JEE Advanced Level Test: Matrices and Determinants - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Level Test: Matrices and Determinants
If B is a non–singular matrix and A is a square matrix, then det (B–1 AB) is equal to
If the system of equations x + 2y + 3z = 4, x + λy + 2z = 3, x + 4y + μz = 3 has an infinite anumber of solutions then
If a, b, c are non zeros, then the system of equations (α + a) x + αy + αz = 0
αx + (α + b)y + αz = 0
αx + αy + (α + c) z = 0
has a non–trivial solution if
αx + αy + (α + c) z = 0
has a non–trivial solution if
Let 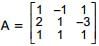 and
and 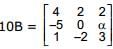 . If B is the inverse of matrix A, then α is
. If B is the inverse of matrix A, then α is
The value of a for which system of equations,
a3x + (a + 1)3 y + (a + 2)3z = 0,
ax + (a + 1) y + (a + 2) z = 0,
x + y + z = 0, has a non–zero solution is
Two matrices A and B are multiplied to get AB, if
then which one of the following holds for all n ≥ 1, by the principle of mathematical induction ?
is the unit matrix of order 2 and a, b are arbitrary constants, then
is equal to
Identity the correct statement(s)
If a, b, c > 0 & x, y, z ∈ R then the determinant
IF x, y , z ∈ R Δ = 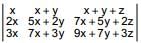 = -16 then value of x is
= -16 then value of x is
If A, B, C are angles of a triangle ABC, then
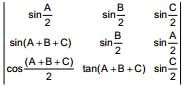
is less than or equal to
Let f(x) = 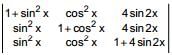 then the maximum value of f(x) is
then the maximum value of f(x) is
D =  is (where a, b, c are the sides opposite to angles A, B, C respectively in a triangle)
is (where a, b, c are the sides opposite to angles A, B, C respectively in a triangle)



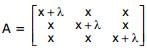 , then A-1 exists if
, then A-1 exists if 
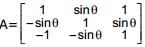 where 0 ≤ θ < 2π, then
where 0 ≤ θ < 2π, then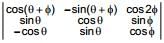 is
is 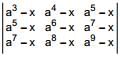 is
is 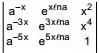 , then
, then 















