Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 10 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 10
What is the direction of flow of electrons in an electrolytic cell?
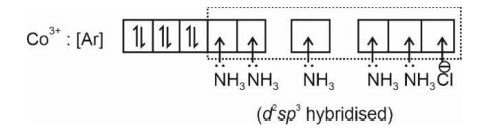
The spin only magnetic moment of the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl] Cl2 in BM is
The hybridization of cobalt in the above coordination entity is
The coordination number of cobalt in the above coordination entity is
The primary valence of Co in above coordination entity is
What is the standard potential E° of the cell
Zn | Zn2+ (IM) || I- (IM) | CuI | Cu of Eo Zn2+ | Zn = -0.76 V and Eo Cu+ | Cu = -0.17 V?
When initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life period of a zero order reaction
An endothermic reaction A → B has an activation energy 15 kcal/mole and energy of reaction 5 kcal/mole. The activation energy of the reaction B → A is
The molar conductance of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
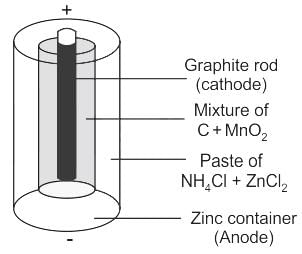
In a dry cell, which of the following are used as electrolytes?
What happens to the vapor pressure of a solution when a non-volatile solute is added?
According to Raoult's Law, what is the relationship between the vapor pressure of a solvent and the mole fraction of the solvent?
What is the effect of adding NaCl to water on the vapor pressure of the solution?
What is Raoult's Law used to describe in this paragraph?
In the solution described in the passage, what happens as the concentration of NaCl increases?
Consider the following statements:
(A) Werner’s theory proposed primary and secondary valences for coordination compounds.
(B) The ligands in a homoleptic complex are all of the same type.
(C) The coordination number of a metal in a complex is determined by the number of sigma bonds formed by the ligands.
(D) In an octahedral complex, the splitting of d orbitals occurs with t2g orbitals at lower energy.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Consider the following statements:
(A) The crystal field splitting energy (Δo) in octahedral complexes is determined by the nature of the ligands.
(B) The coordination number of a complex is the number of ligands bonded to the central metal.
(C) Tetrahedral complexes always exhibit low-spin behavior.
(D) Ligands in a heteroleptic complex are of different types.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Consider the following statements:
(A) In a coordination compound, the metal ion always forms ionic bonds with the ligands.
(B) The coordination number of a metal ion in a complex can vary depending on the ligands involved.
(C) Coordination compounds can exhibit geometrical isomerism in certain cases.
(D) The bond between the central metal and the ligand is always ionic in nature.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of a salt bridge?
Which of the following factors does not affect the electrode potential of an electrode?
In which of the following solutions will the Van’t Hoff Factor for the solute be greater than 1?
The depression of freezing point of a solution of acetic acid in benzene is – 0.2°C. If the molality of acetic acid is 0.1 m, then find the ratio of the normal mass to the abnormal mass. (Assume Kf of acetic acid = 4.0°C m-1)
Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the least boiling point?
Acetic acid associates as dimers in benzene. What is the Van’t Hoff factor (i) if the degree of association of acetic acid is 50%?
What is the Van’t Hoff Factor for 1 mole of BaCl2, assuming 100% dissociation?
What is the value of the Van’t Hoff factor (i) for solutes that dissociate in water?
What is defined as the concentration of dissolved solute in a solvent beyond which none of it, if added to the solvent, will increase the concentration further more?
When CO2 is introduced into aerated drinks and sealed, what is the nature of the graph between partial pressure of CO2 and its concentration in the drink?



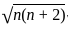 BM
BM