Chapter-1 Nutrition In Plants Test-2 - Class 7 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Chapter-1 Nutrition In Plants Test-2
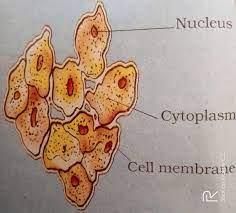
The bodies of living organisms are made up of tiny units called:
Carbon dioxide+Water,In presence of Sunlight and chlorophyll=?
A stoma is surrounded by a pair of kidney shaped cells called?
The water and the minerals are absorbed by the?
The mode of nutrition in which organism take in nutrients from dead a decaying matter is called?
State whether the following is true or false: product of photosynthesis is not a protein
Which part of the plants takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their?
All organism need ___________ and utilise it to get energy for growth and maintenance of their body.
Green plants synthesise food for themselves by the process of ______________.
Plants like cuscuta are parasites. They take food from the _____________plant.
Plants use simple chemical substances like carbon dioxide,water and Minerals for the synthesis of ?
Chlorophyll,water,carbon dioxide and sunlight are the essential requirements for ________________.
Complex chemical substances such as ______________ are the products of photosynthesis.
A few plants and all animals are dependent on others for their nutrition and are called ______________