Economics Mock Test- 1 - Class 9 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Economics Mock Test- 1
Modern farming methods were tried in India for the first time in
The poorest states in India are:
i) Orissa
ii) Bihar
iii)Punjab
iv) Haryana
i) Orissa
ii) Bihar
iii)Punjab
iv) Haryana
In which state have the land reform measures helped to reduce poverty?
Which state has focused more on human resource development?
In which state is the public distribution system responsible for the reduction in poverty?
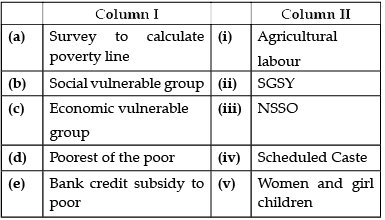
There is inequality of income within a family. Persons who are poorest of the poor in the family are ____________ .
(i) Women
(ii) Girl
(iii) Children
(iv) Old people
Infant mortality rate refers to the death of a child under the age of
Choose the non-market activities
(i) Vilas sells fish in the village market
(ii) Vilas cooks food for his family
(iii) Sakal works in a private firm
(iv) Sakal looks after his younger brother and sister
Choose the primary sector activities
(i) Forestry
(ii) Poultry farming
(iii) Animal husbandry
(iv) Manufacturing
Which of the following is responsible for high poverty rates?
Which crop registered the largest increase in production as a result of Green Revolution?
Which of the following sectors is related to agriculture, forestry and dairy?
People of Palampur sell milk in the near by large village named
Disguised unemployment occurs when the number of persons working on a farm is
In which part of the country, grain banks have been set up by NGO's?
Buffer stock is the stock of food grains procured by the government through :
Percentage of seasonal as well as chronic hunger in India over the years has :
Read the text given below and answer the following questions:
In our daily life, we come across many people who we think are poor. They could be landless labourers in villages or people living in overcrowded jhuggis in cities. They could be daily wage workers at construction sites or child workers in dhabas. They could also be beggars with children in tatters. We see poverty all around us. In fact, every fourth person in India is poor. This means, roughly 270 million (or 27 crore) people in India lived in poverty in 2011-12. This also means that India has the largest single concentration of the poor in the world. Since poverty has many facets, social scientists look at it through a variety of indicators. Usually the indicators used relate to the levels of income and consumption. A person is considered poor if his or her income or consumption level falls below a given “minimum level” necessary to fulfill basic needs. What is necessary to satisfy basic needs is different at different times and in different countries. Therefore, the poverty line may vary with time and place. Each country uses an imaginary line that is considered appropriate for its existing level of development and its accepted minimum social norms. The proportion of people below the poverty line is also not the same for all social groups and economic categories in India. In poor families all suffer, but some suffer more than others. Women, elderly people and female infants are systematically denied equal access to resources available to the family. Therefore women, children (especially the girl child) and old people are the poorest of the poor.
Q. What does poverty mean?
Read the text given below and answer the following questions:
Poverty in India also has another aspect or dimension. The proportion of poor people is not the same in every state. States like Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Orissa had above all India poverty levels. Bihar and Orissa continue to be the two poorest states with poverty ratios. There has been a substantial reduction in global poverty. Poverty declined substantially in China and Southeast Asian countries as a result of rapid economic growth and massive investments in human resource development. There were a number of causes for the widespread poverty in India. One historical reason is the low level of economic development under the British colonial administration. The policies of the colonial government ruined traditional handicrafts and discouraged development of industries like textiles. Removal of poverty has been one of the major objectives of Indian developmental strategy. In these circumstances, there is a clear need for targeted anti-poverty programmes. Although there are so many schemes which are formulated to affect poverty directly or indirectly. These anti-poverty programmes are Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, Prime Minister Rozgar Yozana, Rural Employment Generation Programme, Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana, etc.
Q. Which of the following states have traditionally succeeded in reducing poverty with the help of high agricultural growth rates: