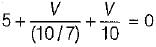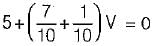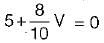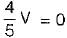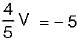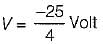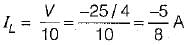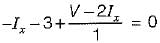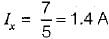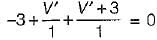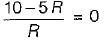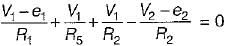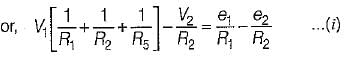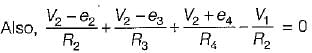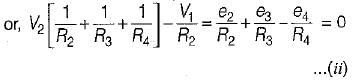Test: Basic Nodal & Mesh Analysis- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Nodal & Mesh Analysis- 2
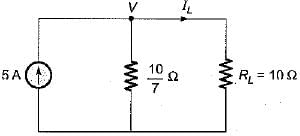
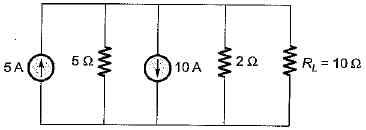
For the circuit shown below, the value of current through RL is

In nodal analysis, if there are N nodes in the circuit, then how many equations will be written to solve the network ?
In the node voltage technique of solving networks, choice of a reference node does not
1. affect the operation of the circuit.
2. change the voltage across any element.
3. affect the pd between any pair of nodes.
4. affect the voltages of various nodes.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are true?
1. affect the operation of the circuit.
2. change the voltage across any element.
3. affect the pd between any pair of nodes.
4. affect the voltages of various nodes.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are true?
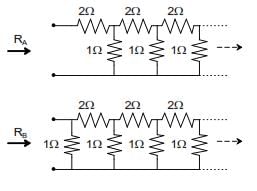
RA and RB are the input resistances of circuits as shown below. The circuits extend infinitely in the direction shown. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
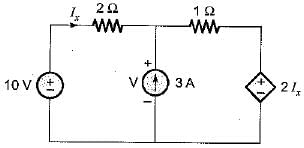
In the circuit shown below, the value of lx is
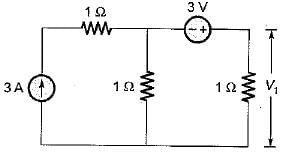
The value of V1 in the circuit shown in the given figure is
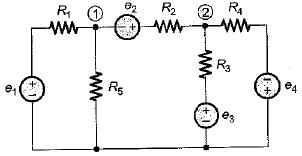
Consider the electrical network shown below.
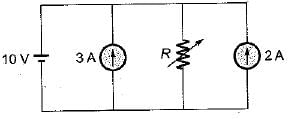
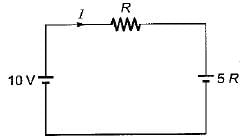
Determine the value of R such that current supplied by the voltage source is zero?
Assertion (A): In the method of solution of the network using nodal analysis, the assumption is made that the node potential is always higher than the other voltages appearing in the equation.
Reason (R): Nodal analysis is used to find the branch currents.
The nodal equations of the circuit shown below are respectively given by