Indian Constitution - Practice Test (1) - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Polity and Constitution (Prelims) by IAS Masters - Indian Constitution - Practice Test (1)
A new state can be formed by the Parliament under :
____________ was an act of the British Parliament that increased the size of the legislative councils in India.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match List I (Item in the Indian Constitution) with List II (Country from which it was derived and select the correct answer
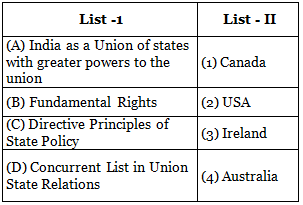
Below the options are given in the A B C D order

Below the options are given in the A B C D order
The Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution deals with the administration and control of Scheduled Areas and Scheduled Tribes in the four states of
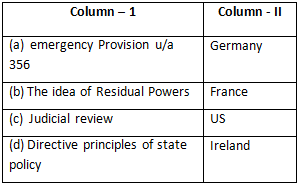
Which among the following is NOT matched properly:
Prohibition of discrimination on grounds as provided in Article 15 of the Constitution is a fundamental right classifiable under:
Which among the following must be passed by both the houses by a special majority?
The Institution of Speaker and Deputy speaker originated in India under the provision of
Which act is the ‘Act for the Good Government of India’?
Who is called the ‘Father of Communal electorate’?
By which amendment of the Constitution, Article 323A (Administrative tribunals) & Article 323B (Tribunals for other matters) in a new part XIV A was inserted in the Indian Constitution?
In which case Supreme Court has declared the Preamble as the part of the constitution?
Consider the following statements:
Assertion (A): The Parliament can redraw the political map of India according to its will
Reason (R): The territorial integrity of any state is not guaranteed by the Constitution
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following about Finance Commission:
1. It considers applications for grants-in-aid from States.
2. It supervises and reports on whether the Union and State governments are levying taxes in accordance with the budgetary provisions.
Which statement is INCORRECT?
Who decides the reasonableness of the restrictions placed on Fundamental rights in India?
Consider the following statements:
1. The Constitution of India is federal.
2. It has provided to the Central Government more powers than the state government.
Which is a correct statement?
Consider the following and choose the correct option:
1. The President can pardon death sentence while Governor cannot.
2. The President can pardon sentences inflicted by court martial while the Governor cannot.
The Chairman of the UPSC holds the office for a term of:
A Joint Public Service Commission can be created by:
President’s rule is imposed in a state under:
The words ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ were added to the Preamble by:
What is NOT true about the Election Commission?
What is the strength of the Public Accounts Committee?
|
36 videos|144 docs|138 tests
|
|
36 videos|144 docs|138 tests
|

















