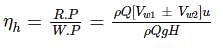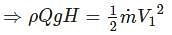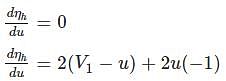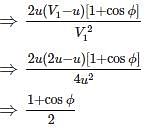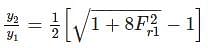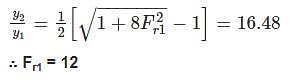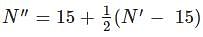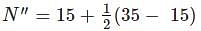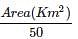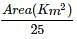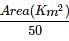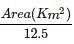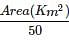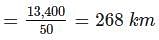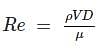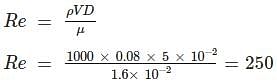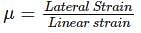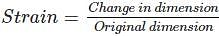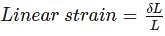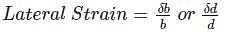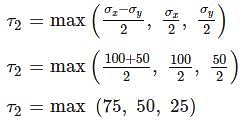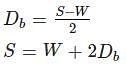JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 6 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test Series 2025 - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 6
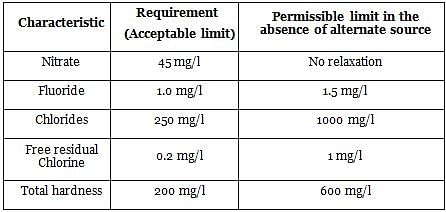
As per IS : 10500-2012, for drinking water, in the absence of alternate source of water, the permissible limit for fluorides is
In triangulation, the best shape of the triangle is______ triangle with base angle equal to _____.
If there are n number of events in the networks diagram then the number of dual role event will be
Fish plates are used in rail joints to :
- Maintain the continuity of rails
- Provide for any expansion or contraction
- Transfer the load to the ballast
- Maintain correct alignment
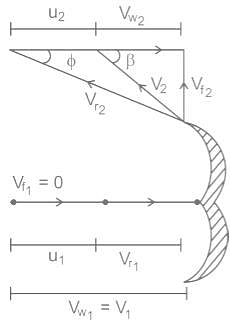
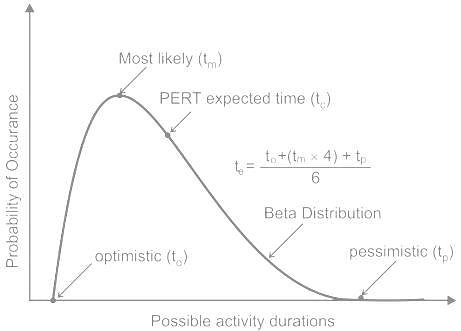
If ‘ϕ’ is the angle of blade tip at outlet, then maximum hydraulic efficiency of an impulse turbine is
The minimum depth of foundation for the load bearing wall of a building is restricted to
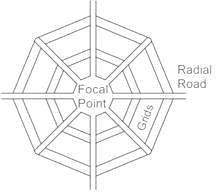
The Nagpur Road Plan which is the First 20-year Road Development Plan assumes which of the following patterns of the road network?
If the sequent depth ratio of a hydraulic jump in a rectangular channel is 16.48, the Froude number at the beginning of the jump is
The observed N value from a standard penetration test conducted on a saturated sandy soil stratum is 35. The corrected N value for dilatancy can be estimated as:
The road length of National Highway by Third Road Plan Formulae, in a certain district in India having its area as 13,400 sq.km will be
The following Four statements (S1, S2, S3, S4) in connection with soil behaviour are given.
S1: Consolidation is a function of total stress
S2: Permeability of Coarse grained soil is inversely proportional to the specific surface at a given porosity.
S3: For a fully saturated soil the pore pressure parameter is equal to zero.
S4 : Terzaghi's theory of consolidation considers only primary consolidation.
Which of the above statement(s) is /are incorrect?
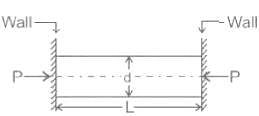
If the bar shown in the figure is heated, _______ stresses would be developed in it.
In a pipe of diameter 5 cm, water is flowing at a rate of 8 cm/sec. If the dynamic viscosity of water is 1.6 × 10-2 Pa-s, what type of flow is present?
As per IS-456: 2000, Side face reinforcemnet shall be provided along the two faces of a reinforced concrete beam, when the depth of the web exceeds
If 'L' is the length of the cantilever slab measured parallel to the fixed edge, the effective width of the cantilever slab shall not exceed: (For slabs carrying the concentrated load)
Consider the following statements regarding Bulk modulus of Elasticity:
I. It is a constant.
II. It varies with temperature.
III. It varies with pressure.
Which of the following is correct?
The ratio of lateral strain to linear strain is known as
Calculate the number of sleepers required for constructing a railway track of 640 m long broad gauge section when the sleeper density is M + 5.
The minimum 28-day cube compressive strength prescribed in the Indian standard code IS 1343 for pre-tensioned member is_____.
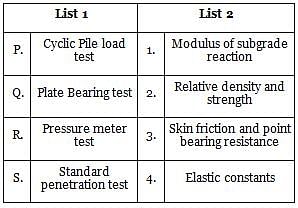
Match the items in List 1 (Name of field exploration) with those in List 2 (soil properties) and select the correct option.
Use codes for matching
A scaled drawing of the proposed construction site showing all the relevant features such as entry and exit points to the site, storage area for materials, toilets, workers quarters, etc. is called
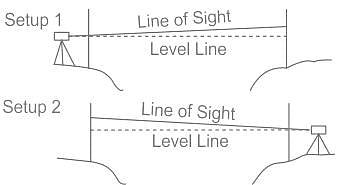
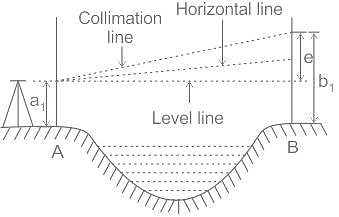
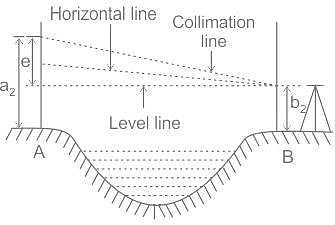
Which type of levelling is used to measure across large gaps such as rivers or valleys?
If a point in a strained material is subjected to two mutually perpendicular stresses, σx = 100 MPa (T) and σy = 50 MPa (C), then what will be the magnitude of maximum shear stress?
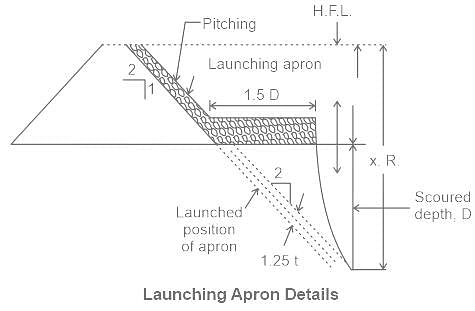
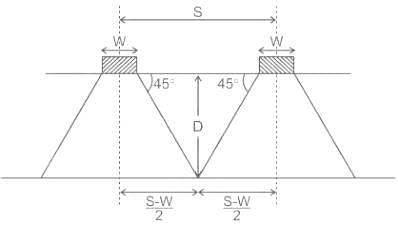
If D is the depth of scour below original bed, then the width of launching apron is generally taken as
Sleeper spacing is the width of the sleeper + ______.
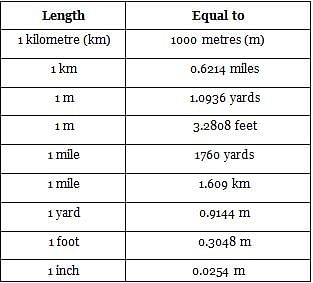
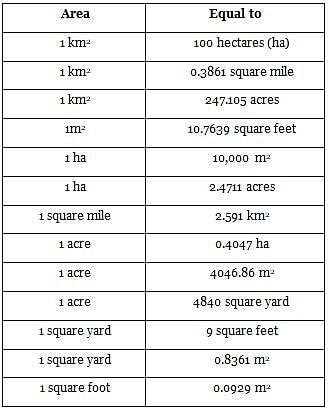
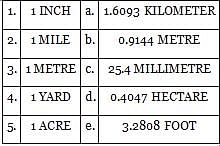
Match the following units with their respective conversions.
A detailed estimate that is prepared when there is a requirement of additional work during the progress of the original work is known as: