CTET & State TET Exam > CTET & State TET Tests > Science (Plant Kingdom) - CTET & State TET MCQ
Science (Plant Kingdom) - CTET & State TET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Science (Plant Kingdom)
Science (Plant Kingdom) for CTET & State TET 2025 is part of CTET & State TET preparation. The Science (Plant Kingdom) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the CTET & State TET exam syllabus.The Science (Plant Kingdom) MCQs are made for CTET & State TET 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Science (Plant Kingdom) below.
Solutions of Science (Plant Kingdom) questions in English are available as part of our course for CTET & State TET & Science (Plant Kingdom) solutions in
Hindi for CTET & State TET course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CTET & State TET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Science (Plant Kingdom) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for CTET & State TET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for CTET & State TET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 1
Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 2
Which of the following is/are plant disease/s:
I. Citrus Canker
II. Rust of the Wheat
III. Yellow vein Mosaic of bhindi
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 2
Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 3
Which protein is naturally found in some grains including wheat, barley and rye?
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 5
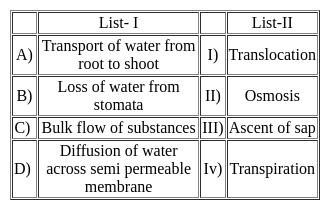
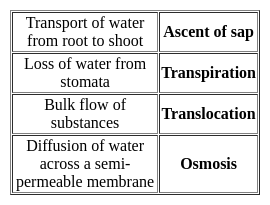
Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 6
Which of the following pair is correct?
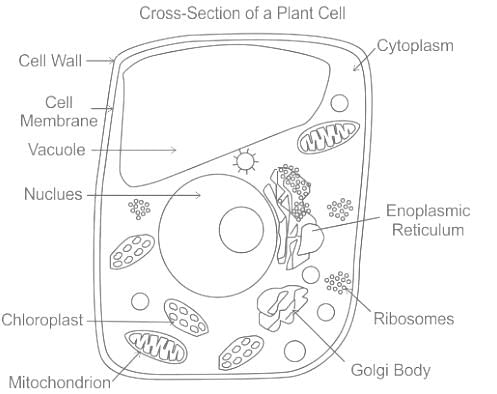
I. Plant cell - number of small vacuoles
II. Animal cell - big central vacuole
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 7
Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 8
Which of the following statements is/are true regarding fungi
A. They are plants
B. They cannot perform photosynthesis
C. All fungi are unicellular
D. some fungi help in producing antibiotics
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 9
Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 10
Which of the following is NOT classified as macronutrient in plant nutrition?
Detailed Solution for Science (Plant Kingdom) - Question 10
Information about Science (Plant Kingdom) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Science (Plant Kingdom) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Science (Plant Kingdom), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF