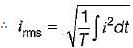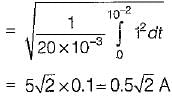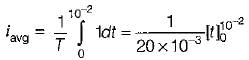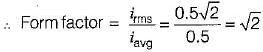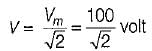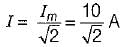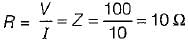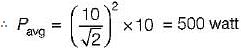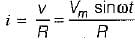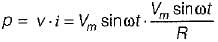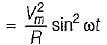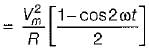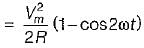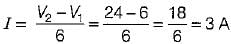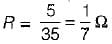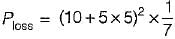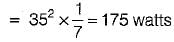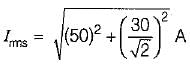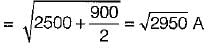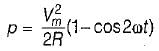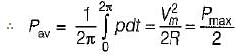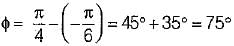Test: AC Power Analysis- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: AC Power Analysis- 2
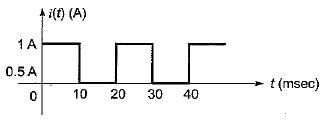
A non-alternating periodic waveform is shown below, It’s from factor is

The voltage and current in an a.c, circuit are given by
v = 100 sin 314t; i = 10 sin 314t
The average power in the circuit is
v = 100 sin 314t; i = 10 sin 314t
The average power in the circuit is
The expression for instantaneous power dissipated in a resistor R connected across a sinusoidal alternating voltage source represented as v = Vm sin ωt is given by
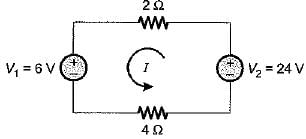
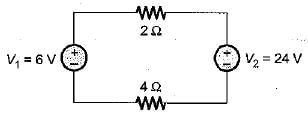
The power delivered by the two voltage sources of 6 V and 24 V as shown below will be
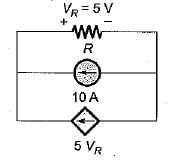
The power loss in watts in the resistor R shown below is
The root mean square value of the current wave given by i = (50 + 30 sin t) A will be
Assertion (A): In an alternating circuit, if the current is (4 - j3) amperes and the impressed voltage is (100 - j50) volts, the reactive power in the circuit is 100 VA.
Reason (R): True power is the real part of (VI).
In a purely resistive circuit, the average power
Pav is______the peak power Pmax.
A series circuit containing passive elements has the following current and applied voltage:
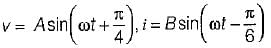
The circuit elements