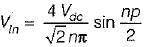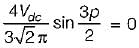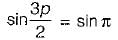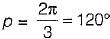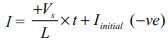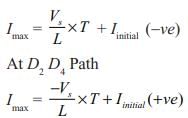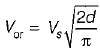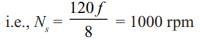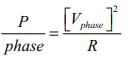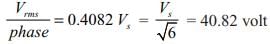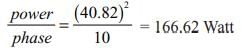Test: Inverters- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Inverters- 2
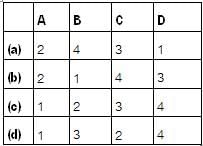
Match List-I (Type of Inverter circuits) with List-II (Applications/Limitations) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Adjustable voltage inverter
B. Pulse width modulated inverter
C. Current source inverter
D. Voltage source inverter
List-II
1. Limited speed range of motor
2. Capable of regeneration
3. Good input power factor at al! frequencies
4. Possibility of short circuit across the source
Codes:
List-I
A. Adjustable voltage inverter
B. Pulse width modulated inverter
C. Current source inverter
D. Voltage source inverter
List-II
1. Limited speed range of motor
2. Capable of regeneration
3. Good input power factor at al! frequencies
4. Possibility of short circuit across the source
Codes:

A 200 V DC voltage is supplying power to an RCL load through a single-phase full bridge through a
R = 10 Ω, L = 60 mH, C = 100 μF.
If the output frequency is 50 Hz, The maximum thyristor current is
R = 10 Ω, L = 60 mH, C = 100 μF.
If the output frequency is 50 Hz, The maximum thyristor current is
A single phase IGBT bridge inverter, compared to a single pulse PWM control, multiple pulse PWM
In a single-pulse modulation of PWM inverters if pulse width is 120° then
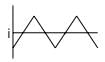
A single phase inverter as shown in figure below
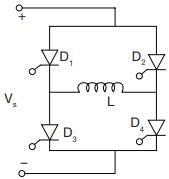
Which of the current wave form is true
A single-phase full bridge inverter can operate in load-commutation mode in case load consists of
An inverter has a periodic output voltage with the output waveform as shown in figure.
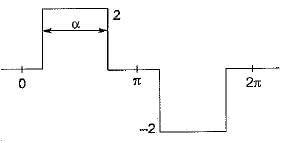
When the conduction angle a = 120°, the rms value of the output voltage is
Assertion (A): The terminal voltage of a voltage source inverter remains substantially constant with variations in load.
Reason (R): Any short-circuit across the terminals of a voltage source inverter causes current to rise very fast.
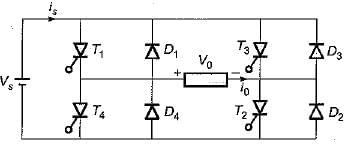
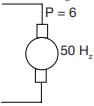
A thyristor controlled induction motor working at a slip of 0.02 fed from voltage controlled source inverter as shown
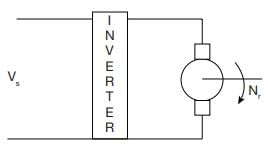
Operated at 50 Hz, 6 pole machine. The speed of rotor will be
A three phase 120 degree mode voltage source inverter connected to a resistive inductive load, R = 10 W, L = 200 mH. What will be the load power if inverter source voltage is 100 V dc.


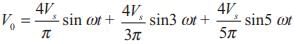
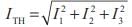


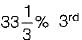 harmonic,
harmonic, 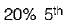 harmonic and
harmonic and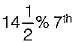 harmonic.
harmonic.