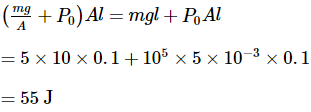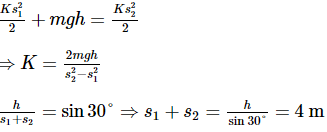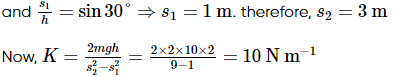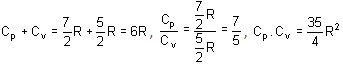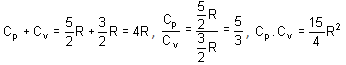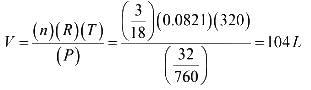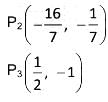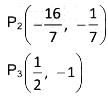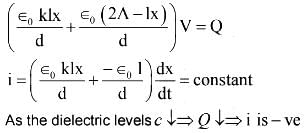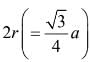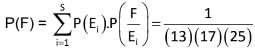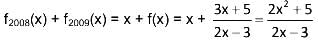JEE Advanced Mock Test - 1 (Paper II) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Advanced Mock Test - 1 (Paper II)
Refractive index of an equilateral prism is √2
There are three optical media, 1,2 and 3 with their refractive indices μ1 > μ2 > μ3 (TIR-total internal reflection)
A vernier callipers has 1 mm marks on the main scale. It has 20 equal divisions on the vernier scale which match with 16 main scale divisions. For this vernier calipers, the least count is
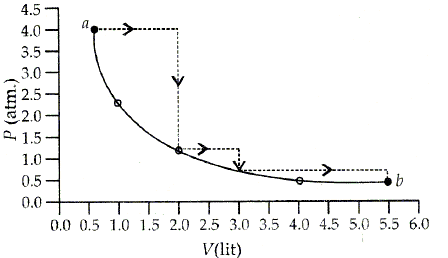
One mole of an ideal gas is taken from a to b along two paths denoted by the solid and the dotted lines as shown in the graph below. If the work done along the solid line path is ws and that along the dotted line path is wd, then the ratio wd/ws is
(Round off up to 2 decimal places)
Two soap bubbles A and B are kept in a closed chamber where the air is maintained at pressure 8 N/m2. The radii of bubbles A and B are 2 cm and 4 cm, respectively. Surface tension of the soap-water used to make bubbles is 0.04 N/m. Find the ratio nA/nB, where nA and nB are the number of moles of air in bubbles A and B, respectively. [Neglect the effect of gravity.]
(Round off upto 2 decimal places)
Two spherical bodies A (radius 6 cm) and B (radius 18 cm) are at temperatures T1 and T2, respectively. The maximum intensity in the emission spectrum of A is at 500 mm and in that of B is at 1500 nm. Considering them to be black bodies, what will be the ratio of the rate of total energy radiated by A to that by B?
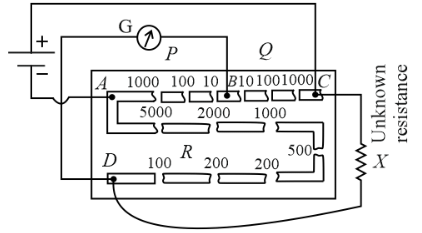
In the figure shown below, the maximum possible unknown resistance X (in Ω), that can be measured by the post office box is given by a × 10b Ω in scientific notation, then find the value of a−b?
(in this experiment, we take out only one plug in arm AB and only one plug in arm BC, but in arm AD we can take out many plugs).
A cylinder supports a piston of mass 5 kg5 kg and cross-sectional area 5×10−3 m2 enclosing a gas at 27°C. The gas is slowly heated to 77°C such that the piston rises by 0.1 m. The piston is now clamped at this new position and the gas is cooled down to its initial temperature. If atmospheric pressure is 1 atm, then the difference in heat supplied during heating and heat rejected during cooling is _____J.
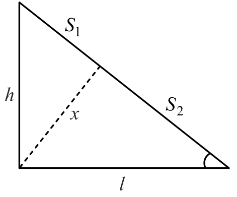
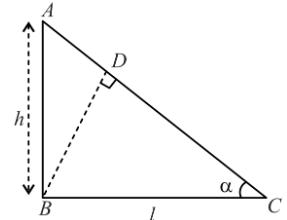
Consider a frictionless plane of height h = 2 m m and angle α=30°. One end of an electric string is connected to point B, the other end is passed through an orifice at point D on the plane and connected to a body of mass m = 2 kg initially stationary at point A. This body comes to rest at point C at the bottom of the inclined plane. The line drawn from point B to point D is perpendicular to side AC. Knowing that the length of the string is unstretched state is equal to the length of segment BD. Determine the elastic constant in N m−1. Take g = 10 m s−2
In figure all the pulleys and strings are massless, and all the surfaces are frictionless. A small block of mass m is placed on fixed wedge (take g = 10 ms-2):
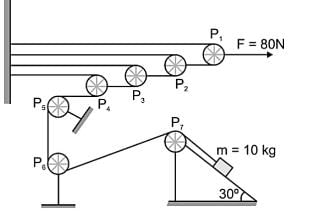
The acceleration of m is____.
In figure all the pulleys and strings are massless, and all the surfaces are frictionless. A small block of mass m is placed on fixed wedge (take g = 10 ms-2):
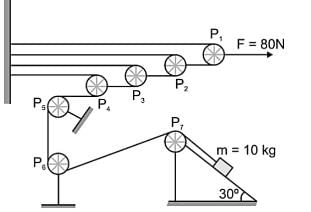
The acceleration of pulley P4 is _____.
Coefficient of mutual inductance for the given coils does not depend on
Work function of metal A is equal to the ionization energy of hydrogen atom in first excited state. Work function of metal B is equal to the ionization energy of He+ ion in second orbit. Photons of same energy E are incident on both A and B. Maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from A is twice that of photoelectrons emitted from B.
The difference in maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons from A and from B
Directions: The following question has four choices, out of which one or more is/are correct.
Which of the following can result in exactly 1 mol of K4[Fe(CN)6] stoichiometrically using the given compounds as the only source of carbon?
Directions: The following question has four choices, out of which ONE or MORE are correct.
Cv and Cp denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. Then,
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Assume that water vapour behaves as an ideal gas and the volume occupied by the liquid water is negligible compared to the volume of the container. A sample of liquid water of mass 3 g is injected into an evacuated 76 L flask maintained at 320 K. At this temperature the vapour pressure of water is 32 mm of Hg. (1/0.0821 = 12.2)
Now give the answers to following questions:
What % of the water will be vaporized, when the system comes to equilibrium?
Assume that water vapour behaves as an ideal gas and the volume occupied by the liquid water is negligible compared to the volume of the container. A sample of liquid water of mass 3 g is injected into an evacuated 76 L flask maintained at 320 K. At this temperature the vapour pressure of water is 32 mm of Hg. (1/0.0821 = 12.2)
Now give the answers to following questions:
What should be the minimum volume (in litre) of the flask if no liquid water is to be present at equilibrium?
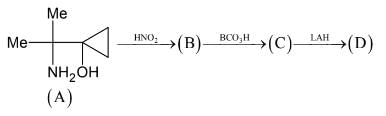
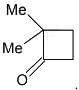
The Molecular Formula of compound (B) is CxHyOz. Then the value of x + y + z = ____
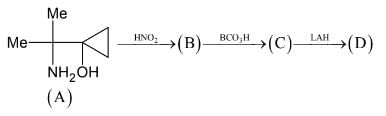
The Molecular mass (gm/mole) of compound (D) is :
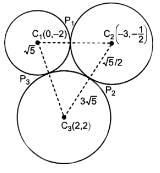
Let each of the circles
S1 = x2 + y2 + 4y - 1 = 0,
S2 = x2 + y2 + 6x + y + 8 = 0,
S3 = x2 + y2 - 4x - 4y - 37 = 0
Touches the other two. Let P1, P2, P3 be the points of contacts of S1 and S2, S2 and S3, S3 and S1 respectively and C1, C2, C3 be the centre of S1, S2, S3 respectively
The value of 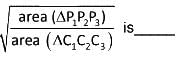
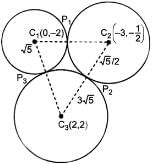
Let each of the circles
S1 = x2 + y2 + 4y - 1 = 0,
S2 = x2 + y2 + 6x + y + 8 = 0,
S3 = x2 + y2 - 4x - 4y - 37 = 0
Touches the other two. Let P1, P2, P3 be the points of contacts of S1 and S2, S2 and S3, S3 and S1 respectively and C1, C2, C3 be the centre of S1, S2, S3 respectively
Length of direct common tangent for S1 and S3____.
Let f(x) and g(x) be two differentiable functions, defined as
f(x) = x2 + xg'(1) + g”(2) and g(x) = f(1)x2 + x f'(x) + f”(x).
The value of 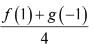 is
is
Let f(x) and g(x) be two differentiable functions, defined as
f(x) = x2 + xg'(1) + g”(2) and g(x) = f(1)x2 + x f'(x) + f”(x).
The value of 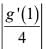 is ____
is ____
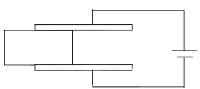
A dielectric slab of area A passes between the capacitor plates of area 2A with a constant speed v. The variation of current (i) through the circuit as function of time (t) can be qualitatively represented as
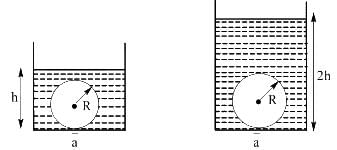
Two identical cylinders have a hole of radius a (a<<R) at its bottom. A ball of radius R is kept on the hole and water is filled in the cylinder such that there is no water leakage from bottom. In case-1 water is filled upto height h and in second case it is filled upto height 2h. If F1 is force by liquid on sphere in case-1 and F2 is force by liquid on sphere in case-2 then.
In a crystal structure of an element, atoms are present in fcc arrangement as well as intetrahedral voids. Which of the following relation between the atomic radius and the edge lengthis correct?
Which one of the following reactions is not correct?
From a pack of 52 playing cards; half of the cards are randomly removed without looking at them. From the remaining cards, 3 cards are drawn randomly. The probability that all are king.
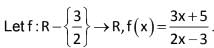 let f1(x) = f(x), fn(x) = f(fn-1(x)) for n ≥ 2, n ∈ N, then f2008 (x) + f2009 (x) =
let f1(x) = f(x), fn(x) = f(fn-1(x)) for n ≥ 2, n ∈ N, then f2008 (x) + f2009 (x) =
|
356 docs|142 tests
|


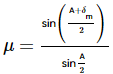
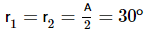

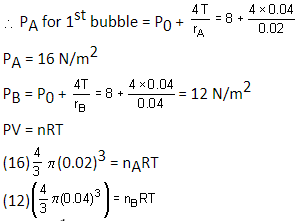
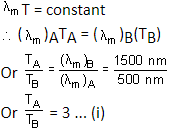
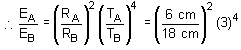 (Using (i))
(Using (i))