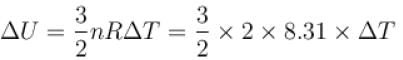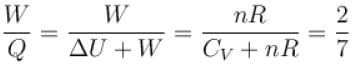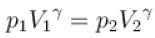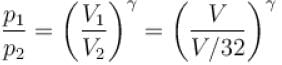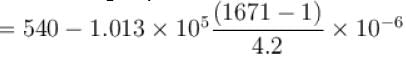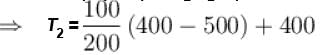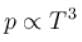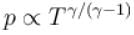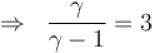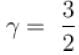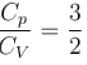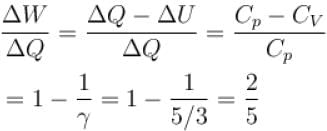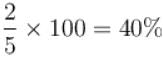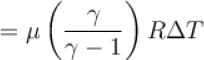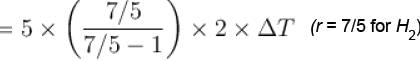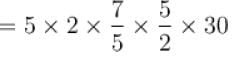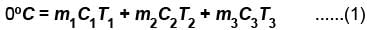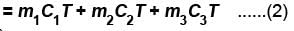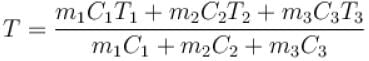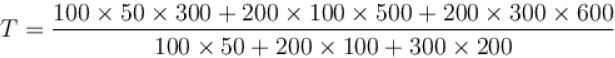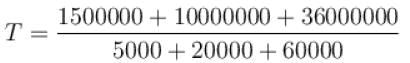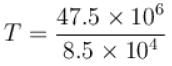First Law Of Thermodynamics NAT Level – 2 - IIT JAM MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - First Law Of Thermodynamics NAT Level – 2
5000J of heat are added to two moles an ideal monoatomic gas, initially at a temperature of 500K, while the gas performs 7500J of work. What is the final temperature of the gas ? (in Kelvin)
For a diatomic ideal gas near room temperature, what fraction of heat supplied is available for external work if gas is expanded at constant pressure
A gas has pressure p and volume V. It is now compressed adiabatically to 1/32 times the original volume. If (32)1.4 = 128, the final pressure in terms of p is
1cm3 of water at its boiling point absorbs 540 calories of heat to become steam with a volume of 1671 cm3. If the atmospheric pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2 and mechanical equivalent of heat = 4.19 J/calorie, the energy spent in this process in overcoming intermolecular forces is (in calories)
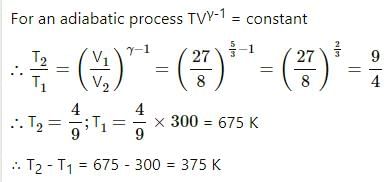
An ideal gas at 27ºC is compressed adiabatically to 8/27 of its original volume. If γ = 5/3 then the rise in temperature (in Kelvin) of the gas __.
Two systems with heat capacities 100cal/gm-K and 200cal/gm-K interact thermally and come to a common temperature 400K. If the initial temperature of system 1 is 500K, what was the initial temperature of systems (in Kelvin) scale
During an adiabatic processes, the pressure of a gas is found to be proportional to the cube of its absolute temperature. The ratio Cp /CV for the gas is
When an ideal gas 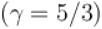 is heated under constant pressure, then what percentage of given heat energy will be utilized in doing external work?
is heated under constant pressure, then what percentage of given heat energy will be utilized in doing external work?
5 mole of hydrogen gas is heated from 30ºC to 60ºC at constant pressure. Heat given to the gas is in calories (given R = 2cal/mole-ºC)
Three liquids with masses m1, m2, m3 are thoroughly mixed. If their specific heats are C1, C2 and C3 and their temperature T1, T2, T3, then the temperature of the mixture is given that