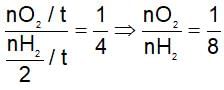Gaseous State - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Gaseous State
The numerical value of RT/PV for a gas at critical condition is ....times of RT/PV at normal condition.
The rate of diffusion of SO2,CO2, PCI3 and SO3 are in the following order:
Oxygen gas is collected by downward displacement of water in a jar. The level of water inside the jar is adjusted to the height of water outside the jar. When the adjustment is made, the pressure exerted by the oxygen is equal to:
Longest mean free path under similar conditons of P and T stands for:
Average speed of the molecules of a gas in a container moving in one direction is:
The liquefaction behaviour of temporary gases like CO2 approaches that of permanent gases like N2,O2, etc., as we go:
The ratio of average speed of an oxygen molecule to the rms speed of a nitrogen molecules at the same temperature is:
An open vessel containing air is heated from 300 K to 400 K. The fraction of air originally presemt which goes out of it is:
A 0.5 dm3 flask contains gas A and another flask of 1dm3 conatins gas B at the same temperature. If density of gas A is 3.0 gdm-3 and of gas B is 1.5 g dm-3 and molar mass of A= 1/2 molar mass of B, then he ratio of pressure exerted by gases is:
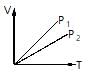
V versus T curves at contant pressure P1 and P2 for an ideal gas are shown in figure. Which is correct?
A 2.24 litre cylinder containing O2 gas at 270C and 2 atm is found to develop a leakage. When the leakage was repaired, the pressure dropped to 100 cm of Hg at 270C. The number of mole of gas escaped out during leakage is:
Four one litre flasks are separately filled with gases, O2,F2,CH4 and CO2 under the same conditions. The ratio of number of molecules in these gases.
A certain gas diffuses from two different vessels A and B. The vessel A has a circular orifice while vessel B has square orifice of length equal to the radius of the orifice of vessel A. The ratio of the rates of diffusion of the gas form vessel A to vessel B, assuming same temperature and pressure is:
If 1 litre of a gas A at 600 mm and 0.5 litre of gas B at 800 mm are taken in a 2 litre bulb. The resulting pressure is:
A gaseous mixture contains 1 g of H2, 4g of He, 7 g of N2 and 8 g of O2. The gas having the highest partial pressure is:
The average speed of an ideal gas molecule at 270C is 0.3 m sec-1. The average speed at 9270C will be...m sec-1.
In a experiment during the analysis of a carbon compound, 145 mL of H2 was collected at 760 mm Hg pressure and 270C.The mass of H2 is nearly:
If a mixture of gases has a total pressure of 100 cm Hg and the partial pressure of nitrogen in the mixture is 25 mm Hg, then the per cent of nitrogen in the mixture is:
The rms speed of gas molecules at a temperatre 27 K and pressure 1.5 bar is 1x104 cm/sec. If both temperature and pressure are raised three times, the rms speed of the gas will be:
In a closed flask of 5 litre, 1.0 g of H2 is heated from 300 to 600 K. Which statement is not correct?
Equal moles of hydrogen and oxygen gases are placed in a container with a pin-hole through which both can escape. What fraction of the oxygen escape in the time required for one-half of the hydrogen to escape?



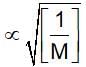

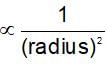
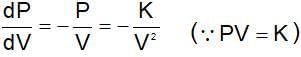
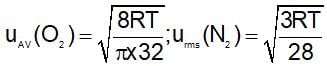
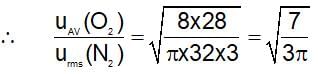
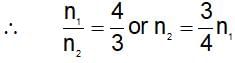
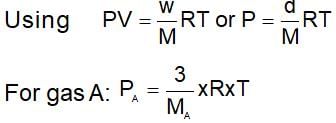
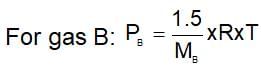
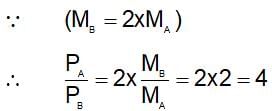
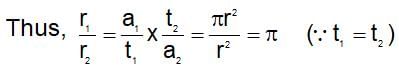
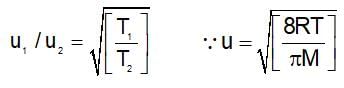
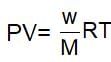
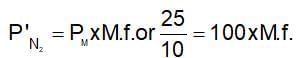
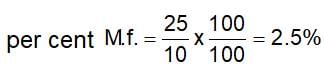
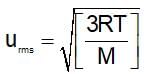
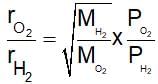
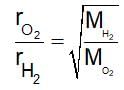
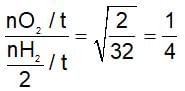 (t is same)
(t is same)