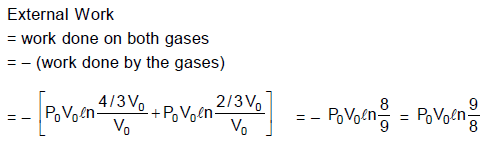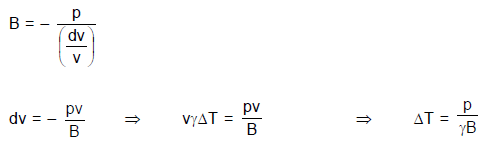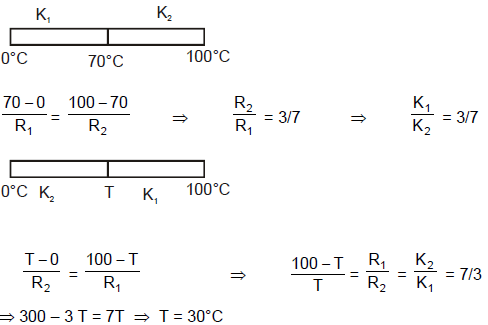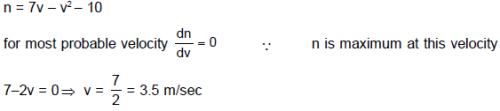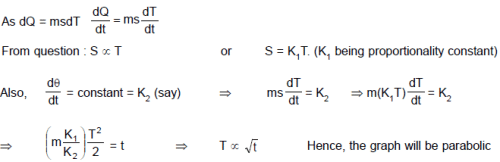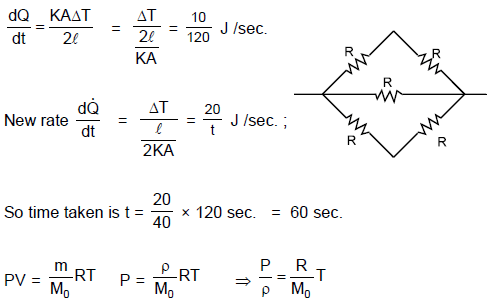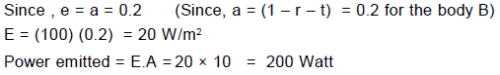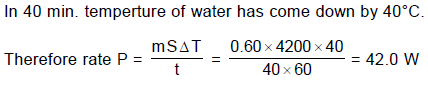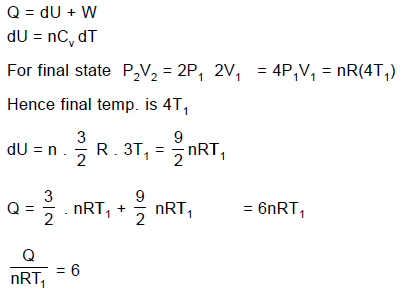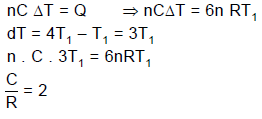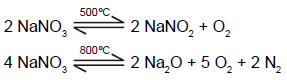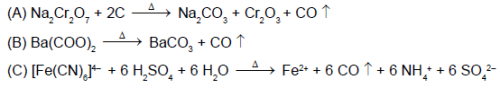JEE Advanced Test- 11 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Test- 11
A piston can freely move inside a horizontal cylinder closed from both ends. Initially, the piston separates the inside space of the cylinder into two equal parts each of volume V0 , in which an ideal gas is contained under the same pressure p0 and at the same temperature. What work has to be performed in order to increase isothermally the volume of one part of gas 2 times compared to that of the other by slowly moving the piston ?
A uniform pressure P is exerted by an external agent on all sides of a solid cube at temperature t ºC. By what amount should the temperature of the cube be raised in order to bring its volume back to its original volume before the pressure was applied if the bulk modulus is B and co-efficient of volumetric expansion is  ?
?
Two rods of same dimensions, but made of different materials are joined end to end with their free ends being maintained at 100ºC and 0ºC respectively. The temperature of the junction is 70ºC. Then the temperature of the junction if the rods are interchanged will be equal to :
Assume a sample of an ideal gas in a vessel. Where velocity of molecules are between 2 m/sec to 5 m/sec and velocity of molecules (v) and number of molecules (n) are related as n = 7v – v2 – 10. The most probable velocity in sample is. Where v is measured in m/sec.
If specific heat capacity of a substance in solid and liquid state is proportional to temperature of the substance, then if heat is supplied to the solid initially at – 20°C (having melting point 0°C) at constant rate. Then the temperature dependence of substance with time will be best represented by :
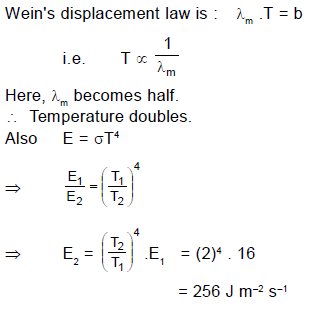
A hot black body emits the energy at the rate of 16 J m–2 s–1 and its most intense radiation corresponds to 20,000 Å. When the temperature of this body is further increased and its most intense radiation corresponds to 10,000 Å, then the energy radiated in Jm–2 s–1 will be :
Two identical rectangular rods of metal are welded end to end in series between temperature 0°C and 100°C and 10 J of heat is conducted (in steady state process) through the rod in 2.00 min. If 5 such rods are taken and joined as shown in figure maintaining the same temperature difference between A and B, then the time in which 20 J heat will flow through the rods is :
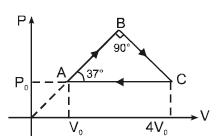
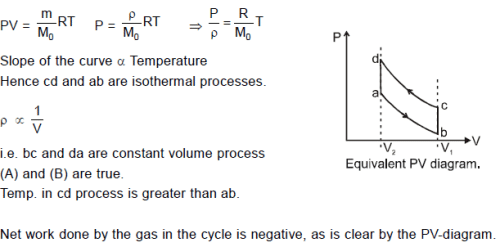
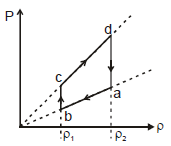
An ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process abcda which is shown by pressure- density curve.
The emissive power of a black body at T = 300 K is 100 Watt/m2. Consider a body B of area A = 10 m2 coefficient of reflectivity r = 0.3 and coefficient of transmission t = 0.5 and at temperature 300 K. Then which of the following is correct :
The ends of a rod of uniform thermal conductivity are maintained at different (constant) temperatures. After the steady state is achieved :
Number of collisions of molecules of a gas on the wall of a container per m2 will :
Statement -1 : It is possible for both the pressure and volume of a monoatomic ideal gas of a given amount to change simultaneously without causing the internal energy of the gas to change.
Statement-2: The internal energy of an ideal gas of a given amount remains constant if temperature does not change. It is possible to have a process in which pressure and volume are changed such that temperature remains constant.
Statement-1 : Molar heat capacity of an ideal monoatomic gas at constant volume is a constant at all temperatures.
Statement-2 : As the temperature of an monoatomic ideal gas is increased, number of degrees of freedom of gas molecules remains constant.
Statement-1 : Burns sustained from steam at 100ºC are usually more serious than those sustained by boiling water (at 100ºC)
Statement-2 : To convert 1gm of water at 100ºC to 1 gm of steam at 100ºC, 540 calories of heat is to be supplied. Hence 1gm of steam at 100ºC has more heat content than 1 gm of water at 100ºC
Statement-1 : If the absolute temperature of a gas is doubled, the final rms-velocity of the gas particles becomes √2 times the initial value.
Statement-2: The average translational kinetic energy of molecules in a gas is equal to both and 3/2KT.( where vrms, k and T have usual meanings)
A 0.60 kg sample of water and a sample of ice are placed in two compartments A and B that are separated by a conducting wall, in a thermally insulated container. The rate of heat transfer from the water to the ice through the conducting wall is constant P, until thermal equilibrium is reached. The temperature T of the liquid water and the ice are given in graph as functions of time t. Temperature of the each compartment remain homogeneous during whole heat transfer process.
Given specific heat of ice = 2100 J/kg-K
Given specific heat of water = 4200 J/kg-K
Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.3 × 105 J/kg
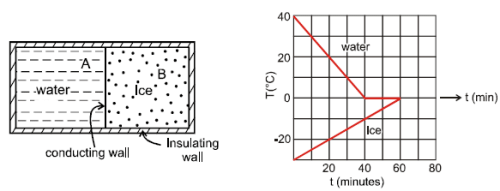
Q. The value of rate P is
A 0.60 kg sample of water and a sample of ice are placed in two compartments A and B that are separated by a conducting wall, in a thermally insulated container. The rate of heat transfer from the water to the ice through the conducting wall is constant P, until thermal equilibrium is reached. The temperature T of the liquid water and the ice are given in graph as functions of time t. Temperature of the each compartment remain homogeneous during whole heat transfer process.
Given specific heat of ice = 2100 J/kg-K
Given specific heat of water = 4200 J/kg-K
Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.3 × 105 J/kg

Q. The initial mass of the ice in the container is equal to
A 0.60 kg sample of water and a sample of ice are placed in two compartments A and B that are separated by a conducting wall, in a thermally insulated container. The rate of heat transfer from the water to the ice through the conducting wall is constant P, until thermal equilibrium is reached. The temperature T of the liquid water and the ice are given in graph as functions of time t. Temperature of the each compartment remain homogeneous during whole heat transfer process.
Given specific heat of ice = 2100 J/kg-K
Given specific heat of water = 4200 J/kg-K
Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.3 × 105 J/kg

Q. The mass of the ice formed due to conversion from the water till thermal equilibrium is reached, is equal to
A quantity of an ideal monoatomic gas consists of n moles initially at temperature T1. The pressure and volume both are then slowly doubled in such a manner so as to trace out a straight line on a P-V diagram.
Q. For this process, the ratio is equal to (where W is work done by the gas) :
A quantity of an ideal monoatomic gas consists of n moles initially at temperature T1. The pressure and volume both are then slowly doubled in such a manner so as to trace out a straight line on a P-V diagram.
Q. For the same process, the ratio is equal to (where Q is heat supplied to the gas) :
A quantity of an ideal monoatomic gas consists of n moles initially at temperature T1. The pressure and volume both are then slowly doubled in such a manner so as to trace out a straight line on a P-V diagram.
Q. If C is defined as the average molar specific heat for the process then C/R has value
A sample of gas goes from state A to state B in four different manners, as shown by the graphs. Let W be the work done by the gas and DU be change in internal energy along the path AB. Correctly match the graphs with the statements provided.
Column I
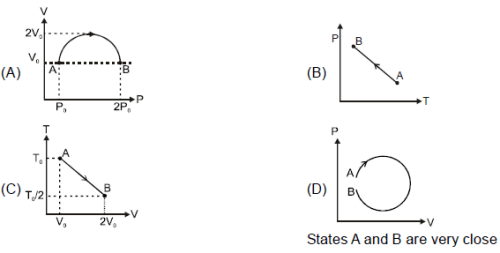
Column II
(p) W is positive (q) ΔU is negative (r) W is negative (s) ΔU is positive (t) heat rejected ΔQ < 0
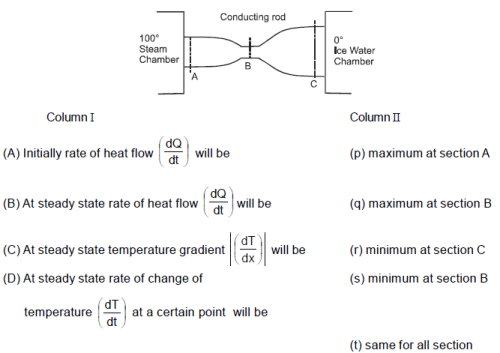
A copper rod (initially at room temperature 20°C) of non-uniform cross section is placed between a steam chamber at 100°C and ice-water chamber at 0°C.
Which of the following orders is correct for the size ?
(1) Mg2+ < Na+ < F– < Al (2) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Li+ < K+ (3) Fe4+ < Fe3+ < Fe2+ < Fe (4) Mg > Al > Si > P
Which reactions involves a change in the electron–pair geometry for the under lined atoms ?
Anhydrous AlCl3 is covalent. From the data given below
Lattice Energy = 5137 KJ/mol.
ΔH hydration for Al3+ = – 4665 KJ/mol
ΔH hydration for Cl– = – 381 KJ/mol
Identify the correct statement.
In which of the following molecules / ions are all the bond angles not equal ?
In which of the following reaction carbon monoxide is obtained as one of the products ?