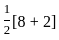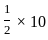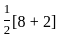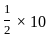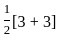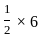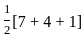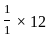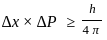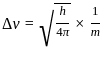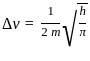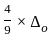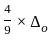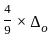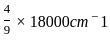MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 3 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 3
सटीक मुहावरा चुनकर, निम्नलिखित वाक्य की पूर्ति कीजिये -
'मुझे ________ नहीं आता, जो भी काम करता हूँ, पुख्ता करता हूँ।'
'मुझे ________ नहीं आता, जो भी काम करता हूँ, पुख्ता करता हूँ।'
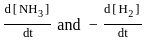 is:
is:
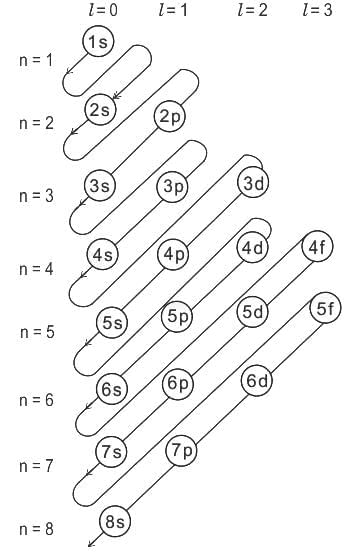
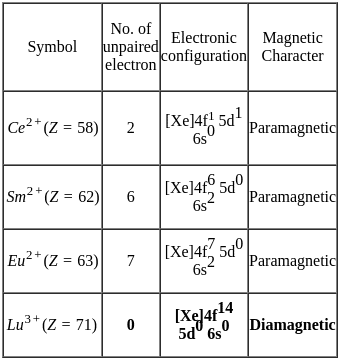
Which of the following options does not represent ground state electronic configuration of an atom?
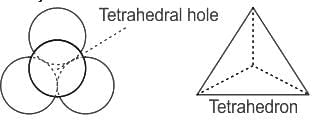
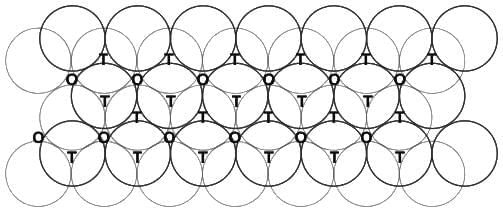
What is the total number of tetrahedral voids in FCC structure?
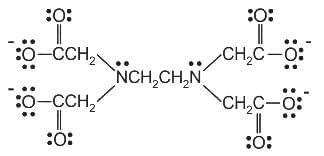
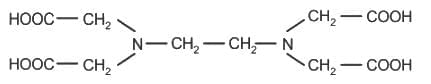
The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is
A first order reaction has a specific reaction rate of 10-2 sec-1. How much time will it take for 20g of the reaction to reduce to 5g.
Which of the following pairs can be distinguished by Lucas test?
According to the adsorption theory of catalysis, the speed of the reaction increases because:
The solid NaCl is bad conducotor of electricity since
The temperature at which the real gases obey ideal gas laws is called?
Which compound amongst the following is not an aromatic compound?
3 O2(g) 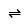 2 O3(g)
2 O3(g)
for the above reaction at 298 K, Kc is found to be 3.0 × 10-59. If the concentration of O2 at equilibrium is 0.040 M then concentration of O3 in M is
N2 + 3H2 ⇋ 2NH3 + Heat
The Le Chatelier's principle suggests that are required to drive the reaction to the right and thus form NH3.
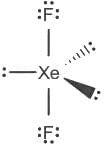
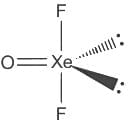
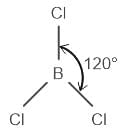
The correct order of hybridization of central atom in the following molecules will be:
→ XeF2, XeOF2, BCI3, and ICl4-
Ethylene diaminetetraacetate (EDTA) ion is :
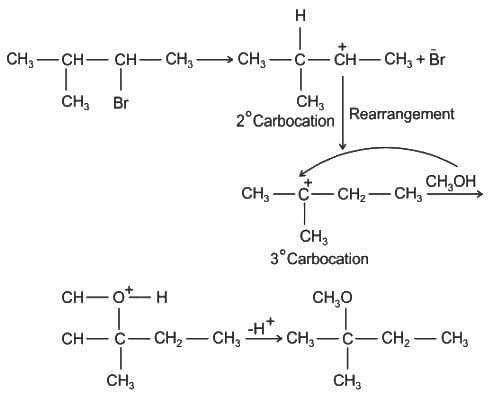
The major product of the following reaction is:



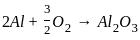
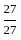
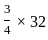
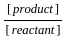
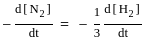 =
= 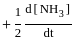
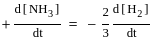
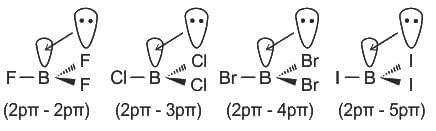
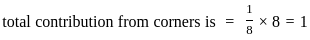
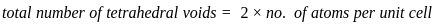
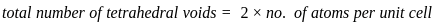
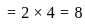
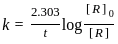 .
.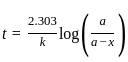
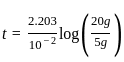
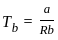 . Where
. Where 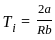 . Where
. Where 
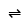
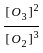
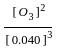
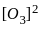 = 3 × 10-59 × 0.040 × 0.040 × 0.040
= 3 × 10-59 × 0.040 × 0.040 × 0.040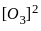 = 19.2 × 10-64
= 19.2 × 10-64