
The figure corresponds to a

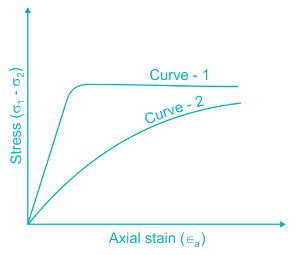
The stress-strain behavior of soils as shown in the figure corresponds to:

Choose the incorrect statement:
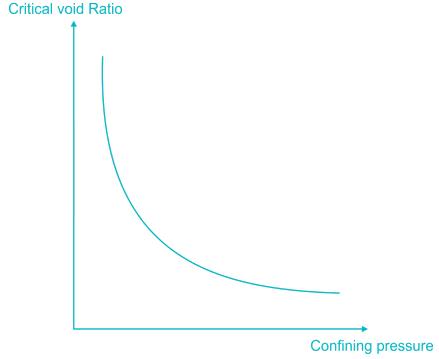
1) Greater the confining pressure, smaller the critical void ratio.
2) A saturated loose sand is likely to liquify when subjected to earthquake shocks.
3) Failure envelope of over consolidated clay is a curve and not straight line.
4) For normally consolidated clays, ϕ decrease with an increase in plasticity.
A sample of dry sand was subjected to tri - axial test with a confining pressure of 250 kN/m2. The angle of internal friction is found to be 36°. The sample is likely to fail at deviator stress of ________ kN/m2.
A multi-storied building is to be completed over a fine clayey soil within three months. In order to analyze the shear strength of the foundation soil which of the following shear strength test will be most suitable.
A cylindrical specimen of saturated clay, 3.5 cm in diameter and 8 cm in height were tested in an unconfined compression testing machine. The specimen fails under an axial load of 0.3 kN when the axial deformation was 8 mm. The unconfined compressive strength of the soil is
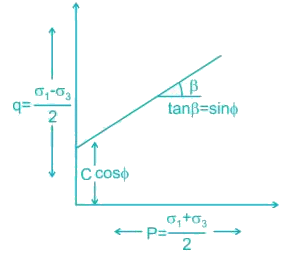
Stress path equation for tri - axial test upon application of deviatoric stress is 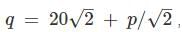 the respective value of cohesion, C (kPa) and angle of internal friction is
the respective value of cohesion, C (kPa) and angle of internal friction is
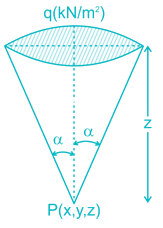
A commercial building circular in the plan is situated at a particular site. If the total load from the building including its self-weight is 150 kN/m2, determine the vertical stress (kN/m2) at a depth of 8 m below the C.G of the load area. Assume the diameter of the building to be 3 m.
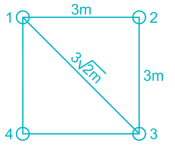
A water tank is supported on 4 columns, which form a square of side 3m. The total load of the water tank is 400 ton. Assuming the load on each footing as point load, find the vertical stress induced at a depth of 3m under any one of the footings? (In t/m2)
A soil sample was consolidated under a cell pressure of 8 kg/cm2, pore water pressure of 4.5 kg/cm2. With no drainage permitted the cell pressure was raised to 10 kg/cm2 results in increased pore water pressure to 5.75 kg/cm2. The axial load was then increased to give a deviator stress of 6.25 kg/cm2 (with the cell pressure at 10 kg/cm2), pore pressure is now noted to be 7.15 kg/cm2. The ratio of pore pressure coefficients B to A is ______.
|
31 docs|280 tests
|