IBPS Clerk Mains Mock Test - 8 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - IBPS Clerk Mains Mock Test - 8
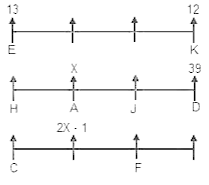
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Step 1: Those numbers which are immediately followed by a consonant and immediately preceded by a vowel are written at the left end in increasing order.
Step 2: After completing step 1, vowels are interchanged with preceding element.
Step 3: After completing step 2, Even numbers which are Perfect Square are written at the left end in ascending order.
S Q A D F W @ E 1 B T R # O % 5 3 U Z C G Y 2 4 & H I M 9 7 $ 8 6 L N ? K
If all the consonants in the above arrangement are dropped, then which of the following will be the seventh element from the left end in step 2?
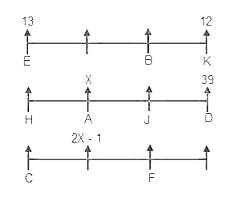
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Step 1: Those numbers which are immediately followed by a consonant and immediately preceded by a vowel are written at the left end in increasing order.
Step 2: After completing step 1, vowels are interchanged with preceding element.
Step 3: After completing step 2, Even numbers which are Perfect Square are written at the left end in ascending order.
S Q A D F W @ E 1 B T R # O % 5 3 U Z C G Y 2 4 & H I M 9 7 $ 8 6 L N ? K
How many such vowels are there in the above arrangement each of which are immediately preceded by a consonant and followed by a consonant in step 2?
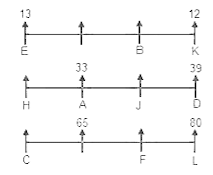
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Step 1: Those numbers which are immediately followed by a consonant and immediately preceded by a vowel are written at the left end in increasing order.
Step 2: After completing step 1, vowels are interchanged with preceding element.
Step 3: After completing step 2, Even numbers which are Perfect Square are written at the left end in ascending order.
S Q A D F W @ E 1 B T R # O % 5 3 U Z C G Y 2 4 & H I M 9 7 $ 8 6 L N ? K
How many odd numbers are there which are immediately followed by a vowel in Step 3?
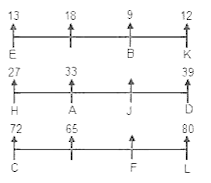
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Step 1: Those numbers which are immediately followed by a consonant and immediately preceded by a vowel are written at the left end in increasing order.
Step 2: After completing step 1, vowels are interchanged with preceding element.
Step 3: After completing step 2, Even numbers which are Perfect Square are written at the left end in ascending order.
S Q A D F W @ E 1 B T R # O % 5 3 U Z C G Y 2 4 & H I M 9 7 $ 8 6 L N ? K
Which element is 8th to the right of 17th element from the right end in step 3?
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Step 1: Those numbers which are immediately followed by a consonant and immediately preceded by a vowel are written at the left end in increasing order.
Step 2: After completing step 1, vowels are interchanged with preceding element.
Step 3: After completing step 2, Even numbers which are Perfect Square are written at the left end in ascending order.
S Q A D F W @ E 1 B T R # O % 5 3 U Z C G Y 2 4 & H I M 9 7 $ 8 6 L N ? K
Which of the following element is the twelfth to the right of the tenth element from the left end in step 3?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
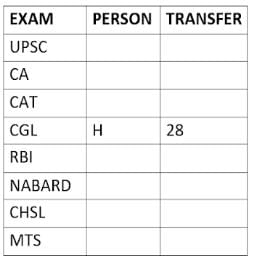
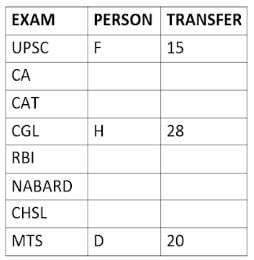
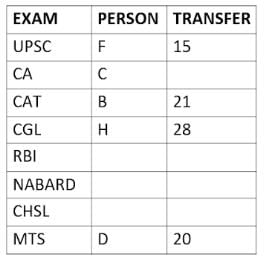
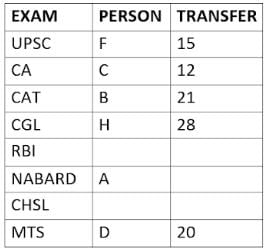
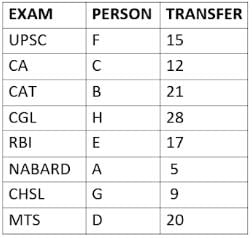
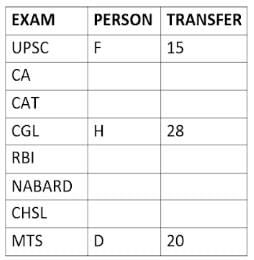
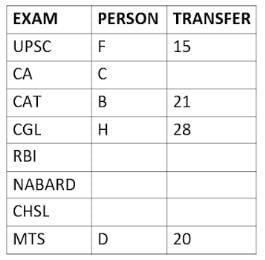
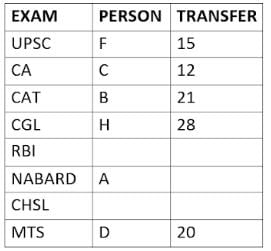
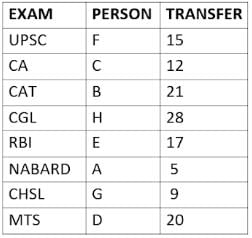
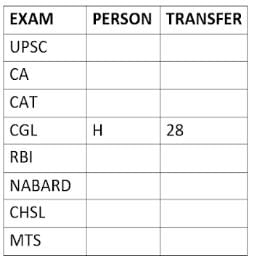
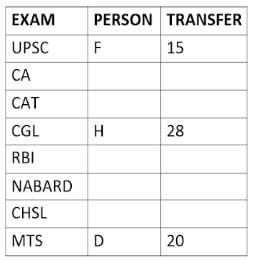
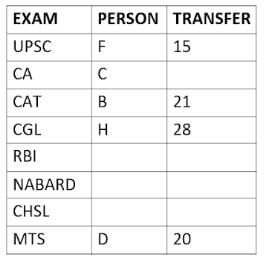
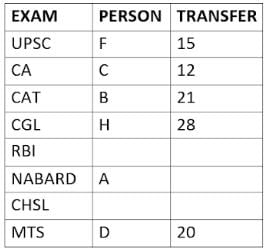
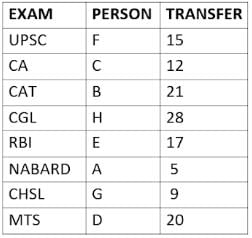
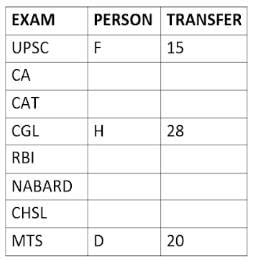
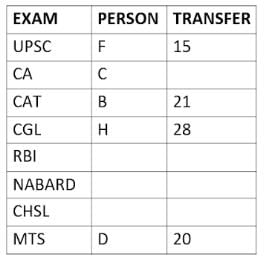
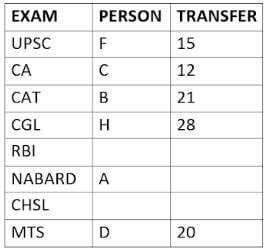
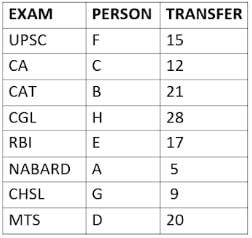
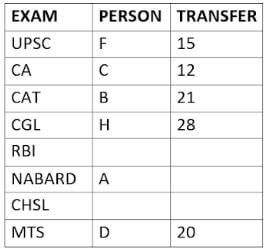
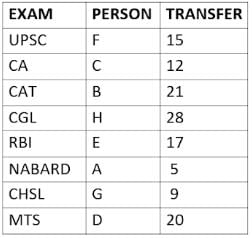
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H, are working in different sectors based on the exam in which they appeared. These eight people appeared for (or cleared) eight different exams namely, UPSC, CA, CAT, CGL, RBI, NABARD, CHSL, and MTS but not necessarily in the same order. Also, the exams are mentioned in decreasing order of their difficulty level. Also, these people were transferred many times in their carrier. No two person was transferred the same number of times.
The person who cleared RBI was transferred 5 more times than the person who cleared CA. The difficulty level of the exam which C cleared is just below the difficulty level of the exam which was cleared by F. The person who cleared NABARD was transferred 4 fewer times than the person who cleared CHSL. A did not appear for either RBI or CHSL. The total number of transfers of C is 60% of the total number of transfers of D and also, C was transferred 3 more times than G. B appeared for the exam which is difficult than the exam for which H appeared and B got 7 fewer transfers than H. The total number of transfers of D and the person who cleared UPSC is 35. The exam that H took was more difficult than at least four exams. D cleared either MTS or CGL. The person who appeared for UPSC was transferred 5 fewer times than the person who appeared for MTS. Neither G nor H appeared for either CA or CAT. No person appeared for the more difficult exam than F. F was transferred 13 fewer times than H who was transferred the maximum number of times. The total number of transfers of H and F is 43.
Who cleared CAT exam?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H, are working in different sectors based on the exam in which they appeared. These eight people appeared for (or cleared) eight different exams namely, UPSC, CA, CAT, CGL, RBI, NABARD, CHSL, and MTS but not necessarily in the same order. Also, the exams are mentioned in decreasing order of their difficulty level. Also, these people were transferred many times in their carrier. No two person was transferred the same number of times.
The person who cleared RBI was transferred 5 more times than the person who cleared CA. The difficulty level of the exam which C cleared is just below the difficulty level of the exam which was cleared by F. The person who cleared NABARD was transferred 4 fewer times than the person who cleared CHSL. A did not appear for either RBI or CHSL. The total number of transfers of C is 60% of the total number of transfers of D and also, C was transferred 3 more times than G. B appeared for the exam which is difficult than the exam for which H appeared and B got 7 fewer transfers than H. The total number of transfers of D and the person who cleared UPSC is 35. The exam that H took was more difficult than at least four exams. D cleared either MTS or CGL. The person who appeared for UPSC was transferred 5 fewer times than the person who appeared for MTS. Neither G nor H appeared for either CA or CAT. No person appeared for the more difficult exam than F. F was transferred 13 fewer times than H who was transferred the maximum number of times. The total number of transfers of H and F is 43.
The person who cleared NABARD is transferred how many times so far?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H, are working in different sectors based on the exam in which they appeared. These eight people appeared for (or cleared) eight different exams namely, UPSC, CA, CAT, CGL, RBI, NABARD, CHSL, and MTS but not necessarily in the same order. Also, the exams are mentioned in decreasing order of their difficulty level. Also, these people were transferred many times in their carrier. No two person was transferred the same number of times.
The person who cleared RBI was transferred 5 more times than the person who cleared CA. The difficulty level of the exam which C cleared is just below the difficulty level of the exam which was cleared by F. The person who cleared NABARD was transferred 4 fewer times than the person who cleared CHSL. A did not appear for either RBI or CHSL. The total number of transfers of C is 60% of the total number of transfers of D and also, C was transferred 3 more times than G. B appeared for the exam which is difficult than the exam for which H appeared and B got 7 fewer transfers than H. The total number of transfers of D and the person who cleared UPSC is 35. The exam that H took was more difficult than at least four exams. D cleared either MTS or CGL. The person who appeared for UPSC was transferred 5 fewer times than the person who appeared for MTS. Neither G nor H appeared for either CA or CAT. No person appeared for the more difficult exam than F. F was transferred 13 fewer times than H who was transferred the maximum number of times. The total number of transfers of H and F is 43.
Which exam did G clear?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H, are working in different sectors based on the exam in which they appeared. These eight people appeared for (or cleared) eight different exams namely, UPSC, CA, CAT, CGL, RBI, NABARD, CHSL, and MTS but not necessarily in the same order. Also, the exams are mentioned in decreasing order of their difficulty level. Also, these people were transferred many times in their carrier. No two person was transferred the same number of times.
The person who cleared RBI was transferred 5 more times than the person who cleared CA. The difficulty level of the exam which C cleared is just below the difficulty level of the exam which was cleared by F. The person who cleared NABARD was transferred 4 fewer times than the person who cleared CHSL. A did not appear for either RBI or CHSL. The total number of transfers of C is 60% of the total number of transfers of D and also, C was transferred 3 more times than G. B appeared for the exam which is difficult than the exam for which H appeared and B got 7 fewer transfers than H. The total number of transfers of D and the person who cleared UPSC is 35. The exam that H took was more difficult than at least four exams. D cleared either MTS or CGL. The person who appeared for UPSC was transferred 5 fewer times than the person who appeared for MTS. Neither G nor H appeared for either CA or CAT. No person appeared for the more difficult exam than F. F was transferred 13 fewer times than H who was transferred the maximum number of times. The total number of transfers of H and F is 43.
Who cleared RBI and how many transfers he has experienced so far?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H, are working in different sectors based on the exam in which they appeared. These eight people appeared for (or cleared) eight different exams namely, UPSC, CA, CAT, CGL, RBI, NABARD, CHSL, and MTS but not necessarily in the same order. Also, the exams are mentioned in decreasing order of their difficulty level. Also, these people were transferred many times in their carrier. No two person was transferred the same number of times.
The person who cleared RBI was transferred 5 more times than the person who cleared CA. The difficulty level of the exam which C cleared is just below the difficulty level of the exam which was cleared by F. The person who cleared NABARD was transferred 4 fewer times than the person who cleared CHSL. A did not appear for either RBI or CHSL. The total number of transfers of C is 60% of the total number of transfers of D and also, C was transferred 3 more times than G. B appeared for the exam which is difficult than the exam for which H appeared and B got 7 fewer transfers than H. The total number of transfers of D and the person who cleared UPSC is 35. The exam that H took was more difficult than at least four exams. D cleared either MTS or CGL. The person who appeared for UPSC was transferred 5 fewer times than the person who appeared for MTS. Neither G nor H appeared for either CA or CAT. No person appeared for the more difficult exam than F. F was transferred 13 fewer times than H who was transferred the maximum number of times. The total number of transfers of H and F is 43.
What is the total number of transfers for the people who cleared the top three easiest exams?
Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is /are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: T < Z ≤ R; U < Y > S; S = R; R > U;
Conclusions:
I. U > Z
II. S = U
III. Y > T
IV. U = Z
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
1. All letters are coded numbers 1 – 9 in ascending order. For example, A is coded 1, B is coded 2, I is coded 9 and J is coded 1 and so on.
2. If there are two same vowels in the word then both the vowels are coded %.
3. If the word starts and ends with a consonant then the last letter is coded &.
4. If the word starts and ends with a vowel then the first letter is coded $.
5. If the word starts with a consonant and ends with a vowel then their codes are interchanged.
6. If the word starts with a vowel and ends with a consonant then both these letters are coded @.
The conditions mentioned above are to be followed in a given order if a word satisfies more than one condition.
What would be the code for the word EVOLVE?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
1. All letters are coded numbers 1 – 9 in ascending order. For example, A is coded 1, B is coded 2, I is coded 9 and J is coded 1 and so on.
2. If there are two same vowels in the word then both the vowels are coded %.
3. If the word starts and ends with a consonant then the last letter is coded &.
4. If the word starts and ends with a vowel then the first letter is coded $.
5. If the word starts with a consonant and ends with a vowel then their codes are interchanged.
6. If the word starts with a vowel and ends with a consonant then both these letters are coded @.
The conditions mentioned above are to be followed in a given order if a word satisfies more than one condition.
What would be the code for the word ELECTION?
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
1. All letters are coded numbers 1 – 9 in ascending order. For example, A is coded 1, B is coded 2, I is coded 9 and J is coded 1 and so on.
2. If there are two same vowels in the word then both the vowels are coded %.
3. If the word starts and ends with a consonant then the last letter is coded &.
4. If the word starts and ends with a vowel then the first letter is coded $.
5. If the word starts with a consonant and ends with a vowel then their codes are interchanged.
6. If the word starts with a vowel and ends with a consonant then both these letters are coded @.
The conditions mentioned above are to be followed in a given order if a word satisfies more than one condition.
What would be the final code for the MOBILE?
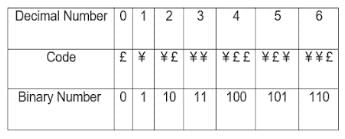
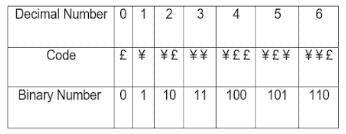
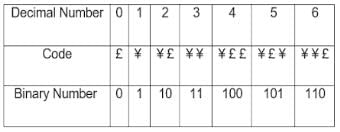
Directions: In a certain code, the code for '0' is '£', and the code for '1' is '¥'
Subsequently,
'1' is represented by '¥'
'2' is represented by '¥ £'
'3' is represented by '¥ ¥ '
'4' is represented by '¥ £ £'
'5' is represented by '¥ £ ¥'
Based on the above pattern, answer the question follows,
The code '¥ ¥ £ ¥ ¥ ¥ ¥' represents which of the following number?
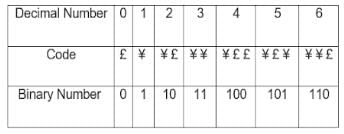
Directions: In a certain code, the code for '0' is '£', and the code for '1' is '¥'
Subsequently,
'1' is represented by '¥'
'2' is represented by '¥ £'
'3' is represented by '¥ ¥ '
'4' is represented by '¥ £ £'
'5' is represented by '¥ £ ¥'
Based on the above pattern, answer the question follows,
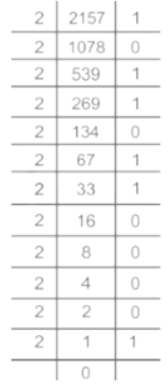
Which of the following will be the code for '2157'?
Directions: In a certain code, the code for '0' is '£', and the code for '1' is '¥'
Subsequently,
'1' is represented by '¥'
'2' is represented by '¥ £'
'3' is represented by '¥ ¥ '
'4' is represented by '¥ £ £'
'5' is represented by '¥ £ ¥'
Based on the above pattern, answer the question follows,
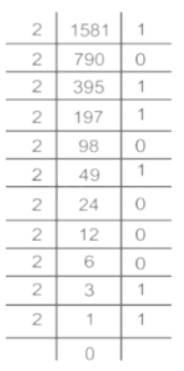
Which of the following will be the code for '1581'?
Directions: In a certain code, the code for '0' is '£', and the code for '1' is '¥'
Subsequently,
'1' is represented by '¥'
'2' is represented by '¥ £'
'3' is represented by '¥ ¥ '
'4' is represented by '¥ £ £'
'5' is represented by '¥ £ ¥'
Based on the above pattern, answer the question follows,
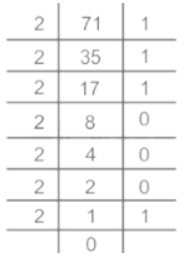
The code '¥ £ ¥ £ £ £ ¥' represents which of the following number?
Directions: In the given questions, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusions I, II and III given below the statements is/are definitely true.
Statements:
B > K, M = K, L ≤ M, D < L
Conclusions:
I. M > D
II. M = B
III. L = K
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
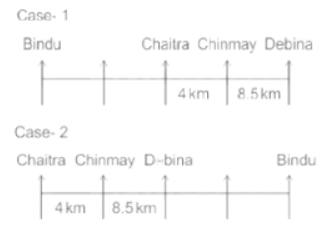
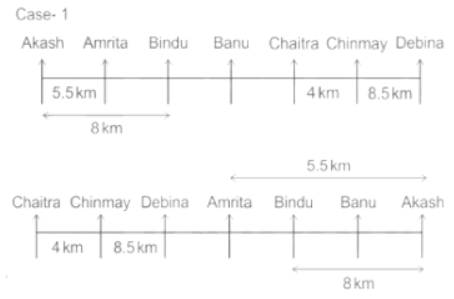
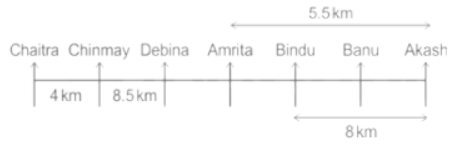
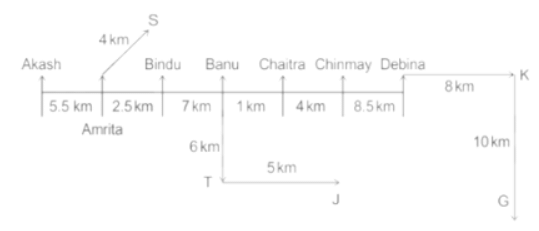
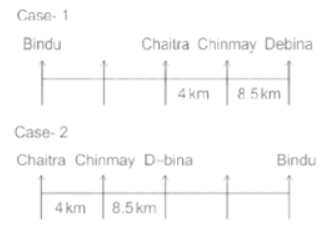
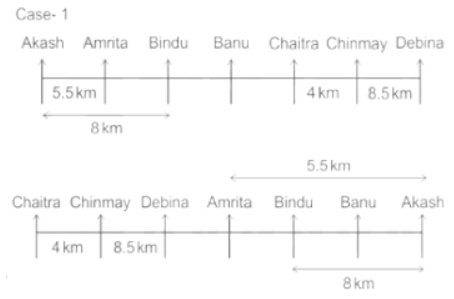
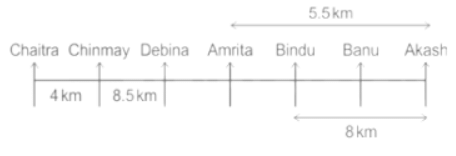
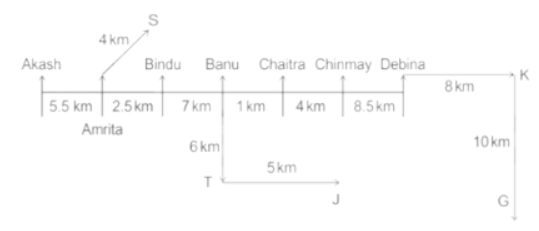
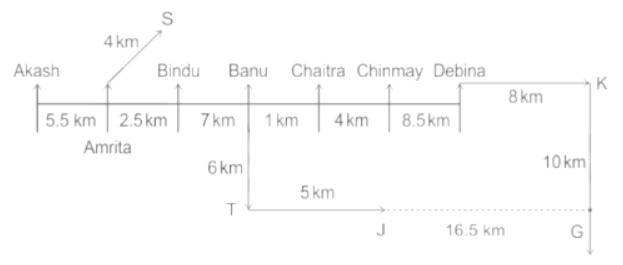
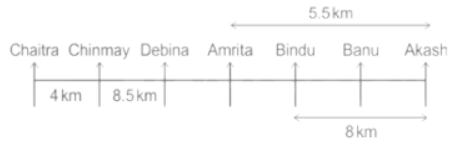
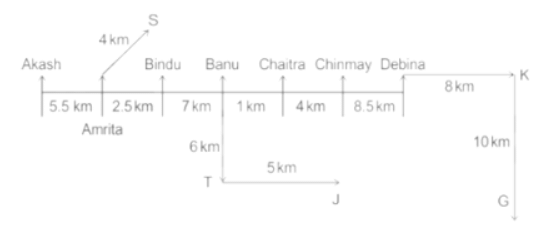
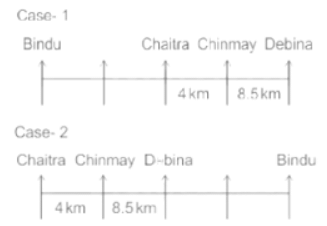
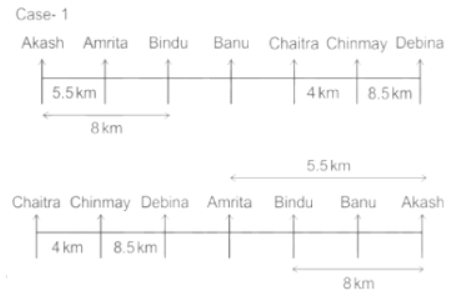
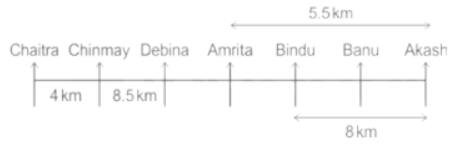
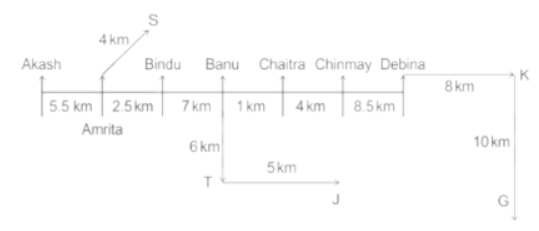
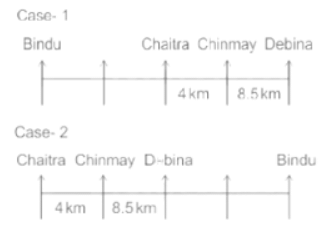
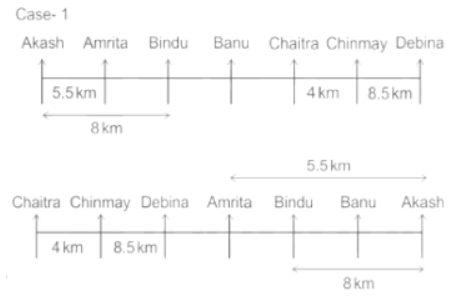
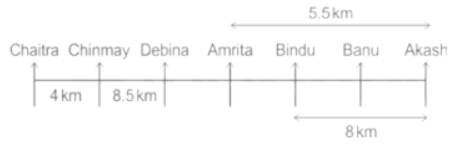
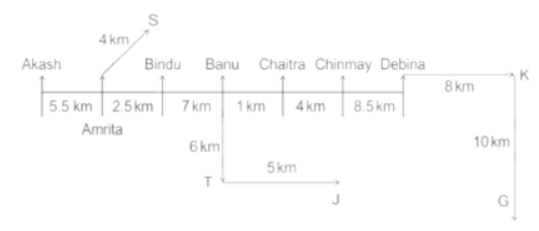
Seven people Debina, Bindu, Amrita, Chaitra, Akash, Chinmay, Banu are sitting on row facing in same direction. All of them are sitting at distance of 1 Km, 2.5 Km, 4 km and so on from their immediate neighbours but not necessarily in the same order.
Banu is sittings second to right of Amrita who is sitting 5.5Km away from Akash.
Chinmay is sitting immediate left of Debina at a distance of 8.5 Km. Distance between Akash and Bindu who is sitting one of the places to left of Banu is 8 Km. Only two persons are sitting between Bindu and Chinmay who is sitting 4 Km away from Chaitra. Distance between Banu and the one who is sitting second to left of Chaitra is 7 Km. Debina starts to move in East direction, after moving 8 Km reached to K, and then she started to walk in south direction to reach G which is 10 km from K. The person who is sitting immediate right of Bindu starts to walk for 6 Km in south direction and reached T then the person turns to left and starts running for 5 Km to reach J. Amrita starts to move in north-east direction, after walking 4 Km reached to S which is north of Bindu
Who is sitting third from left end?
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Seven people Debina, Bindu, Amrita, Chaitra, Akash, Chinmay, Banu are sitting on row facing in same direction. All of them are sitting at distance of 1 Km, 2.5 Km, 4 km and so on from their immediate neighbours but not necessarily in the same order.
Banu is sittings second to right of Amrita who is sitting 5.5Km away from Akash.
Chinmay is sitting immediate left of Debina at a distance of 8.5 Km. Distance between Akash and Bindu who is sitting one of the places to left of Banu is 8 Km. Only two persons are sitting between Bindu and Chinmay who is sitting 4 Km away from Chaitra. Distance between Banu and the one who is sitting second to left of Chaitra is 7 Km. Debina starts to move in East direction, after moving 8 Km reached to K, and then she started to walk in south direction to reach G which is 10 km from K. The person who is sitting immediate right of Bindu starts to walk for 6 Km in south direction and reached T then the person turns to left and starts running for 5 Km to reach J. Amrita starts to move in north-east direction, after walking 4 Km reached to S which is north of Bindu
If Banu walks 16. 5Km from J in East direction, then in which direction Banu will be from point K?
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Seven people Debina, Bindu, Amrita, Chaitra, Akash, Chinmay, Banu are sitting on row facing in same direction. All of them are sitting at distance of 1 Km, 2.5 Km, 4 km and so on from their immediate neighbours but not necessarily in the same order.
Banu is sittings second to right of Amrita who is sitting 5.5Km away from Akash.
Chinmay is sitting immediate left of Debina at a distance of 8.5 Km. Distance between Akash and Bindu who is sitting one of the places to left of Banu is 8 Km. Only two persons are sitting between Bindu and Chinmay who is sitting 4 Km away from Chaitra. Distance between Banu and the one who is sitting second to left of Chaitra is 7 Km. Debina starts to move in East direction, after moving 8 Km reached to K, and then she started to walk in south direction to reach G which is 10 km from K. The person who is sitting immediate right of Bindu starts to walk for 6 Km in south direction and reached T then the person turns to left and starts running for 5 Km to reach J. Amrita starts to move in north-east direction, after walking 4 Km reached to S which is north of Bindu
What is the distance between Chaitra and K?
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Seven people Debina, Bindu, Amrita, Chaitra, Akash, Chinmay, Banu are sitting on row facing in same direction. All of them are sitting at distance of 1 Km, 2.5 Km, 4 km and so on from their immediate neighbours but not necessarily in the same order.
Banu is sittings second to right of Amrita who is sitting 5.5Km away from Akash.
Chinmay is sitting immediate left of Debina at a distance of 8.5 Km. Distance between Akash and Bindu who is sitting one of the places to left of Banu is 8 Km. Only two persons are sitting between Bindu and Chinmay who is sitting 4 Km away from Chaitra. Distance between Banu and the one who is sitting second to left of Chaitra is 7 Km. Debina starts to move in East direction, after moving 8 Km reached to K, and then she started to walk in south direction to reach G which is 10 km from K. The person who is sitting immediate right of Bindu starts to walk for 6 Km in south direction and reached T then the person turns to left and starts running for 5 Km to reach J. Amrita starts to move in north-east direction, after walking 4 Km reached to S which is north of Bindu
Who are sitting at the left extreme end?
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Seven people Debina, Bindu, Amrita, Chaitra, Akash, Chinmay, Banu are sitting on row facing in same direction. All of them are sitting at distance of 1 Km, 2.5 Km, 4 km and so on from their immediate neighbours but not necessarily in the same order.
Banu is sittings second to right of Amrita who is sitting 5.5Km away from Akash.
Chinmay is sitting immediate left of Debina at a distance of 8.5 Km. Distance between Akash and Bindu who is sitting one of the places to left of Banu is 8 Km. Only two persons are sitting between Bindu and Chinmay who is sitting 4 Km away from Chaitra. Distance between Banu and the one who is sitting second to left of Chaitra is 7 Km. Debina starts to move in East direction, after moving 8 Km reached to K, and then she started to walk in south direction to reach G which is 10 km from K. The person who is sitting immediate right of Bindu starts to walk for 6 Km in south direction and reached T then the person turns to left and starts running for 5 Km to reach J. Amrita starts to move in north-east direction, after walking 4 Km reached to S which is north of Bindu
What is the distance between S and Bindu?
Direction: In the following problems, there is one question and some statements given below the question. You have to decide whether the data given in the statements is sufficient to answer the question. Read all the statements carefully and find out which of the statements is/are sufficient to answer the given question. Choose the correct alternative for each question.
Who among Y, Z, A and B is the heaviest?
I. Z is heavier than B.
II. Y is not as heavy as either A or Z.
III. B is neither the heaviest nor the lightest.
Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
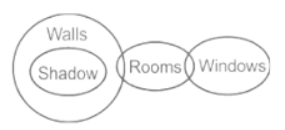
Statements:
All shadow are walls.
Some walls are rooms.
Some rooms are windows
Conclusions:
I. Some windows are walls.
II. Some windows are shadow.
III. Some rooms are walls.
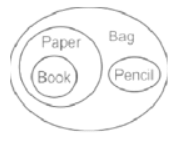
Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All book are paper.
All paper are bag.
All pencil are bag.
Conclusions:
I. Some paper are pencil.
II. Some bag are book.
III. All book are bag.
Direction : In the following problems, there is one question and some statements given below the question. You have to decide whether the data given in the statements is sufficient to answer the question. Read all the statements carefully and find out which of the statements is/are sufficient to answer the given question. Choose the correct alternative for each question.
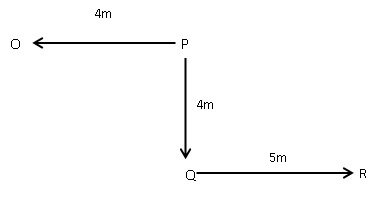
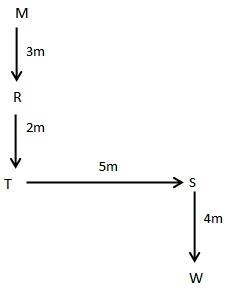
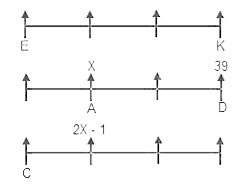
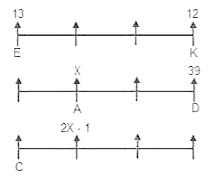
In which direction is point M with respect to point N?
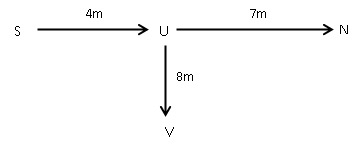
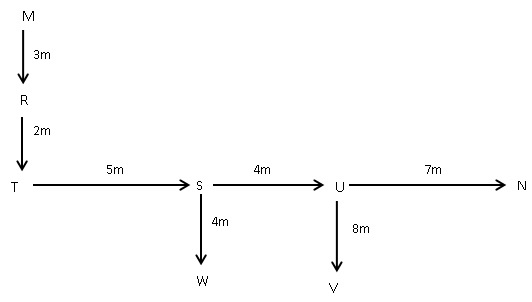
I. O is 4m to the west of P, P is 4m to the north of Q. R is 5m to the east of Q.
II. R is 3m to the south of M. S is 5m to the east of T. T is 2m to the south of R. W is 4m to the south of S.
III. U is 7m to the west of N. S is 4m to the west of U. V is 8m to the south of U.
Directions: In the question below is given a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II. You have to assume everything in the statement to be true and on the basis of the information given in the statement, decide which of the suggested course of action logically follow(s) for pursuing.
Statement:
Students at times are not able to pass home exams marginally.
Course of action:
I. Borderline cases should be allowed to take a re-test.
II. Minimum Passing marks for home exams should be revised and brought down to a lower level.
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
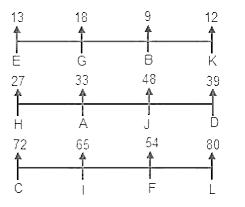
Twelve people of a family, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, and L are sitting in three rows facing north. Each row has four seats at equal distance. The seats of these rows are arranged in such a way that the first seat of the first row is exactly in front of the first seat of the second row and the first seat of the second row is exactly in front of the first seat of the third row and so on. Also, these people are sitting in such a way that the people sitting in the first row are younger than 20 years, the people sitting in the row immediately behind it i.e. row 2 are older than 20 years but younger than 50 years and the people sitting in the row that is immediately behind row 2 are older than 50 years. Also, the age of each of these people is a natural number.
J is 6 years younger than F but 30 years younger than G. The difference between the ages of A and L is 47 years. The age of B is one third the age of the person who is sitting immediately behind E but half the age of the person who is sitting to his immediate left. The difference between the ages of the two people who are sitting on the extreme ends in the third row is 8 years. The age of H is 45 years less than the person sitting immediately behind him. L is 15 years older than the person who is sitting second to his left. J is sitting immediately in front of F. B is sitting to the immediate left of the person who is sitting right in front of D. E is sitting two seats ahead of C whose age is numerically an even number. H is sitting second to the left of J and H is 21 years younger than J. The age of the person sitting right behind A is 1 year less than twice the age of A. The age of K is 1 year less than thrice the age of the person who is sitting immediately behind him. A is sitting second to the left of the person who is 39 years old. K is sitting third to the right of E and the sum of their ages is 25 years.
Who is the youngest person in the 2nd row?