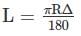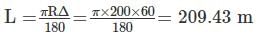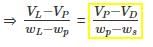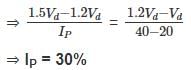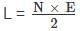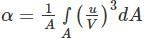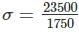JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 5 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test Series 2025 - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 5
An accurate estimate is prepared in detail item-wise by:
The type of Bitumen for which the viscosity has been decreased by a volatile dilutant is known as
A circular curve has a 200m radius and 60 deflection angle. What is its length of curve?
For a clay, SL = 20%, PL = 40%. The total volume at PL & LL was 1.20 Vd and 1.50 Vd respectively wherein Vd = dry volume. Then, the plasticity Index Pl of the soil is
Slenderness ratio of an RC column is the ratio of its length to its
If a transition curve is introduced between a straight and a curve such that a super elevation of 15 cm is introduced over a curve and if the rate of super elevation is 1 in 500, then length (m) of the transition curve will be
In a UU Triaxial compression test on a ϕ = 0 soil, failure was observed at a deviatoric stress of 60 kN/m2 under a confining stress 50 kN/m2 of the confining stress is increased to 100 kN/m2, the deviatoric stress at failure is
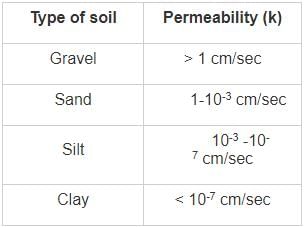
Stokes law is valid only If the size of the particle is
The design procedure accepting Hooke’s law is known as ________.
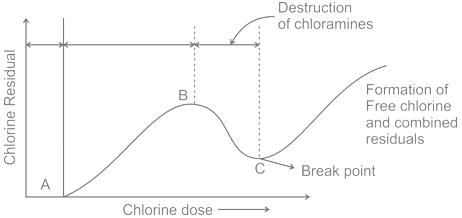
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?
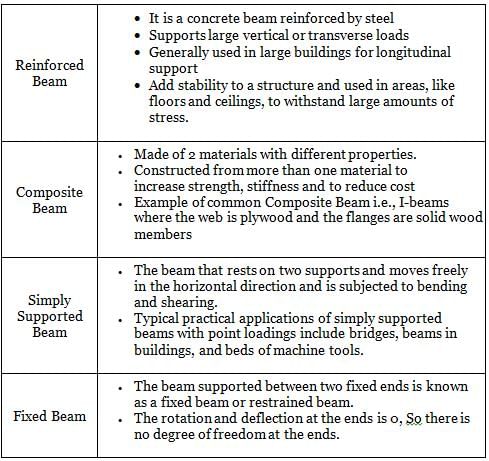
Match the following types of beams with their respective functionalities.
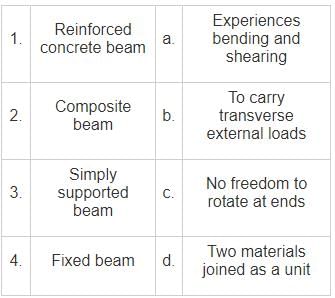
Which of the following angles can be set with the help of French cross-staff ?
Which of the following parameters is not a part of typical construction project lifecycle till commissioning?
The energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe is _______.
The process of maintaining or improving the performance of a soil as a constructional material, usually by the use of admixtures, is known as:
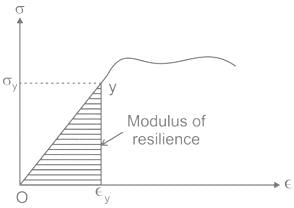
Which one of the following is the capacity of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically and then, upon unloading, to have this energy recovered?
A mild steel flat 175 mm wide, 10 mm thick and 4.5 m long and is carrying an axial load of 23.5 kN. Determine stress developed in this case.
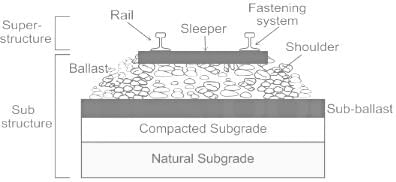
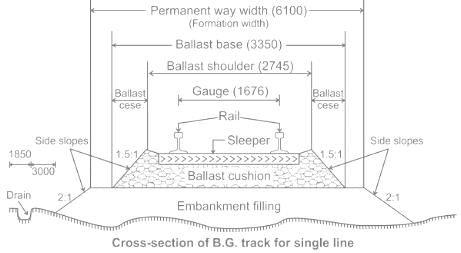
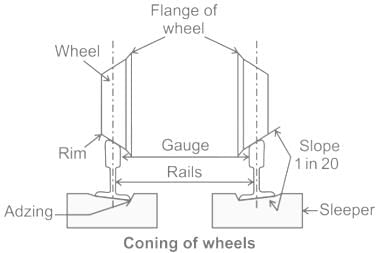
The longitudinal movement of the rails in a track is technically known as
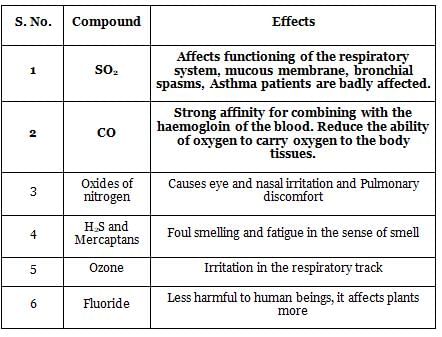
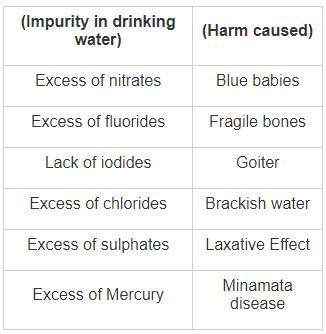
Column I lists various impurities in drinking water and Column II lists effects/ diseases caused by these impurities.
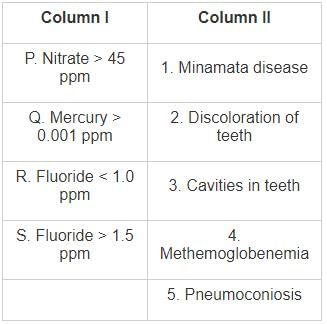
The correct match of the column I with column II is
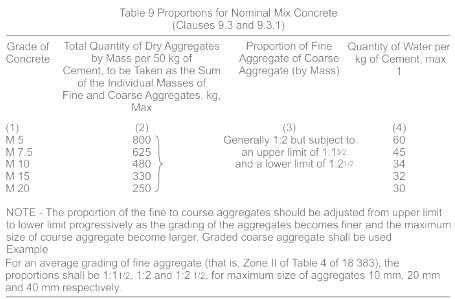
If strictly comparable results are to be obtained in compaction factor test, then test is to be carried out at a constant time interval of