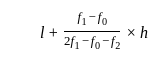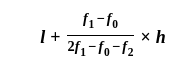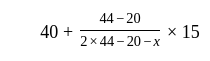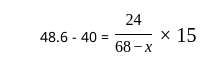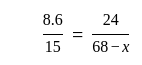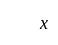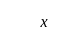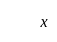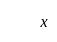MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Commerce) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test MH SET Mock Test Series 2025 - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Commerce)
Which one of the following is not the correct property of normal distribution?
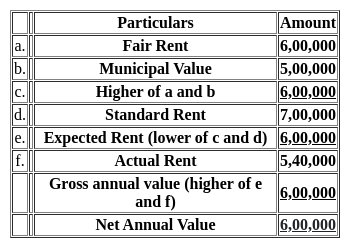
Which one of the following is the Net Annual Value (NAV) of house for the given details?
Municipal value = Rs. 5,00,000
Fair Rental value = Rs. 6,00,000
Standard Rent = Rs. 7,00,000
Actual Rent (Annual Rent) = Rs. 5,40,000
Municipal Tax = Rs. 15,000 (due but not paid)
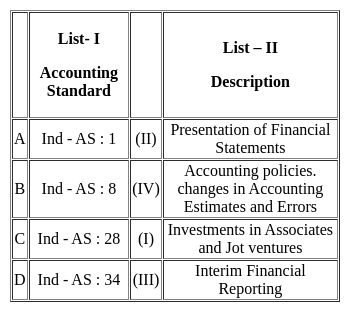
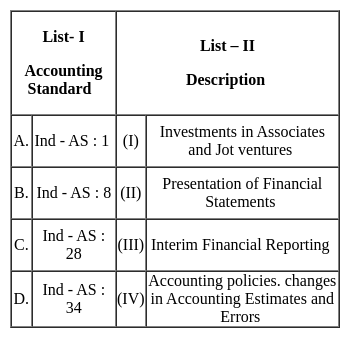
Match List I with List II:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below -
Assertion (A): Weighted average cost of capital should be used as a hurdle rate for accepting or rejecting a capital budgeting proposal.
Reason (R): It is because by financing in the proportions specified and accepting the project, yielding more than the weighted average required return, the firm is able to increase the market price of its stock.
Breach of contract can be of ____________ breach.
Deductions under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act, 1961 are allowed after excluding which of the following incomes from the gross total income?
(i) Income from house property
(ii) Long-term capital gains
(iii) Short-term capital gains under Section 111A
(iv) Income from lotteries
The Regression Coefficient is independent of the change of
(A) Scale only
(B) Origin only
(C) Both Scale and Origin
(D) Neither Scale nor Origin
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The sponsor of a mutual fund is similar to which of the following?
The most appropriate concept to be adopted for physical distribution of goods is:
When goods in the domestic market are sold at a high price and in the foreign market at a low price, it is a situation of:
The first Indian to suggest a model for human resource valuation and accounting is:
Assertion (A): There is no difference between futures and forwards excepting that the former requires a margin.
Reason (R): Futures are standardised, marked to market and traded in organised exchanges. Forwards are tailor-made instruments and traded on the OTC market.
Codes:
Which of the following is not the example of only upward communication?
Match the items of List I with the items of List II and choose the correct answer from the code given below.
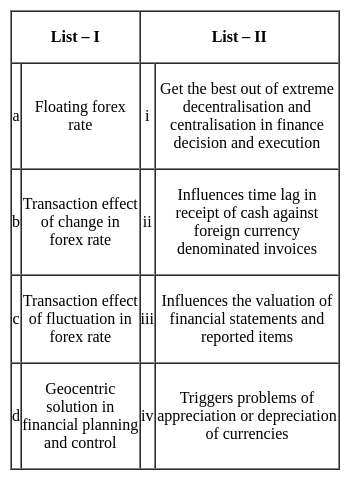
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) are the Financial Intermediaries engaged primarily in the business of:
i. Accepting Deposits
ii. Lending loans and advances
iii. Leasing
iv. Hire purchasing
The main objective of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is to:
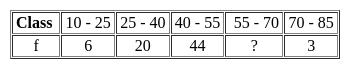
If the mode of the above distribution is 48.6, then the missing frequency will be
The explicit cost is the ________, which equates the present value of cash inflows with the present value of cash outflows.
Which of the following is not a disadvantage of using mean?
|
60 tests
|