JEE Main Practice Test- 3 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Practice Test- 3
A point object moves on a circular path such that distance covered by it is given by function 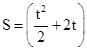 Meter (t in second). The ratio of the magnitude of acceleration at t = 2 sec. And t = 5 sec. is 1: 2 then radius of the circle is
Meter (t in second). The ratio of the magnitude of acceleration at t = 2 sec. And t = 5 sec. is 1: 2 then radius of the circle is
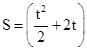 Meter (t in second). The ratio of the magnitude of acceleration at t = 2 sec. And t = 5 sec. is 1: 2 then radius of the circle is
Meter (t in second). The ratio of the magnitude of acceleration at t = 2 sec. And t = 5 sec. is 1: 2 then radius of the circle isAt time t = 0, a 2 kg particle has position vector 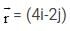 m relative to the origin. Its velocity is given by
m relative to the origin. Its velocity is given by 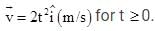 The torque acting on the particle about the origin at t = 2s, is :
The torque acting on the particle about the origin at t = 2s, is :
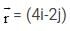 m relative to the origin. Its velocity is given by
m relative to the origin. Its velocity is given by 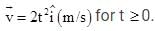 The torque acting on the particle about the origin at t = 2s, is :
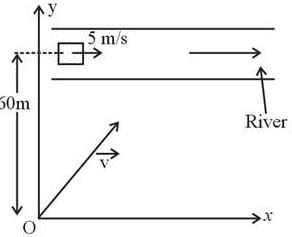
The torque acting on the particle about the origin at t = 2s, is :A box is floating in the river of speed 5m/s. The position of the block is shown in the figure at t=0. A stone is thrown from point O at time t = 0 with a velocity 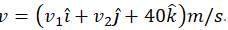 Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
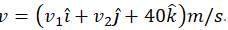 Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from the mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s . The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant
A uniform electric field E is present horizontally along the paper throughout the region and uniform magnetic field B0 is present horizontally (perpendicular to plane of paper in inward direction) right to the line AB. A charge particle having charge q and mass m is projected vertically upward and it crosses the line AB after time t0. Find the speed of projection if particle moves with constant velocity after t0 . (Given qE = mg)
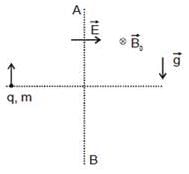
Two blocks P and Q are connected by a light inextensible string passing over a smooth pulley fixed as shown in the Figure. The coefficient of friction of blocks P and Q to the table is μ = 0.3; the mass of the block Q is 20 kg. The mass of the block P for the block just to slip is
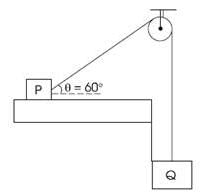
A monochromatic light source of wavelength λ is placed at S. Three slits S1, S2 and S3 are equidistant from the source S and the point P on the screen. S1P-S2P=λ/6 and S1P-S3P = 2λ/3. If I be the intensity at P when only one slit is open, the intensity at P when all the three slits are open is
On a hypothetical planet satellite can only revolve in quantized energy level i.e. magnitude of energy of a satellite is integer multiple of a fixed energy. If two successive orbit have radius R and 3R/2 what could be maximum radius of satellite
In a transistor amplifier when the signal changes by 2 V, the base current changes by 150 μA and collector current by 15 mA. If collector load  Find the voltage gain of amplifier.
Find the voltage gain of amplifier.
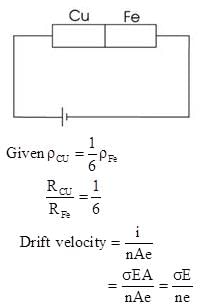
Copper and iron wires of same length and diameter are in series and connected across a battery. The resistivity of copper is about one-sixth of the iron. If E1 and E2 are the electric fields in the copper and iron wires respectively, then which of the following is correct?
E, m, p and G denote energy, mass, angular momentum and gravitational constant. Then 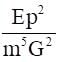 has the dimensions of
has the dimensions of
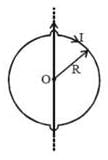
A circular conducting loop of radius R carries a current I. Another straight infinite conductor carrying current I passes through the diameter of this loop as shown in the figure. The magnitude of force exerted by the straight conductor on the loop is :-
Find the intensity of electromagnetic wave if the electric field in electromagnetic wave is 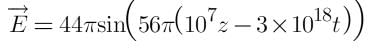
The displacement of a particle is represented by the equation y= 40cos3 ωt. The motion is
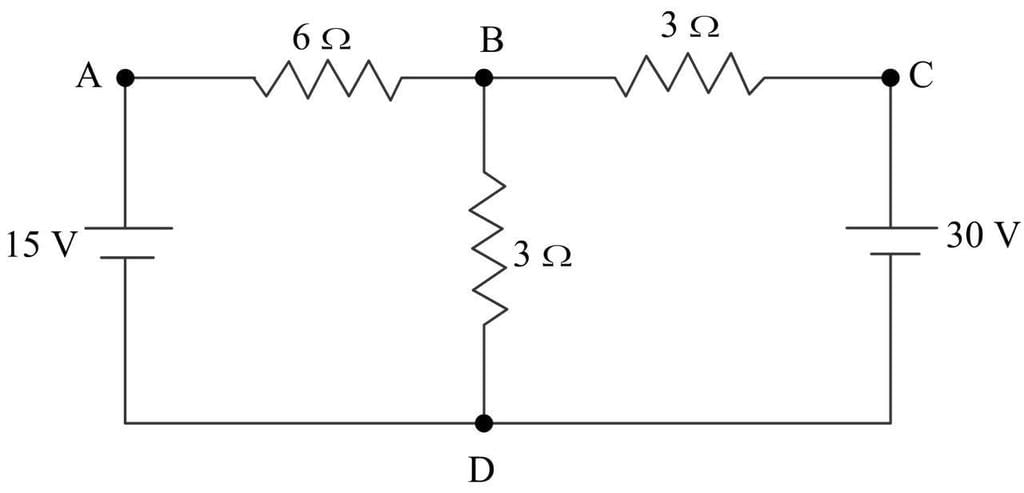
In the circuit shown in figure find the current in branch BD of the circuit :
A particle undergoes from position O(0, 0, 0) to A (a, 2a, 0) via path 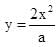 in x-y plane under the action of a force which varies with particle’s (x, y, z) coordinate as
in x-y plane under the action of a force which varies with particle’s (x, y, z) coordinate as 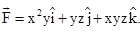 Work done by the force
Work done by the force 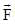 is: (all symbols have their usual meaning and they are in SI unit.)
is: (all symbols have their usual meaning and they are in SI unit.)
One million small identical drops of water, all charged to the same potential, are combined to form a single large drop. If E is the sum of the electrostatic energy of each small drop, the combined energy of the large drop is
An unknown particle 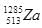 originally at rest emits 5 alpha particles with speed 11385 km/h. Find the recoil speed of the unknown daughter nucleus.
originally at rest emits 5 alpha particles with speed 11385 km/h. Find the recoil speed of the unknown daughter nucleus.
The number of AM broadcast stations that can be accommodated at a 150 kHz band width, if the highest frequency modulating carrier is 5 kHz is
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the stopping potential for photoelectric current is 3V0 and when the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is V0. The threshold wavelength of this surface for photoelectric effect is Kλ. Calculate the value of K.
A monochromatic beam of electrons accelerated by a potential difference V falls normally on the plane containing two narrow slits separated by a distance d. The interference pattern is observed on a screen parallel to the plane of the slits and at a distance of D from the slits. Fringe width is found to be w1w1. When electron beam is accelerated by the potential difference 4V the fringe width becomes ω2. Find the ratio 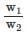 (Given d << D)
(Given d << D)
A target element A is bombarded with electrons and the wavelengths of the characteristic spectrum and measured. A second characteristic spectrum is also obtained, because of an impurity in the target. The wavelength of the Ka lines are 196 pm (element A) and 169 pm (impurity). If the atomic number of impurity is z = (10 x – 1). Find the value of x. (atomic number of element A is 27).
What is the minimum height (in 102 m) of a brick column of uniform cross section for which column breaks due to its own weight?
[Patmospheric = 100 kPa, ρ = 1.8 × 103kg/m3. Breaking stress σ = 3.7 M Pa]
A sound source emits frequency of 175 Hz when moving towards a rigid wall with speed 5 m/s and observer is moving away from wall with same speed 5 m/s. Both source and observer moves on a straight line which is perpendicular to the wall. The number of beats per second heard by the observer will be [Speed of sound = 355 m/s] Source is in between observer and wall.
If P,Q,R and S are elements of 3rd period of p–block in modern periodic table and among these one element is metal and rest are non-metal and their order of electronegativity is also given as
P < Q < R < S .Then in which of the following release of H+ is relatively easier.
In which of the following ‘meta form’ of ‘-ic acid’ is not possible.
If mechanism of reaction is
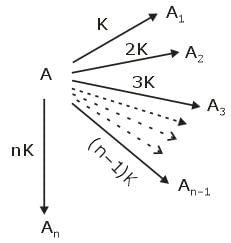
Where k is rate constant then, what is 
which of the following species undergo non–redox thermal decomposition reaction on heating


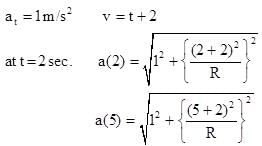
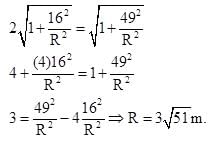
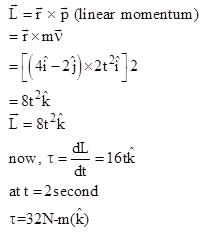

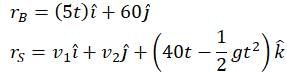
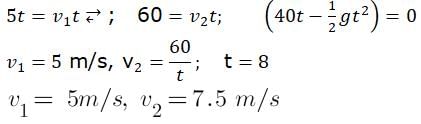
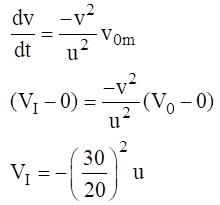
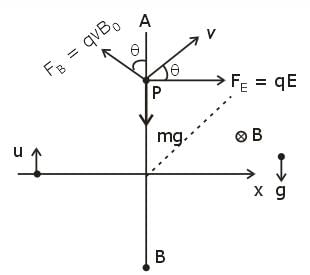
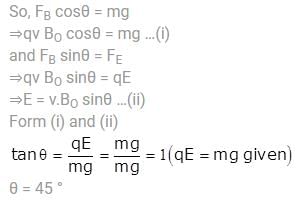
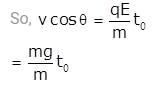
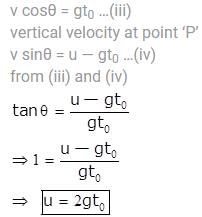
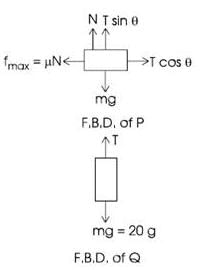
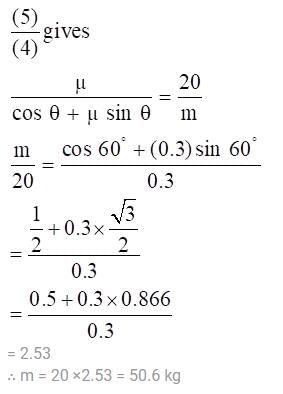
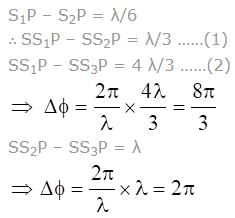
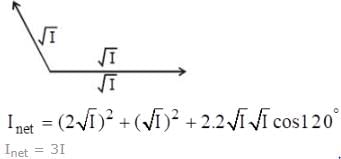
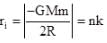
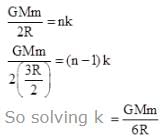
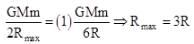
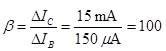
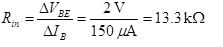
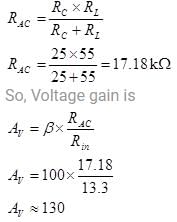
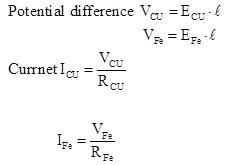
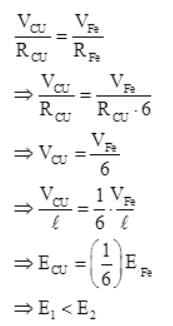
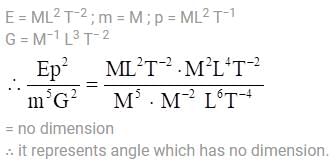
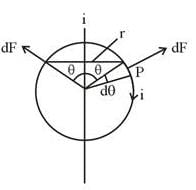
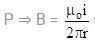 (where r = R sinθ i.e. perpendicular distance of ‘P’ from line)
(where r = R sinθ i.e. perpendicular distance of ‘P’ from line)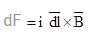
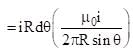
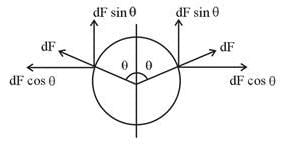
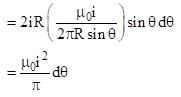
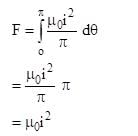
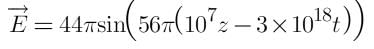 Intensity of Electromagnetic wave in terms of maximum electric field is
Intensity of Electromagnetic wave in terms of maximum electric field is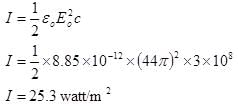



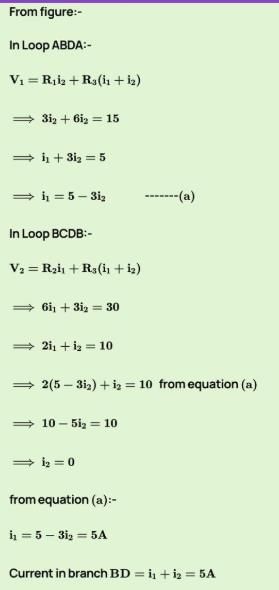
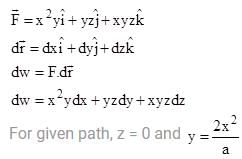
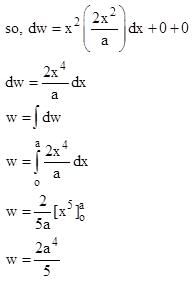
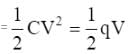
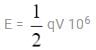
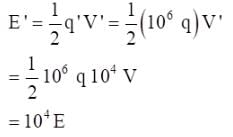
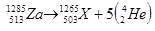
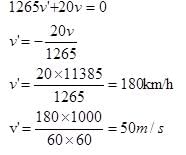
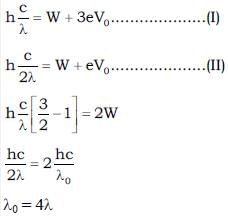
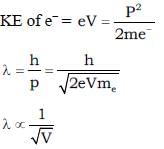
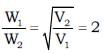
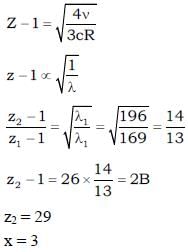
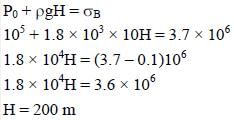
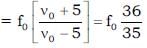
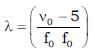
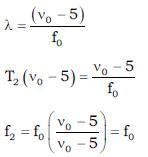
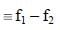
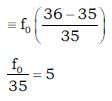
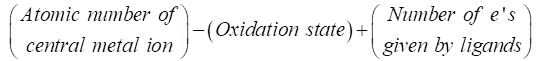 A. [Co(CO)4]–
A. [Co(CO)4]–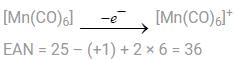
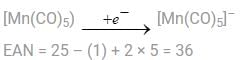
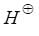
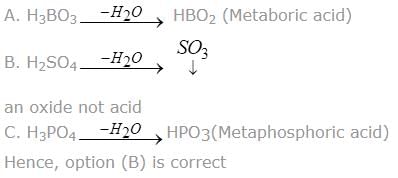
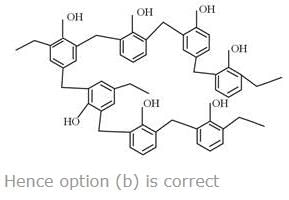

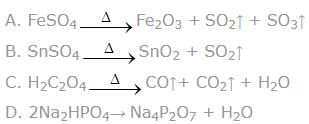 Non–redox decomposition implies no change in oxidation number
Non–redox decomposition implies no change in oxidation number










