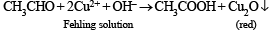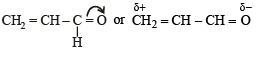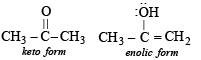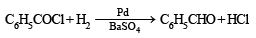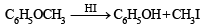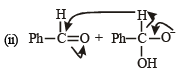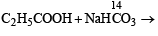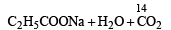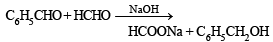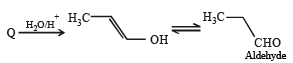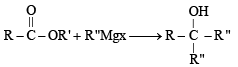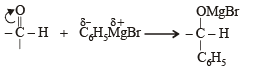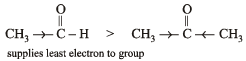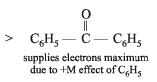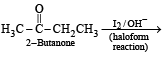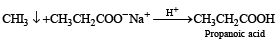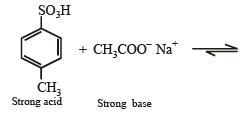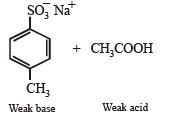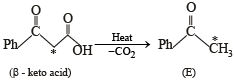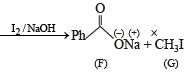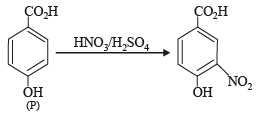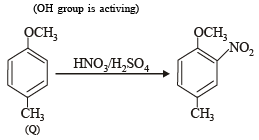JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids
The reagent with which both acetaldehyde and acetone react easily is
When acetaldehyde is heated with Fehling’s solution it gives a precipitate of
The Cannizzaro reaction is not given by
The compound that will not give iodoform on treatment with alkali and iodine is :
Polarisation of electrons in acrolein may be written as
The enolic form of acetone contains
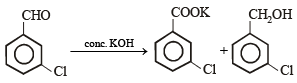
m-Chlorobenzaldehyde on reaction with conc. KOH at room temperature gives
Hydrogenation of benzoyl chloride in the presence of Pd on BaSO4 gives
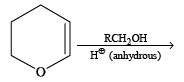
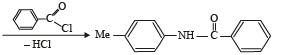
The organic product formed in the reaction
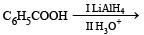
The reaction products of 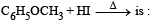
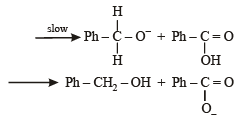
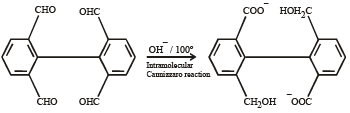
In the Cannizzaro reaction given below,
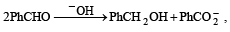
the slowest step is
When propionic acid is treated with aqueous sodium bicarbonate, CO2 is liberated. The ‘C’ of CO2 comes from
The enol form of acetone, after treatment with D2O, gives.
Which one of the following will most readily be dehydrated in acidic condition ?
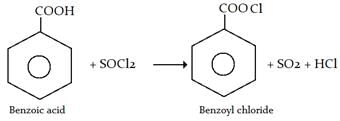
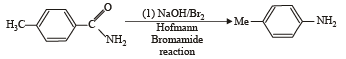
Benzoyl chloride is prepared from benzoic acid by
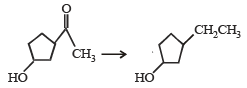
The appropriate reagent for the following transformation is
A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde on heating with aqueous NaOH solution gives
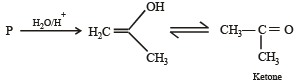
The product of acid hydrolysis of P and Q can be distinguished by
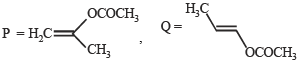
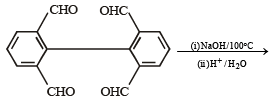
Major product is :
Ethyl ester  The product P will be
The product P will be
An enantiomerically pure acid is treated with a racemic mixture of an alcohol having one chiral carbon. The ester formed will be
The correct order of reactivity of PhMgBr with
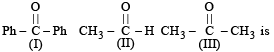
How will you convert butan-2-one to propanoic acid?
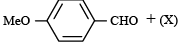
The compound (X) is
4-Methylbenzenesulphonic acid reacts with sodium acetate to give
In the following reaction sequence, the correct structures of E, F and G are
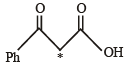
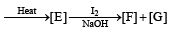
[* implies 13C labelled carbon)
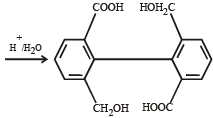
The correct acidity order of the following is
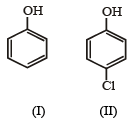
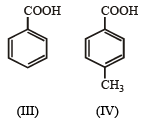
In the reaction
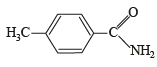
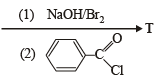
the structure of the product T is :
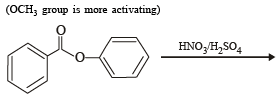
The compounds P, Q and S
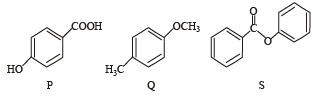
were separately subjected to nitration using HNO3/H2SO4 mixture. The major product formed in each case respectively, is :
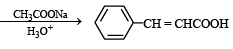
The major product of the following reaction is