Economics: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 2
Which of the following is NOT included in the value added method of calculating national income?
The RBI can influence money supply by changing ______ at which it gives loan to the commercial Banks.
At a particular price level, when aggregate demand for final goods equals aggregate supply of final goods, the product market reaches to its _______.
Match List-I with List-II :
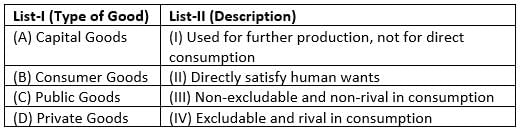
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List-I with List-II :
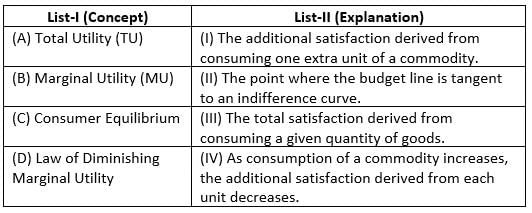
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List-I with List-II :
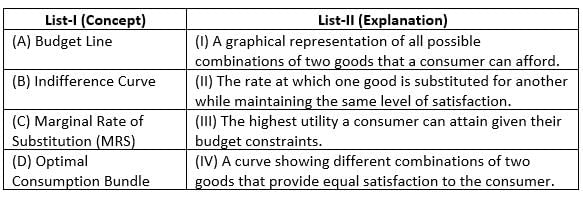
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Which concept explains the decision-making process when a teacher uses limited time to allocate between teaching more hours or spending time on personal development?
The basic assumption regarding resources while drawing a PPC is
A PPC is downward sloping and____________ to the origin. Choose the correct option.
What happens when Marginal Product (MP) is greater than Average Product (AP)?
Assertion (A): Macroeconomics is primarily concerned with the study of aggregate economic phenomena such as total output and price levels.
Reason (R): Microeconomics focuses exclusively on individual markets and does not consider the entire economy.
In short run which of the following factors can be changed easily
Assertion (A): In a market economy, prices serve as signals to both producers and consumers about the scarcity of goods and services.
Reason (R): In a centrally planned economy, the government determines prices based on its production schedules.
A PPC is downward sloping and____________ to the origin. Choose the correct option.
In the long run the market price of a commodity is equal to its minimum average cost of production under the___________?
The important factor influencing the propensity to consume in an economy is
|
39 docs|145 tests
|














