GPSC Prelims Paper 1 Mock Test - 6 - GPSC (Gujarat) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - GPSC Prelims Paper 1 Mock Test - 6
Consider the following statements:
Ajivikas were fatalists who believed that everything was predetermined.
Lokayatas were materialists who rejected the authority of the Vedas.
Makkhali Gosala was an Ajivika teacher and Ajita Kesakambalin was a lokayata teacher.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Ajivikas were fatalists who believed that everything was predetermined.
Lokayatas were materialists who rejected the authority of the Vedas.
Makkhali Gosala was an Ajivika teacher and Ajita Kesakambalin was a lokayata teacher.
Consider the following statements regarding Mahajanpadas:
The kingdom of Magadha was a monarchy whereas the kingdom of Vajji was a republic.
Both Gautam Buddha and Vardhaman Mahavira belonged to ganas or sanghas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
The kingdom of Magadha was a monarchy whereas the kingdom of Vajji was a republic.
Both Gautam Buddha and Vardhaman Mahavira belonged to ganas or sanghas.
With reference to Pre-Mauryan Period, consider the following statements:
-
Village Headman was known as Grama Bhojaka.
-
Use of Iron began in India from the times of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Village Headman was known as Grama Bhojaka.
Use of Iron began in India from the times of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Consider the following statements regarding Pre-Historic India Stone tools were used for
Digging the ground to collect edible roots
Stitching clothes made out of animal skin
Making spears and arrows for hunting
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following sites are identified as a Neolithic Sites?
Daojali Hading
Paiyampalli
Kurnool caves
Inamgaon
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following statements regarding the Brahmo Sabha:
-
Its purpose was to purify Hinduism and to preach theism.
-
Tarachand Chakravarti was the first secretary of the Brahmo Sabha.
-
It was opposed to idolatry.
-
The new society was to be based on the Vedas only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With respect of Swadesh Bandhab Samiti set up during the Swadeshi Movement, which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following are the features of Nagara style of Temple Architecture:
Elaborate walls and gateways.
Presence of river goddess.
Absence of a water tank or reservoirs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following style/school of painting uses gold leaf and gemstones and are mostly created on glass and board?
Consider the following statements regarding Mauryan Empire:
They maintained a large standing army including Navy.
Administration of important cities were carried out by committees consisting of 5 members each.
Administration of armed forces was carried by Board of 30 members.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Oommen V Oommen Report which was recently in the news is related to which of the following?
Consider the following statements regarding Gupta age:
During the Gupta period, castes proliferated into numerous sub-castes.
One of the reasons for the increase in the number of castes was the absorption of many tribal people into the Brahmanical society through the process of land grants.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Tattvabodhini Sabha:
It was founded by Raja Ram Mohan Roy.
Tatvabodhini Patrika a journal of Tattvabodhini Sabha promoted a systematic study of India’s past in the English language.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference Dayanand Saraswati, which of the following statements is not correct?
Consider the following statements:
The Bhakti movement preached the principle of monotheism.
Idol Worshiping started flourishing in this movement
This movement advocated salvation and could obtain deep devotion and faith in guru.
Which of the given above statements are not correct?
Consider the statements regarding Ashokan Edicts:
These are written mainly in Brahmi and Prakrit script.
The Third Major Rock Edict narrates the story of Kalinga war.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
“He was an important poet in the early phase of the Gupta period and wrote thirteen plays. He wrote in Sanskrit, but his dramas also contain a substantial amount of Prakrit. He was the author of a drama called Daridra Charudatta, which was later refashioned as Mrichchhakatika or the Little Clay Cart”.
He was:
Consider the following regarding Asokan religious policy:
He didn’t tried to disrupt existing social order by his dhamma policy.
He disapproved rituals and killing of all animals and birds.
He appointed officers named ‘rajukas’ for propagating dhamma.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
‘Thoda’ is a martial art of Himachal Pradesh.
The earliest coins of Ancient India was punch marked coins, made up of gold.
‘Barygaza’ was the Ancient port situated in western India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following Sanskrit grammarians :
1. Panini
2. Katyayana
3. Patanjali
Which one of the following is the correct chronological order of the persons in the History of ancient India ?
The Deccan policy of Aurangzeb was/were motivated by which of the following reasons ?
1. The influence of the Marathas in that region
2. The attitude of the Shia kingdoms of Deccan
3. The rebellious activities of his son Akbar
Select the correct answer from the codes given below :
Consider the following statements with reference to the administration of the Gupta Empire :
1. Like Mauryas, Guptas consolidated every kingdom into a single administrative unit
2. Pradesa was a larger unit of the administration compared to Bhukti
3. They differentiated Civil and Criminal Laws
4. They have collected land tax and excise duties
How many statements given above is/are correct ?
With reference to the Later Vedic texts, consider the following statements :
1. There was a reference to large numbers and complex arithmetical calculations in Later Vedic texts
2. References to the sabha and samiti were discontinued in Later Vedic texts
3. Later Vedic texts indicate a close relationship between the king and purohit
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
With reference to the Bhakti traditions and ideas, a style called the ‘ultabasi’ was adopted by :
With reference to Medieval India, consider the following pairs :
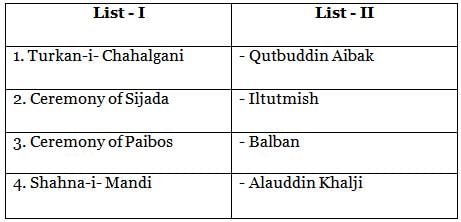
Q. How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements with reference to Balban :
1. He adopted a policy of expansion rather than consolidation
2. He gave the Sultanate two of its basic coins called Tanka and Jittal
3. He was he was known as Lakh Baksh
4. He formulated the theory of kingship
How many statements given above is/are correct ?
With reference to the Bhakti movement in medieval India, consider the following statements:
1. Vallabhacharya propounded thePushtimarg sect based on the worship of Lord Shiva.
2. Dadu Dayal propagated the Nirguna Saint tradition in present-day Gujarat and Rajasthan.
3. Surdas was a sixteenth-century saint who composed songs centered around Krishna.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Who was the author of Daridracharudatta(Charudatta in poverty) which was the storyof the courtesan Vasantasena and laterdeveloped into the more famous playMrichakatika, by Shudraka?
With reference to Vijayanagara Empire,which one of the following is the correctchronological order of the ruling dynasties?



















