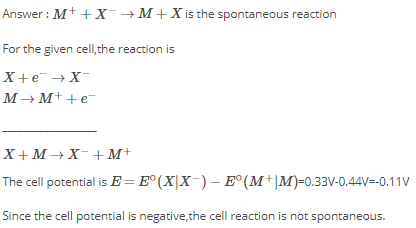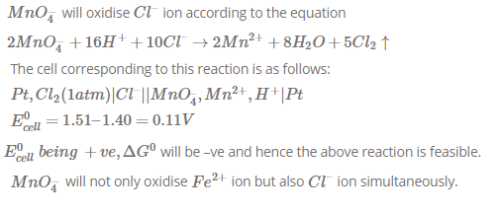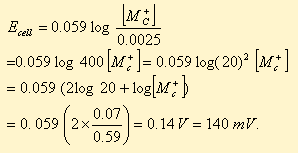MCQ (Previous Year Questions) - Electrochemistry (Level 2) - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - MCQ (Previous Year Questions) - Electrochemistry (Level 2)
A gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y and 1M Z at 25ºC. If the reduction potential of Z > Y> X. then [JEE-1999]
For the electrochemical cell, M|M+||X-|X, Eº(M+/M) = 0.44 V and Eº(X/X-)= 0.33V. From this data, one can deduce that [JEE-2000]
The reaction,
3ClO- (aq) → ClO3- (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) [JEE-2001]
is an example of
The correct order of equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of LiCl, NaCl and KCl is [JEE-2001]
Saturated solution of KNO3 is used to make salt bridge because [JEE-2001]
Standard electrode potential data are useful for understanding the suitablity of an oxidant in a redox titration. Some half cell reactions and their standard potentials are given below. [JEE-2002]
MnO4-(aq) + 8H+(aq) + 5e- → Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l); Eº = 1.51 V
Cr2O72- (aq) +14H+(aq) + 6e- → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l); Eº = 1.38 V
Fe3+(aq) + e- → Fe2+(aq) ; Eº = 0.77 V
Cl2(g) + 2e- → 2Cl-(aq) ; Eº = 1.40 V
Identify the only incorrect statment regarding quantitative estimation of aqueous Fe(NO3)2
In the electrolytic cell, flow of electrons is from [JEE-2003]
Zn|Zn2+(a=0.1M)||Fe2+(a=0.01 M)|Fe. the emf of the above cell is 0.2905 V Equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is [JEE-2004]
The half cell reactions for rusting of iron are: [JEE-2005]
Tollen's reagent is used for the detection of aldehyde when a solution of AgNO3 is added to glucose with NH4OH then gluconic acid is formed.
Ag+ + e- → Ag ; Eºred = 0.8 V
C6H12O6 + H2O → C6H12O7 (Gluconic acid) + 2H+ + 2e- ; Eºred = –0.05 V
Ag(NH3)2++ e- → Ag(s) + 2NH3 ; Eº = –0.337 V
[Use 2.303 × = 0.0592 and
= 38.92 at 298 K ] [JEE-2006]
2Ag+ + C6H12O6 + H2O → 2Ag(s) + C6H12O7 + 2H+
Find ln K of this reaction
Redox reactions play a pivoted role in chemistry and biology. The values of standard redox potential (Eº) of two half-cell reactions decide which way the reaction is expected to proceed. A simple example is a Daniel cell in which zinc goes into solution and copper gets deposited. Given below are a set of half-cell reactions (acidic medium) along with their Eº(V with respect to normal hydrogen electrode) values. Using this data obtain the correct explanations to Questions [JEE-2007]
I2 + 2e- → 2I- Eº = 0.54
Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl- Eº = 1.36
Mn3+ + e- → Mn2+ Eº = 1.50
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ Eº = 0.77
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O Eº = 1.23
While Fe3+ is stable, Mn3+ is not stable in acid solution because
Electrolysis of dilute aqueous NaCl solution was carried out by passing 10 milli ampere current. The time required to liberate 0.01 mol of H2 gas at the cathode is (1 Faraday = 96500 C mol_1) [JEE-2008]
Tollen's reagent is used for the detection of aldehyde when a solution of AgNO3 is added to glucose with NH4OH then gluconic acid is formed.
Ag+ + e- – Ag ; Eºred = 0.8 V
C6H12O6 + H2O → C6H12O7 (Gluconic acid) + 2H+ + 2e- ; Eºred = –0.05 V
Ag(NH3)2++ e- → Ag(s) + 2NH3 ; Eº = –0.337 V
[Use 2.303 × = 0.0592 and
= 38.92 at 298 K ] [JEE-2006]
When ammonia is aded to the solution, pH is raised to 11. Which half - cell reaction is affected by pH and by how much?
For the reaction of NO3- ion in an aqueous solution, Eº is +0.96 V. Values of Eº for some metal ions are
given below [JEE-2009]
The pair(s) of metal that is(are) oxidised by NO3- in aqueous solution is(are) :
Tollen's reagent is used for the detection of aldehyde when a solution of AgNO3 is added to glucose with NH4OH then gluconic acid is formed.
Ag+ + e- → Ag ; Eºred = 0.8 V
C6H12O6 + H2O → C6H12O7 (Gluconic acid) + 2H+ + 2e- ; Eºred = –0.05 V
Ag(NH3)2++ e- → Ag(s) + 2NH3 ; Eº = –0.337 V
[Use 2.303 × = 0.0592 and
= 38.92 at 298 K ] [JEE-2006]
Ammonia is always is added in this reaction. Which of the following must be incorrect ?
Among the following the intensive property is (Properties are )
The concentration of potassium ions inside a biological cell is at least twenty times higher than the outside. The resulting potential difference across the cell is important in several processes such as transmission of nerve impulses and maintaining the ion balance. A simple model for such a concentration cell involving a metal M is:
M(s)|M+ (aq; 0.05 molar)| |M+(aq; 1 molar) | M(s)
For the above electrolytic cell the magnitude of the cell potential |Ecell| = 70 mV.
For the above cell
Chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. a large number of atoms/molecules (approximately 6.023×1023) are present in a few grams of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large numbers conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. This concept has implications in diverse areas such as analytical chemistry, biochhemistry, electrochemistry and radiochemistry. The following example illustrates a typical case, involving chemical/electrochemical reaction, which requires a clear understanding of the mole concept.
A 4.0 molar aqueous solution NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrodes (atomic mass : Na = 23, Hg = 200, 1 faraday = 96500 coulombs) [JEE-2007]
The total number of moles of chlorine gas evolved is
In the 0.05 molar solution of M+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar M+ solution, then the magnitude of the
cell potential would be
Chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. a large number of atoms/molecules (approximately 6.023×1023) are present in a few grams of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large numbers conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. This concept has implications in diverse areas such as analytical chemistry, biochhemistry, electrochemistry and radiochemistry. The following example illustrates a typical case, involving chemical/electrochemical reaction, which requires a clear understanding of the mole concept.
A 4.0 molar aqueous solution NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrodes (atomic mass : Na = 23,Hg = 200, 1 faraday = 96500 coulombs) [JEE-2007]
If the cathode is a Hg electrode, the maximum weight (g) of amalgam formed from this solution is
Consider the following cell reaction. [JEE-2011]
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) → 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) Eº = 1.67 V
At [Fe2+] = 10–3 M, P(O2) = 0.1 atm and pH = 3, the cell potential at 25º C is :
Chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. a large number of atoms/molecules (approximately 6.023×1023) are present in a few grams of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large numbers conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. This concept has implications in diverse areas such as analytical chemistry, biochhemistry, electrochemistry and radiochemistry. The following example illustrates a typical case, involving chemical/electrochemical reaction, which requires a clear understanding of the mole concept.
A 4.0 molar aqueous solution NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrodes (atomic mass : Na = 23, Hg = 200, 1 faraday = 96500 coulombs) [JEE-2007]
The total charge (coulombs) required for complete electrolysis is
The electrochemical cell shown below is a concentration cell.
M | M2+ (saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt, Mx2) || M2+ (0.001 mol dm–3) | M The emf of
the cell depends on the difference in concentrations of M2+ ions at the two electrodes. The emf of the
cell at 298 K is 0.059 V. [IIT-2012]
The solubility product (Ksp; mol3 dm–9) of MX2 at 298 K based on the information available for the given
concentration cell is (take 2.303 × R × 298 /F = 0.059 V)
Redox reactions play a pivoted role in chemistry and biology. The values of standard redox potential (Eº) of two half-cell reactions decide which way the reaction is expected to proceed. A simple example is a Daniel cell in which zinc goes into solution and copper gets deposited. Given below are a set of half-cell reactions (acidic medium) along with their Eº(V with respect to normal hydrogen electrode) values. Using this data obtain the correct explanations to Questions [JEE-2007]
I2 + 2e- → 2I- Eº = 0.54
Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl- Eº = 1.36
Mn3+ + e- → Mn2+ Eº = 1.50
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ Eº = 0.77
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O Eº = 1.23
Among the following, identify the correct statement.
The electrochemical cell shown below is a concentration cell.
M | M2+ (saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt, Mx2) || M2+ (0.001 mol dm–3) | M The emf of
the cell depends on the difference in concentrations of M2+ ions at the two electrodes. The emf of the
cell at 298 K is 0.059 V.
The value of ΔG (kJ mol–1) for the given cell is (take 1 F = 96500 C mol–1)