Economics: CUET Mock Test - 1 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 1
A farmer exchanges wheat for cloth.
This system of exchange is referred to as ________
This system of exchange is referred to as ________
Match List-I with List-II :
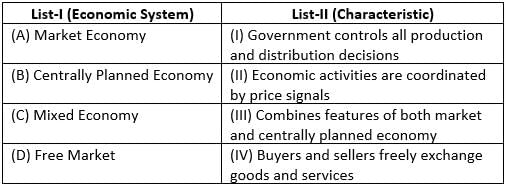
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

Match List-I with List-II :
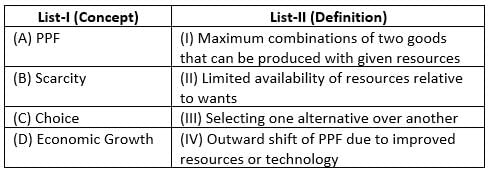
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

Match List-I with List-II :
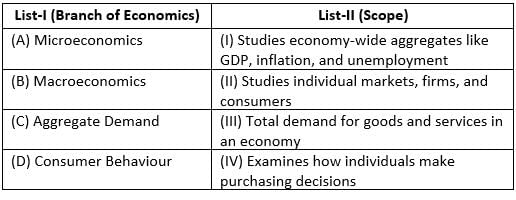
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List-I with List-II :
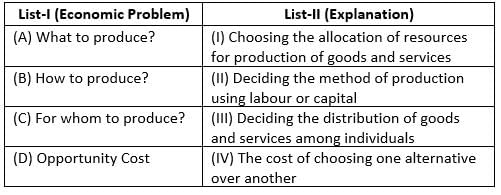
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
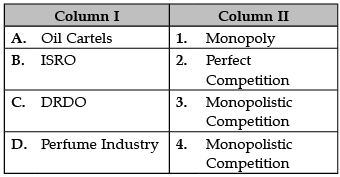
Identify the correctly matched statements from the Column I to that of Column II:
Which of the following best describes the central economic problem arising due to the mismatch between unlimited wants and limited resources?
Which concept explains the decision-making process when a teacher uses limited time to allocate between teaching more hours or spending time on personal development?
One of the characteristics of economic resource is scarcity. Which is the other?
In the short run TPP changes with the change in which of the following factors
Equilibrium price may or may not change with shifts in both demand and supply curve.
Q. According to Reuters, why is the government looking to sell the country's insurer?
Q. The government will privatise _________ Public Sector Banks.
Which of the following companies was NOT mentioned as part of the government’s divestment plans for F/Y 22?
Question 1: What is one of the requirements for the government to facilitate the sale of a stake in LIC?
What is the purpose of LIC floating an RFP for an actuarial firm?
In the context of a centrally planned economy, what role does the government play concerning essential goods and services?
In the long run TPP changes with the change in which of the following factors
|
39 docs|145 tests
|



















