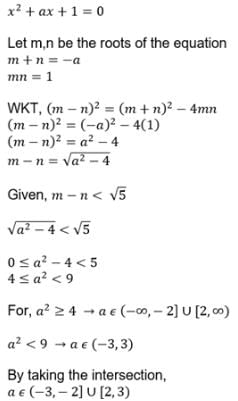JEE Advanced Level Test: Complex Numbers- 3 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Level Test: Complex Numbers- 3
Consider the equation x2 + 2x – n = 0, where n ∈ N and n ∈ [5, 100]. Total number of different values of `n' so that the given equation has integral roots, is
If the equation k (6x2 + 3) + rx + 2x2 – 1 = 0 and 6k (2x2 + 1) + px + 4x2 – 2 = 0 have both roots common, then the value of (2r – p) is
The entire graph of the expression y = x2 + kx – x + 9 is strictly above the x_axis if and only if
If a, b, c are integers and b2 = 4(ac + 5d2), d ∈ N, then roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are
The set of rational numbers is denoted by
If the inequality (m – 2)x2 + 8x + m + 4 > 0 is satisfied for all x Î R, then least integral m is
Find the roots of the equation: x2+ 6x + 5 = 0
If a, b be the roots of 4x2 –16x + l = 0, where l ∈ R such that 1 < a < 2 and 2 < b < 3, then the number of integral solutions of l is
If two roots of the equation x3 – px2 + qx – r = 0 are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign, then
Find the roots of the equation: 3x2 – 3 = 8x
If the quadratic equations 3x2 + ax + 1 = 0 and 2x2 + bx +1 = 0 have a common root, then the value of the expression 5ab – 2a2 – 3b2 is
The least value of expression x2 + 2xy + 2y2 + 4y + 7 is
If a, b, g, d are the roots of the equation x4 – Kx3 + Kx2 + Lx + M = 0, where K, L & M are real numbers, then the minimum value of a2 + b2 + g2 + d2 is
If the roots of the equation x3 + Px2 + Qx – 19 = 0 are each one more than the roots of the equation x3 – Ax2 + Bx – C = 0, where A, B, C, P & Q are constants, then the value of A + B + C is equal to
The equations x3 + 5x2 + px + q = 0 and x3 + 7x2 + px + r = 0 have tworoots in common. If the third root of each equation is represented by x1 and x2 respectivley, then the ordered pair (x1, x2) is
If coefficients of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ¹ 0 are real and roots of the equation are non–real complex and a + c + b < 0, then
If (l2 + l – 2)x2 + (l + 2) x < 1 for all x ∈ R, then l belongs to the interval
The set of possible values of l for which x2 – (l2 – 5l + 5)x + (2l2 – 3l – 4) = 0 has roots, whose sum and product are both less than 1, is
If the difference between the roots of the equation x2 + ax + 1 = 0 is less than √5, then the set of possible values of a is
All the values of m for which both roots of the equation x2 – 2mx + m2 – 1 = 0 are greater than –2 but less than 4 lie in the interval
The value of a for which the sum of the squares of the roots of the equation x2 – (a – 2)x – a – 1 = 0 assume the least value is
If both the roots of the quadratic equation x2 – 2kx + k2 + k – 5 = 0 are less than 5, then k lies in the interval
If one root of the equation x2 + px + 12 = 0 is 4, while the equation x2 + px + q = 0 has equal roots then the value of `q' is
If the sum of the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is equal to the sum of the squares of their reciprocals, then a/c, b/a and c/b are in
The value of `a' for which one root of the quadratic equation (a2 – 5a + 3)x2 + (3a – 1)x + 2 = 0 is twice as large as the other, is