Coordination Chemistry MCQ -1 (Advanced) - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Coordination Chemistry MCQ -1 (Advanced)
The oxidation state of iron in K4 [Fe (CN)6] is
Which of the following complexes is(are) correctly matched with their geometry?
Which of the following complexes is (are) paramagnetic ?
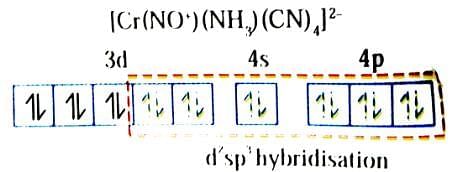
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct for coordination compound K2[Cr(NO+)(NH3)(CN)4]?
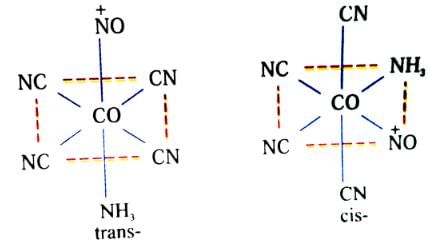
Which of the following compounds/complex ions would not show geometrical isomerism?
In which of the following pair(s) both the complex show optical isomerism ?
Double salts are addition compounds which lose their identity in aqueous solution whereas complexes which are also compounds do not lose their identity in aqueous solution. The coordination compounds show isomerism and find applications in photography, qualitative analysis, metallurgy, water purification and in the treatment of various diseases.
Q.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
Double salts are addition compounds which lose their identity in aqueous solution whereas complexes which are also compounds do not lose their identity in aqueous solution. The coordination compounds show isomerism and find applications in photography, qualitative analysis, metallurgy, water purification and in the treatment of various diseases.
Q.
Which of the following statement is true for complex, [Co(NH3)4Br2]NO2 ?
Double salts are addition compounds which lose their identity in aqueous solution whereas complexes which are also compounds do not lose their identity in aqueous solution. The coordination compounds show isomerism and find applications in photography, qualitative analysis, metallurgy, water purification and in the treatment of various diseases.
Q.
Choose the correct option for the complex [PtCl2(en)2]2+ .
In coordination chemistry there are a variety of methods applied to find out the structures of complexes. One method involves treating the complex with known reagents and from the nature of reaction, the formula of the complex can be predicted. An isomer of the complex Co(en)2(H2O)Cl2B4, on reaction with concentrated H2SO4 (dehydrating agent) it suffers loss in weight and on reaction with AgNO3 solution it gives a white precipitate which is soluble in NH3(aq).
Q.
The correct formula of the complex is :
In coordination chemistry there are a variety of methods applied to find out the structures of complexes. One method involves treating the complex with known reagents and from the nature of reaction, the formula of the complex can be predicted. An isomer of the complex Co(en)2(H2O)Cl2B4, on reaction with concentrated H2SO4 (dehydrating agent) it suffers loss in weight and on reaction with AgNO3 solution it gives a white precipitate which is soluble in NH3(aq).
Q. If all the ligands in the coordination spheres of the above complex be replaxed by SCN -, then the paramagnetic momentof the complex ion (due to spin only) will be:
Co2+ (aq) + SCN- (aq.) →Complexe (X).Ni2+ (aq) + Dimetyhlglyoxime Complex (Y).The coordination number of cobalt and nickel in complexes X and Y are four.
Q.
The IUPAC names of the complexes (X) and (Y) are respectively
Co2+ (aq) + SCN- (aq.) →Complexe (X).
Ni2+ (aq) + Dimetyhlglyoxime Complex (Y).
The coordination number of cobalt and nickel in complexes X and Y are four.
Q.
The geometry of complexes (X) and (Y) are respectively:
Co2+ (aq) + SCN- (aq.) →Complexe (X).
Ni2+ (aq) + Dimetyhlglyoxime Complex (Y).
The coordination number of cobalt and nickel in complexes X and Y are four.
Q.
Select the correct statement the complexes (X) and (Y)
Crystal field theory views the bonding in complexes as arising from electrostatic interaction and considers the effect of the ligand charges on the energies of the metal ion d-orbitals.In this theory, a ligand lone pair is modelled as a point negative charge that repels electrons in the d-orbitals of the central metal ion. The theory concentrated on the resulting splitting of the d-orbitals in two groups with different energies and used that splitting to rationalize and correlate the optical spectra, thermodynamic stability, and magnetic properties of complexes. This energy splitting between the two sets of dorbitals is called the crystal field splitting D.
In general, the crystal field splitting energy D corresponds to wavelength of light in visible region of the spectrum, and colours of the complexes can therefore be attributed to electronic transition between the lower-and higher energy sets of d-orbitals.
In general, the colour that the we see is complementry to the colour absorbed.
Different metal ion have different values of D, which explains why their complexes with the same ligand have different colour.
Similarly, the crystal field splitting also depends on the nature of ligands and as the ligand for the same metal varies from H2O to NH3 to ethylenediamine, D for complexes increases. Accordingly, the electronic transition shifts to higher energy (shorter wavelength) as the ligand varies from H2O to NH3 to en, thus accounting for the variation in colour.
Crystal field theory accounts for the magnetic properties of complexes in terms of the relative values of and the spin pairing energy P. Small values favour high spin complexes, and large Dvalues favour low spin complexes.
The [Ti(NCS)6]3- ion exhibits a single absorption band at 544 nm. W hat will be the crystal field splitting energy (KJ mol-1) of the complex ? (h = 6.626 x 10-34 J.s ; C = 3.0 x 108 m/s; NA = 6.02 x 1023 ions/mole.
Crystal field theory views the bonding in complexes as arising from electrostatic interaction and considers the effect of the ligand charges on the energies of the metal ion d-orbitals.In this theory, a ligand lone pair is modelled as a point negative charge that repels electrons in the d-orbitals of the central metal ion. The theory concentrated on the resulting splitting of the d-orbitals in two groups with different energies and used that splitting to rationalize and correlate the optical spectra, thermodynamic stability, and magnetic properties of complexes. This energy splitting between the two sets of dorbitals is called the crystal field splitting D.
In general, the crystal field splitting energy D corresponds to wavelength of light in visible region of the spectrum, and colours of the complexes can therefore be attributed to electronic transition between the lower-and higher energy sets of d-orbitals.
In general, the colour that the we see is complementry to the colour absorbed.
Different metal ion have different values of D, which explains why their complexes with the same ligand have different colour.
Similarly, the crystal field splitting also depends on the nature of ligands and as the ligand for the same metal varies from H2O to NH3 to ethylenediamine, D for complexes increases. Accordingly, the electronic transition shifts to higher energy (shorter wavelength) as the ligand varies from H2O to NH3 to en, thus accounting for the variation in colour.
Crystal field theory accounts for the magnetic properties of complexes in terms of the relative values of and the spin pairing energy P. Small values favour high spin complexes, and large Dvalues favour low spin complexes.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Crystal field theory views the bonding in complexes as arising from electrostatic interaction and considers the effect of the ligand charges on the energies of the metal ion d-orbitals.In this theory, a ligand lone pair is modelled as a point negative charge that repels electrons in the d-orbitals of the central metal ion. The theory concentrated on the resulting splitting of the d-orbitals in two groups with different energies and used that splitting to rationalize and correlate the optical spectra, thermodynamic stability, and magnetic properties of complexes. This energy splitting between the two sets of dorbitals is called the crystal field splitting D.
In general, the crystal field splitting energy D corresponds to wavelength of light in visible region of the spectrum, and colours of the complexes can therefore be attributed to electronic transition between the lower-and higher energy sets of d-orbitals.
In general, the colour that the we see is complementry to the colour absorbed.
Different metal ion have different values of D, which explains why their complexes with the same ligand have different colour.
Similarly, the crystal field splitting also depends on the nature of ligands and as the ligand for the same metal varies from H2O to NH3 to ethylenediamine, D for complexes increases. Accordingly, the electronic transition shifts to higher energy (shorter wavelength) as the ligand varies from H2O to NH3 to en, thus accounting for the variation in colour.
Crystal field theory accounts for the magnetic properties of complexes in terms of the relative values of and the spin pairing energy P. Small values favour high spin complexes, and large Dvalues favour low spin complexes.
Which of the following complexes are diamagnetic ? [Pt(NH3)4]2+ [Co(SCN)4]2- [Cu(en)2]2+ [HgI4]2-square planar tetrahedral square planar tetrahedral (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
In metal caronyls, there is synergic bonding interaction between metal and carbon monoxide. This leads to increase in strength of metal ligand bond and decrease in bond order of CO in carbonyl complex as compared to bond order in carbon monoxide.
Simple carbonyls are invariably spin-paired complexes except for vanadium metal.
Q.
The increase in bond length in CO as compared to carbon monoxide is due to :
In metal caronyls, there is synergic bonding interaction between metal and carbon monoxide. This leads to increase in strength of metal ligand bond and decrease in bond order of CO in carbonyl complex as compared to bond order in carbon monoxide.
Simple carbonyls are invariably spin-paired complexes except for vanadium metal.
Q. Which amongst the following metal carbonyls are inner orbital complexes with diamagnetic property?
In metal caronyls, there is synergic bonding interaction between metal and carbon monoxide. This leads to increase in strength of metal ligand bond and decrease in bond order of CO in carbonyl complex as compared to bond order in carbon monoxide.
Simple carbonyls are invariably spin-paired complexes except for vanadium metal.
Q.
Which one of the following metal carbonyls involves the d2sp3?hybridisation for the formation of metal-carbon?? bonds and is paramagnetic.
Match the ligands listed in column –I with the characteristic(s) type of ligands listed in column-II
Match the complexes / complex ions given in column – I with the characteristic(s) given in column-II.
The volume (in mL) of 0.1 M AgNO3 required for complex precipitation of chloride ions present in 30 mL of 0.01 M solution of [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2, as silver chloride is close to
Match the complexes listed in column – I with the characteristic(s) type of hybridisation listed in column-II.
Match the complexes listed in column – I with type hybridisation listed in column-II.