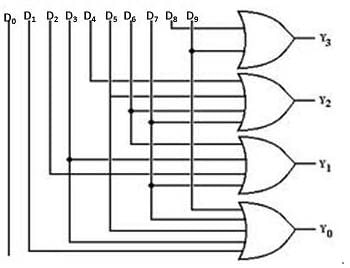
Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Tests > GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 > Test: Encoders - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
Test: Encoders - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Encoders
Test: Encoders for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 preparation. The Test: Encoders questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus.The Test: Encoders MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Encoders below.
Solutions of Test: Encoders questions in English are available as part of our GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 for Electrical Engineering (EE) & Test: Encoders solutions in
Hindi for GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Encoders | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 4
Test: Encoders - Question 5
The discrepancy of 0 output due to all inputs being 0 or D0, being 0 is resolved by using additional input known as ___________
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 5
Test: Encoders - Question 6
If we record any music in any recorder, such types of process is called ___________
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 7
Test: Encoders - Question 8
A single bit comparator compares two numbers A and B and produces three outputs Y1 (if A = B), Y2 (if A > B) and Y3(if A < B) as given below:
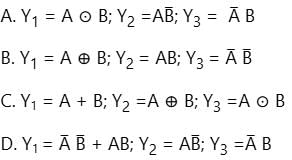
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 8
Test: Encoders - Question 9
For an encoder, if the number of output lines is m, then the number of input lines will be _______ .
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 9
Test: Encoders - Question 10
If half adders and full adders are implements using gates, then for the addition of two 17 bit numbers (using minimum gates) the number of half adders and full adders required will be
Detailed Solution for Test: Encoders - Question 10
|
26 docs|257 tests
|
Information about Test: Encoders Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Encoders solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Encoders, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
26 docs|257 tests
|
Download as PDF