Capacitance MSQ - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - Capacitance MSQ
A parallel plate capacitor is charged from a cell and then isolated from it. The separation between the plates is now increased
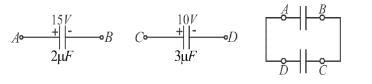
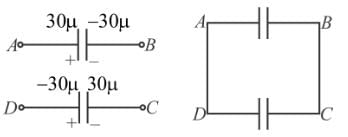
In the figure initial status of capacitance and their connection is shown. Which of the following is correct about this circuit :

Capacitor C1 of the capacitance 1μF and capacitor C2 of capacitance 2μF are separately charged fully by a common battery. The two capacitors are then separately allowed to discharge through equal resistors at time t = 0.
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance 10µF is connected to a cell of emf 10 Volt and fully charged. Now a dielectric slab (k = 3) of thickness equal to the gap between the plates, is very slowly inserted to completely fill in the gap, keeping the cell connected. During the filling process:
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then the battery is disconnected. When the plates of the capacitor are brought closer, then
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor with no dielectric are connected to a voltage source. Now a dielectric of dielectric constant K is inserted to fill the whole space between the plates with voltage source remaining connected to the capacitor.
A capacitor (without dielectric) is discharging through a resistor. At some instant a dielectric is inserted between the plates, then which of the following is not true.
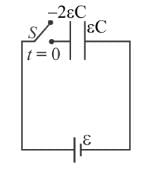
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C has charges on its plates initially as shown in the figure. Now at t = 0, the switch S is closed. Select the correct alternative(s) for this circuit diagram.
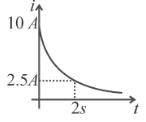
The figure shows, a graph of the current in a discharging circuit of a capacitor through a resistor of resistance 10Ω.


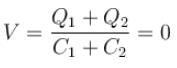

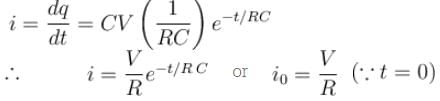
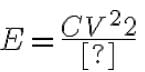
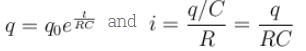
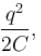 hence energy decrease
hence energy decrease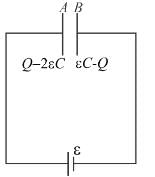
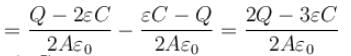
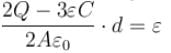
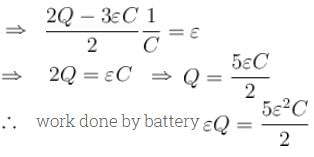
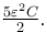
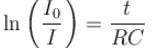
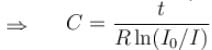
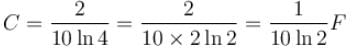
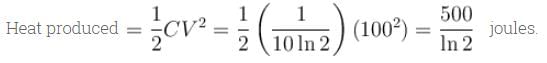
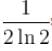 second.
second.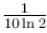 Farad., The total heat produced in the circuit will be
Farad., The total heat produced in the circuit will be 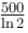 Joules., The thermal power in the resistor will decrease with a time constant
Joules., The thermal power in the resistor will decrease with a time constant 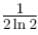 second.
second.










