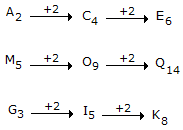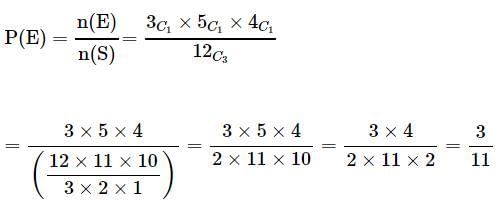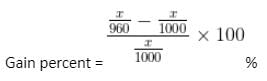EPFO Assistant Mains Mock Test - 5 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - EPFO Assistant Mains Mock Test - 5
Directions to Solve: In each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and
Question: How much was the total sale of the company?
Statements:
I. The company sold 8000 units of product A each costing Rs. 25.
II. This company has no other product line.
Statements:
I. The company sold 8000 units of product A each costing Rs. 25.
II. This company has no other product line.
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions two statements are given and these statements are followed by two conclusions numbered (1) and (2). You have to take the given two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Give answer:
- (A) If only (1) conclusion follows
- (B) If sonly (2) conclusion follows
- (C) If either (1) or (2) follows
- (D) If neither (1) nor (2) follows and
- (E) If both (1) and (2) follow.
Question -
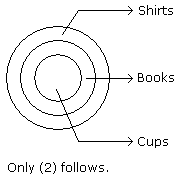
Statements: All cups are books. All books are shirts.
Conclusions:
- Some cups are not shirts.
- Some shirts are cups.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given question.
When a word and number arrangement machine is given an input line of words and numbers, it arranges them following a particular rule. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: engineer 30 marble famous 41 52 seven 61 rough 36 89 jump
Step 1: engineer famous 30 marble 41 52 seven 61 rough 36 89 jump
Step 2: engineer famous 89 61 30 marble 41 52 seven rough 36 jump
Step 3: engineer famous 89 61 jump marble 30 41 52 seven rough 36
Step 4: engineer famous 89 61 jump marble 52 41 30 seven rough 36
Step 5: engineer famous 89 61 jump marble 52 41 rough seven 30 36
Step 6: engineer famous 89 61 jump marble 52 41 rough seven 36 30
Step 6 is the last step of the above input.
Now, as per the rules followed in the above steps, answer the given question based on the following input:
Input: bone 11 alluring 25 major 47 81 enough 49 simple 16 anxious
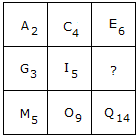
Q. In Step 6, if 'enough' and 'major', and '11' and '49' are interchanged, then how many elements will be placed between '49' and 'enough'?
A person crosses a 600 m long street in 5 minutes. What is his speed in km per hour?
Look at this series: 7, 10, 8, 11, 9, 12,...so on. What number should come next?
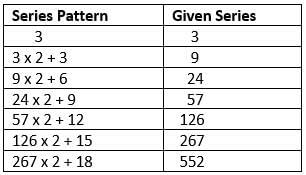
3, 9, 24, 57, ?, 267, 552. What number should come?
3 balls are drawn randomly from a bag contains 3 black, 5 red and 4 blue balls. What is the probability that the balls drawn contain balls of different colors?
The average rainfall for the first 3 days out of five days was recorded to be 0.45 inches. The rainfall on the last two days was in the ratio 2:3. The average of five days was 0.40 inches. What was the rainfall on the last day?
Two equal sums were borrowed at 8% simple interest per annum for 2 years and 3 years respectively. The difference in the interest was Rs. 56. The sum borrowed were
In what time will Rs. 500 give Rs. 50 as interest at the rate of 5% per annum simple interest?
An inlet pipe can fill a tank in 4 hours and an outlet pipe can empty a tank in 3/7 of a tank in 3h. Find the time taken to fill the tank if they start working alternately.
In a company, the salary of a person is directly proportional to his experience. The salary of a fresher is Rs. 20,000 per month and the salary of a person who has an experience of 2 years is Rs. 50,000.
If the company follows the methodology, what will be the salary of a person who has an experience of 5 years?
The number of squares in a board having 10 rows and 9 columns is
A 7-character code is such that only even digits occur at even places and only odd digits occur at odd places, e.g. 1436789. How many such codes can be made from digits 1-9, if repetition of digits is allowed?
An unscrupulous vendor professes to sell guavas at cost price but she uses a weight of 960 gm instead of a 1 kg weight. Her gain percent is
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The following bar graph shows the amount of production and sales over the years.(in tons)
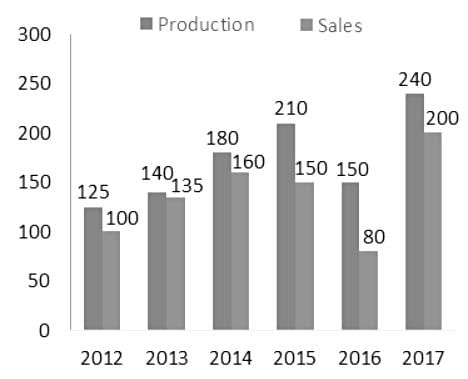
Q. What is the approximate percentage increase in production from 2016 to 2017?
One of the members / expressed doubt if / the Minister was an atheist / No error.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Paragraph 1: The government has announced a list of ‘Institutes of Eminence’ (IoE) among India’s institutions of higher education. This was awaited for the simple reason that finding a place on it would save an educational institution from the clutches of a dreaded regulator. Regulators are meant to ensure that we have a socially desirable outcome, but in the case of higher education in India the opposite seems to have been the case. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has over half a century micro-managed this space to an unimaginable level of silliness. The result has been publicly-funded universities that are cavernous wastes, shattering the aspirations of our youth and producing low-level ‘knowledge’. Evidence of the role of India’s higher-education regulator may be seen in the feature that the few instances when this is not the case the institutions have enjoyed privilege that leaves them protected from its depredations.
Paragraph 2: The latest offering is in the form of a proposed Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). The intention is to leave the HECI to focus on quality while leaving funding of public institutions to the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). Even as we observe the progress of the HECI and wonder if it is going to be any more than old wine in a new bottle, we already have an inkling of what could go wrong. This springs from the government’s announcement of a list of IoEs. The government has chosen three public and three private institutions for this status. The public institutions are the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and the Indian Institutes of Technology at Delhi and Mumbai. The private ones are the Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, the JIO Institute and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education. This list suffers from a serious lack of credibility. Where in it are the universities of India? We understand that the government’s aim is to rectify the low presence of Indian institutions in the global rankings of universities.
Paragraph 3: While the early European universities may have started as academies of the arts they were soon to have medicine and astronomy as areas that they pursued with vigour. Somewhere along the line we seem to have lost this breadth and come to revel in a landscape dominated by engineering schools. These engineering schools, notably the IITs, have done us proud but cannot be equated with the great universities of the world for the simple reason that they are focussed on a narrow domain. Also, if the idea behind IoEs is that they will be left alone and given enhanced financial support, it must be acknowledged that until very recently the IITs have not been meddled with neither have they been starved of resources. The IISc is of course broader than the IITs but does not embrace the social sciences and the humanities, the presence of which would be considered necessary for a university.
Paragraph 4 : If a list of eminent institutions in the country is at all needed, the absence of the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) from the first list of IoEs is striking. Its faculty has brought many of the world’s leading ideas to Indian students and in at least area came close to building a new school of thought, however controversial. It is not as if similar efforts in the social sciences have not occurred elsewhere in India but JNU has perhaps sustained its reputation as a university for longer. It already had schools of Computer Science and the Life Sciences over four decades ago when these were fledgling disciplines giving it a certain breadth early on.
Paragraph 5 : Even as we may wonder at the exclusion of JNU from the list of IoEs released by the government one might wonder at how the private institutions that are on it made the cut. While BITS Pilani may have made a significant contribution to the country at a time when it desperately needed engineers, but is yet not what may be considered a university, the presence of the two others on the list leave one nonplussed. One of them, we are told, has been conferred the status on grounds of its promise, a dubious position to take as this institute has little to show except for the financial heft that will surely undergird it. The other is known largely for its association with the practice of charging capitation fees for education.
Q. Which of the following may be inferred from paragraph 3?
I. Universities should embody knowledge across a wide range of disciplines.
II. There is an emphasis on a depth of knowledge across a broad horizon in Indian Universities today.
III. In India, a lot of focus is given to Institutions which are focused on only few areas.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Paragraph 1 : The government has announced a list of ‘Institutes of Eminence’ (IoE) among India’s institutions of higher education. This was awaited for the simple reason that finding a place on it would save an educational institution from the clutches of a dreaded regulator. Regulators are meant to ensure that we have a socially desirable outcome, but in the case of higher education in India the opposite seems to have been the case. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has over half a century micro-managed this space to an unimaginable level of silliness. The result has been publicly-funded universities that are cavernous wastes, shattering the aspirations of our youth and producing low-level ‘knowledge’. Evidence of the role of India’s higher-education regulator may be seen in the feature that the few instances when this is not the case the institutions have enjoyed privilege that leaves them protected from its depredations.
Paragraph 2 : The latest offering is in the form of a proposed Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). The intention is to leave the HECI to focus on quality while leaving funding of public institutions to the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). Even as we observe the progress of the HECI and wonder if it is going to be any more than old wine in a new bottle, we already have an inkling of what could go wrong. This springs from the government’s announcement of a list of IoEs. The government has chosen three public and three private institutions for this status. The public institutions are the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and the Indian Institutes of Technology at Delhi and Mumbai. The private ones are the Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, the JIO Institute and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education. This list suffers from a serious lack of credibility. Where in it are the universities of India? We understand that the government’s aim is to rectify the low presence of Indian institutions in the global rankings of universities.
Paragraph 3 : While the early European universities may have started as academies of the arts they were soon to have medicine and astronomy as areas that they pursued with vigour. Somewhere along the line we seem to have lost this breadth and come to revel in a landscape dominated by engineering schools. These engineering schools, notably the IITs, have done us proud but cannot be equated with the great universities of the world for the simple reason that they are focussed on a narrow domain. Also, if the idea behind IoEs is that they will be left alone and given enhanced financial support, it must be acknowledged that until very recently the IITs have not been meddled with neither have they been starved of resources. The IISc is of course broader than the IITs but does not embrace the social sciences and the humanities, the presence of which would be considered necessary for a university.
Paragraph 4 : If a list of eminent institutions in the country is at all needed, the absence of the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) from the first list of IoEs is striking. Its faculty has brought many of the world’s leading ideas to Indian students and in at least area came close to building a new school of thought, however controversial. It is not as if similar efforts in the social sciences have not occurred elsewhere in India but JNU has perhaps sustained its reputation as a university for longer. It already had schools of Computer Science and the Life Sciences over four decades ago when these were fledgling disciplines giving it a certain breadth early on.
Paragraph 5 : Even as we may wonder at the exclusion of JNU from the list of IoEs released by the government one might wonder at how the private institutions that are on it made the cut. While BITS Pilani may have made a significant contribution to the country at a time when it desperately needed engineers, but is yet not what may be considered a university, the presence of the two others on the list leave one nonplussed. One of them, we are told, has been conferred the status on grounds of its promise, a dubious position to take as this institute has little to show except for the financial heft that will surely undergird it. The other is known largely for its association with the practice of charging capitation fees for education.
Q. What could be a/some result/s of the function of funding of public institutions being left to the Ministry of Human Resource Development instead of HECI?
I. The government may use its discretion to reward institutions according to its ideological predilections.
II. The Institutions may be forced to comply with even some dubious rules setup by the government.
III. The government can be made accountable for attaining excellence in education.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Paragraph 1 : The government has announced a list of ‘Institutes of Eminence’ (IoE) among India’s institutions of higher education. This was awaited for the simple reason that finding a place on it would save an educational institution from the clutches of a dreaded regulator. Regulators are meant to ensure that we have a socially desirable outcome, but in the case of higher education in India the opposite seems to have been the case. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has over half a century micro-managed this space to an unimaginable level of silliness. The result has been publicly-funded universities that are cavernous wastes, shattering the aspirations of our youth and producing low-level ‘knowledge’. Evidence of the role of India’s higher-education regulator may be seen in the feature that the few instances when this is not the case the institutions have enjoyed privilege that leaves them protected from its depredations.
Paragraph 2 : The latest offering is in the form of a proposed Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). The intention is to leave the HECI to focus on quality while leaving funding of public institutions to the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). Even as we observe the progress of the HECI and wonder if it is going to be any more than old wine in a new bottle, we already have an inkling of what could go wrong. This springs from the government’s announcement of a list of IoEs. The government has chosen three public and three private institutions for this status. The public institutions are the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and the Indian Institutes of Technology at Delhi and Mumbai. The private ones are the Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, the JIO Institute and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education. This list suffers from a serious lack of credibility. Where in it are the universities of India? We understand that the government’s aim is to rectify the low presence of Indian institutions in the global rankings of universities.
Paragraph 3 : While the early European universities may have started as academies of the arts they were soon to have medicine and astronomy as areas that they pursued with vigour. Somewhere along the line we seem to have lost this breadth and come to revel in a landscape dominated by engineering schools. These engineering schools, notably the IITs, have done us proud but cannot be equated with the great universities of the world for the simple reason that they are focussed on a narrow domain. Also, if the idea behind IoEs is that they will be left alone and given enhanced financial support, it must be acknowledged that until very recently the IITs have not been meddled with neither have they been starved of resources. The IISc is of course broader than the IITs but does not embrace the social sciences and the humanities, the presence of which would be considered necessary for a university.
Paragraph 4 : If a list of eminent institutions in the country is at all needed, the absence of the Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) from the first list of IoEs is striking. Its faculty has brought many of the world’s leading ideas to Indian students and in at least area came close to building a new school of thought, however controversial. It is not as if similar efforts in the social sciences have not occurred elsewhere in India but JNU has perhaps sustained its reputation as a university for longer. It already had schools of Computer Science and the Life Sciences over four decades ago when these were fledgling disciplines giving it a certain breadth early on.
Paragraph 5 : Even as we may wonder at the exclusion of JNU from the list of IoEs released by the government one might wonder at how the private institutions that are on it made the cut. While BITS Pilani may have made a significant contribution to the country at a time when it desperately needed engineers, but is yet not what may be considered a university, the presence of the two others on the list leave one nonplussed. One of them, we are told, has been conferred the status on grounds of its promise, a dubious position to take as this institute has little to show except for the financial heft that will surely undergird it. The other is known largely for its association with the practice of charging capitation fees for education.
Q. Which of the following is/are true as per the passage?
I. Among countries with a comparable research output, India with 0.8% R&D spending trails Russia, Brazil, South Korea and even Singapore, according to Unesco data.
II. HECI would focus on funding while quality would be regulated by the Ministry of Human Resource Development.
III. The Institution of Eminence (IoE) status has been given to six institutes, three each from the public and private sectors.
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched:
Relationship between demand for foreign exchange and foreign exchange rate is
Which of the following bank is not an example of a Private Sector Bank?
Who served as the first Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
Under the provisions of which of the following acts does the Reserve Bank of India have the power to regulate, supervise and control the banking sector?
Which of the following statement is correct with respect to Doubtful Assets?
What is the theme of the 7th edition of the India Mobile Congress (IMC 2023)?
What is the objective of the Pradhan Mantri Mega Integrated Textile Regions and Apparel (PM MITRA) Park in Gujarat?
What do the new ESG rating regulations by SEBI require from rating agencies?