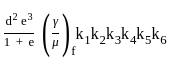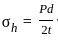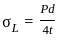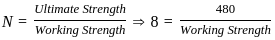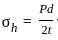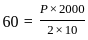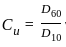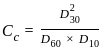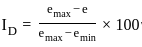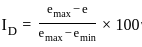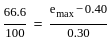BPSC AE Civil Paper 5 (Civil) Mock Test - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test BPSC AE Civil Mock Test Series 2025 - BPSC AE Civil Paper 5 (Civil) Mock Test - 1
What is the main advantage of using the double integration method over other methods for analyzing slopes and deflections?
As per IS: 1892 – 1979; what should be the maximum thickness of cutting edge of sampling tube of 70 mm external diameter which is required for sampling in undisturbed stiff clay soil?
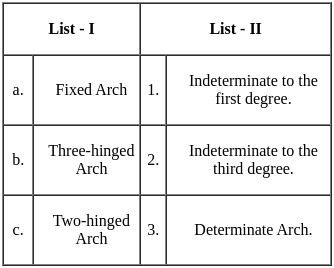
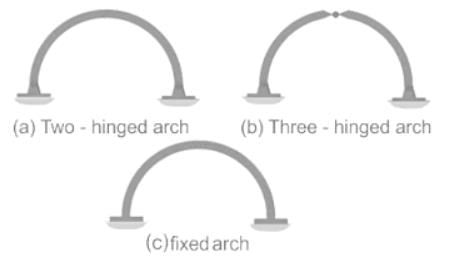
Match List-I (Type of Arch) with List-II (Indeterminacy) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

The minimum cement content (kg/m3) for a pre-specified strength of concrete (using standard notations) premised on 'free water-cement ratio' will be as
The cement concrete from which entrained air and excess water are removed after placing it in position is called
In plate girders, the web plate is provided with stiffness when the ratio of clear depth to thickness of web is greater than
For a soil void ratio = 0.7 and specific gravity of solids 2.7, the head required to cause quicksand over a column of 5 m high sand will be:
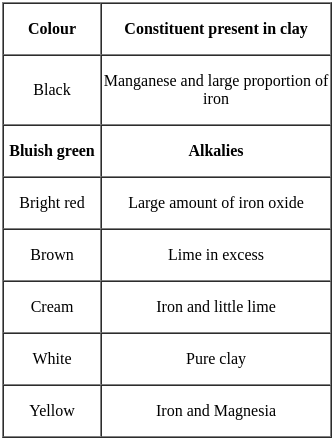
Identify FALSE statement from the following:
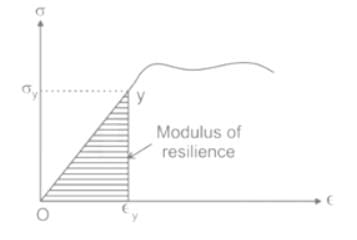
_______ is the phenomenon of a material failing under very little stress due to repeated cycles of loading.
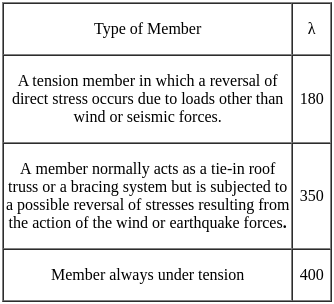
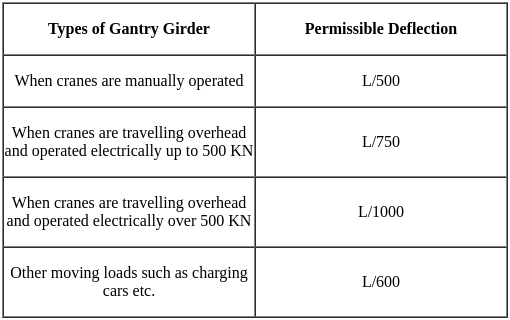
The maximum lateral deflection of a gantry girder between rails:
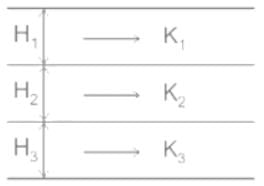
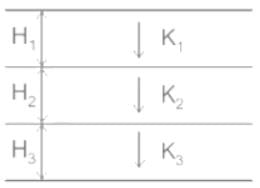
If kx and kz are are the permeabilities in the X and Z directions respectively in a two dimensional flow situation, the effective permeability k, is given by
What is the stiffness factor for a beam simply supported at both ends?
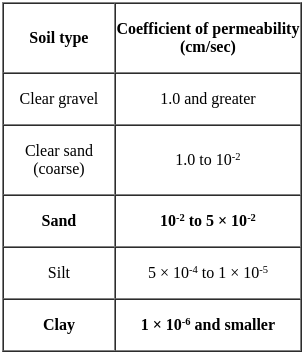
The coefficient of permeability of clay is not more than
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct related to the earthquake resistant design?
Pick up the incorrect statement from the following.
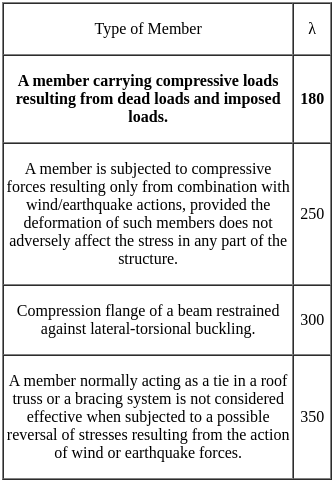
According to IS 800, the maximum effective slenderness ratio for a member carrying compressive loads resulting from dead loads and imposed loads is:
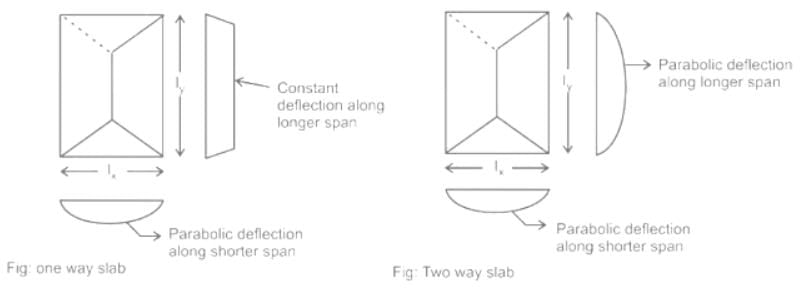
Consider the following statements regarding the slabs :
- When the longer span to shorter span ratio is greater than or equal to two, it is a two-way slab.
- In one-way slab, the load transfer is chiefly by bending in the shorter direction.
- In two-way slabs, the load transferred by bending in both orthogonal directions.
Which of the above statements is/are correct ?
What largest internal pressure can be applied to a cylindrical tank of 2 m diameter and 10 mm wall thickness? (Ultimate tensile strength of steel is 480 MPa and a factor of safety is 8.)
A well-graded sand should have
1. Uniformity coefficient greater than 6.
2. Coefficient of curvature between 1 and 3.
3. Effective size greater than 1 mm.
Choose the correct statement.
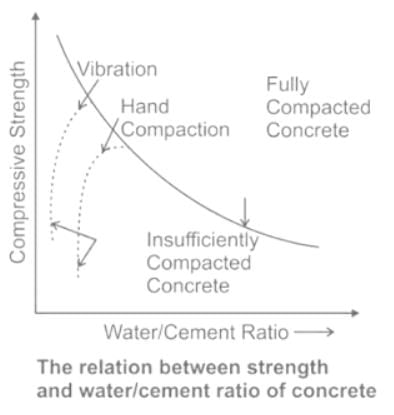
a) The strength of fully compacted concrete is inversely proportional to the water cement ratio.
b) The strength of fully compacted concrete is directly proportional to the water cement ratio.
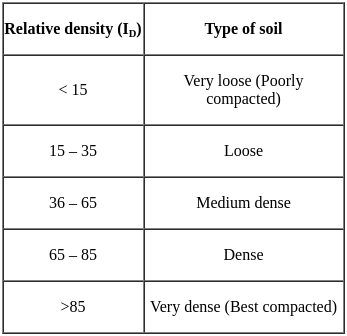
The difference between maximum void ratio and minimum void ratio of a sand sample is 0.30, if the relative density of this sample is 66.6% at a void ratio of 0.40. then the void ratio of this sample at its loosest state will be
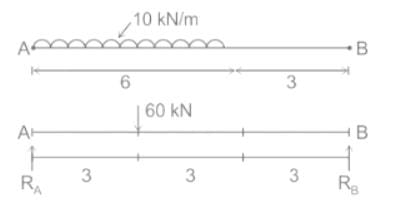
A simply supported beam AB of length 9 m, carries a uniformly distributed load of 10 N/m for a distance of 6 m from end A. What are the reaction forces at A and at B?
Which type of soil classification system is also called American Association of State Highway officials (AASHO)?
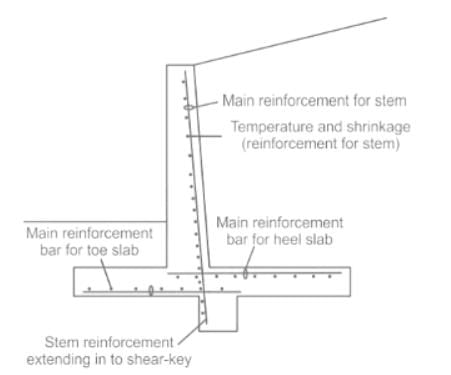
The phenomenon for the internal transfer of forces from one leg to the other is


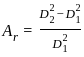
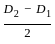
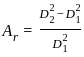

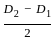
 = 3.05 mm
= 3.05 mm 
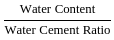
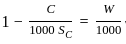 is used to find out the absolute volume of aggregates, where C and W are cement and water content respectively and Sc is specific gravity of cement.
is used to find out the absolute volume of aggregates, where C and W are cement and water content respectively and Sc is specific gravity of cement.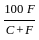 is used to determine the percentage of pulverized ash content in cementing material.
is used to determine the percentage of pulverized ash content in cementing material.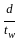 < 85
< 85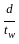 > 85
> 85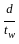 > 200
> 200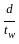 > 250
> 250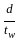 > 400
> 400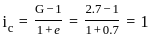
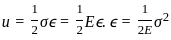
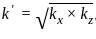
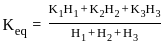
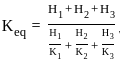
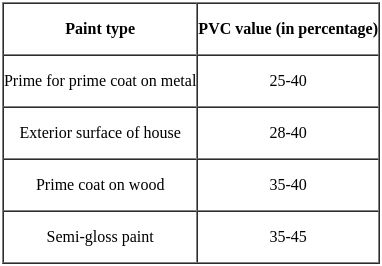
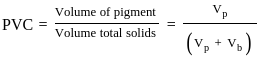 Where, Vp = Volume of pigment, and Vb = Volume of binder.
Where, Vp = Volume of pigment, and Vb = Volume of binder.